Method for extracting and recycling zinc from beneficiation tailing water of lead silver residues of zinc hydrometallurgy
A technology for zinc hydro-smelting and lead-silver slag, which is applied in the field of zinc extraction and recovery, can solve the problems of zinc extraction rate (low transfer efficiency, difficult separation of impurities, large loss of organic phase, etc.), and achieve equipment investment saving, fine and uniform filter pores , Reduce the effect of slag washing process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
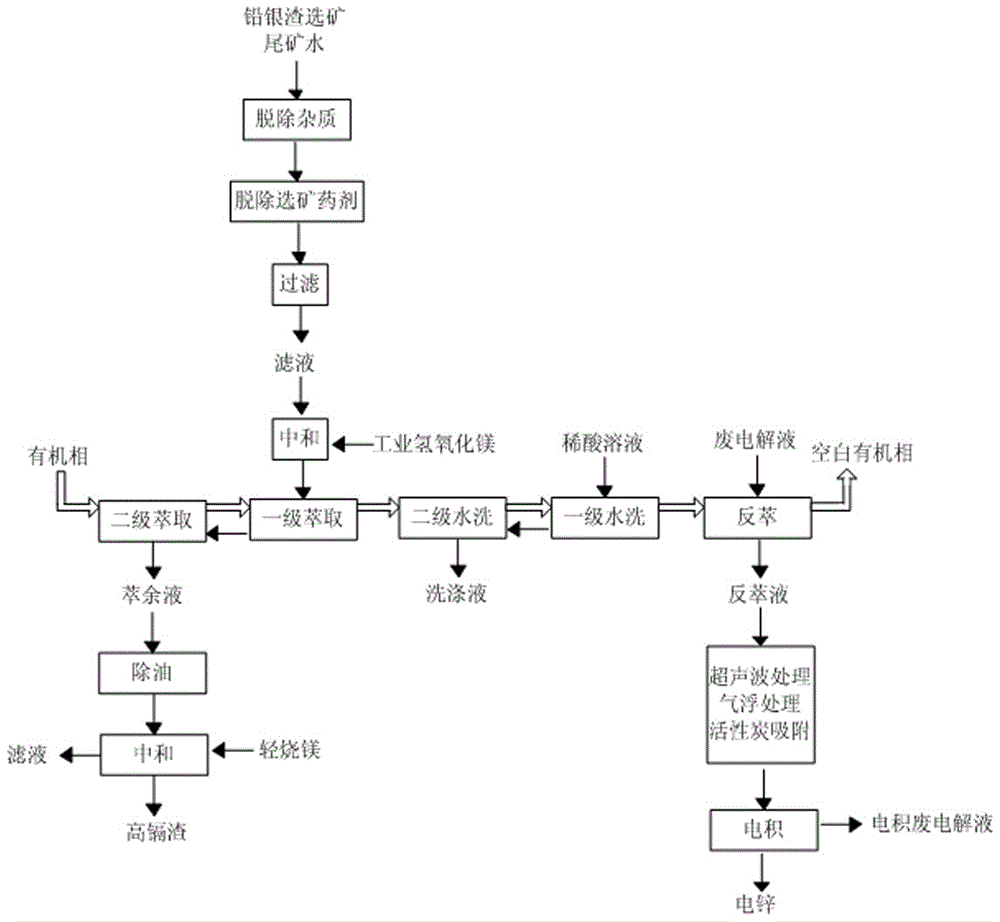
[0045] 1. Add lime to the lead and silver slag beneficiation tailings water of zinc hydrometallurgy to remove impurities, then add activated carbon to remove the beneficiation agent, and then filter to remove the activated carbon particles to obtain the filtrate; the pH value of the filtrate is 5, and the zinc content is 20g / L , containing cadmium 1g / L, and the content of impurities Fe, As, Sb and residual beneficiation agents are all ≤1mg / L;
[0046] 2. Add industrial magnesium hydroxide to the filtrate and stir for 30 minutes. The amount of industrial magnesium hydroxide added is 8~17kg per cubic meter of filtrate to make a slurry;
[0047] 3. Carry out two-stage countercurrent extraction with organic relative slurry to obtain raffinate and loaded organic phase; the organic phase is P204 diluted with sulfonated kerosene, wherein the volume percentage of P204 is 30%; the volume flow rate of organic phase and slurry The ratio is 1.1:1; the raffinate is deoiled by ultrasonic tr...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Method is with embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0054] (1) The pH value of the filtrate is 6, the zinc content is 30g / L, and the cadmium content is 1.5g / L;
[0055] (2) Add industrial magnesium hydroxide to the filtrate and stir for 35 minutes. The amount of industrial magnesium hydroxide added is 8~17kg per cubic meter of filtrate;
[0056] (3) The volume percentage of P204 in the organic phase is 40%; the volume flow ratio of the organic phase to the slurry is 1.2:1; The precipitation time is 35 minutes; the high cadmium residue contains cadmium 19% by weight; the extraction rate of zinc is 94%;
[0057] (4) The dilute acid solution contains 6g / L of sulfuric acid and 1g / L of sodium sulfosalicylate; the volume flow ratio of the dilute acid solution to the loaded organic phase is 9:1;
[0058] (5) The waste electrolyte contains 50g / L of zinc and 145g / L of sulfuric acid; the flow volume ratio of the washed organic phase to the waste electrolyte is 4.5:1; the strippin...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Method is with embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0062] (1) The pH value of the filtrate is 5, the zinc content is 25g / L, and the cadmium content is 1.3g / L;
[0063] (2) Add industrial magnesium hydroxide to the filtrate and stir for 40 minutes. The amount of industrial magnesium hydroxide added is 8~17kg per cubic meter of filtrate;
[0064] (3) The volume percentage of P204 in the organic phase is 35%; the volume flow ratio of the organic phase to the slurry is 1.2:1; the amount of light burned magnesium added is 6.6kg per cubic meter of deoiled raffinate, neutralized The precipitation time is 40 minutes; the high cadmium residue contains cadmium 19% by weight; the extraction rate of zinc is 95%;
[0065] (4) The dilute acid solution contains 5g / L of sulfuric acid and 1g / L of sodium sulfosalicylate; the volume flow ratio of the dilute acid solution to the loaded organic phase is 10:1;
[0066] (5) The waste electrolyte contains 52g / L of zinc and 146g / L of sulfuric ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com