Wolfberry anther culture breeding differential medium
A kind of differentiation medium and technology of Lycium barbarum flower, applied in horticulture, botanical equipment and methods, gardening tools/equipment, etc., can solve the problems of low efficiency of Lycium barbarum anther culture, to speed up the breeding process, improve efficiency, and reduce the degree of browning Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Prepare the culture medium with the following formula:
[0036] Macroelements: KNO 3 950mg / L, NH 4 NO 3 825mg / L, KH 2 PO 4 675mg / L, MgSO 4 ∙7H 2 O 1500mg / L, Glutamine 390mg / L, CaCl 2 ∙2H 2 O 220mg / L;
[0037] Trace elements: MnSO 4 ∙4H 2 O 18mg / L, ZnSO 4 ∙7H 2 O 27.5mg / L, H 3 BO 3 6.25mg / L, KI 0.8mg / L;
[0038] Iron salt and complexing agent: FeSO4 ∙7H 2 O 42.5mg / L, Na 2 -EDTA∙2H 2 O 56mg / L;
[0039] Organic ingredients: inositol 50mg / L, vitamin B1 0.4mg / L, vitamin B6 0.5mg / L, niacin 5.0mg / L, adenine 22.5mg / L, proline 2.0mg / L, folic acid 0.4mg / L , Biotin 0.1mg / L;
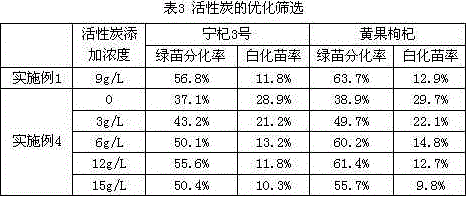
[0040] Inorganic additives: activated carbon 9g / L, N-methyl-nitrosourea 27.5mg / L;
[0041] Plant growth regulator: 2,4-D 1.0mg / L, KT 1.7mg / L;
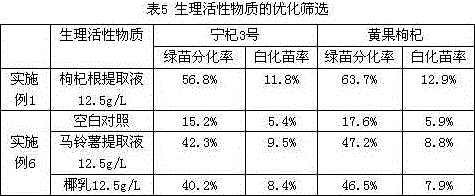
[0042] Physiologically active substances: Lycium barbarum root extract 12.5g / L;
[0043] Carbon source: sucrose 27.5g / L, fructose 13.5g / L;
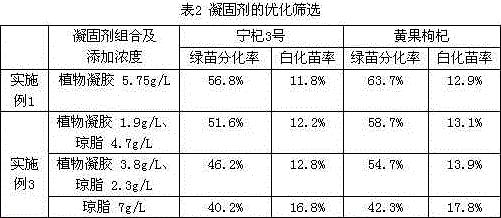
[0044] Coagulant and other additives: plant gel 5.75g / L, sorbitol 22.5g / L, hydrolyzed protein 1.0g / ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Prepare the medium with the following formula (optimized screening of carbon source combination):
[0049] Macroelements: KNO 3 950mg / L, NH 4 NO 3 825mg / L, KH 2 PO 4 675mg / L, MgSO 4 ∙7H 2 O 1500mg / L, Glutamine 390mg / L, CaCl 2 ∙2H 2 O 220mg / L;
[0050] Trace elements: MnSO 4 ∙4H 2 O 18mg / L, ZnSO 4 ∙7H 2 O 27.5mg / L, H 3 BO 3 6.25mg / L, KI 0.8mg / L;
[0051] Iron salt and complexing agent: FeSO 4 ∙7H 2 O 42.5mg / L, Na 2 -EDTA∙2H 2 O 56mg / L;
[0052] Organic ingredients: inositol 50mg / L, vitamin B1 0.4mg / L, vitamin B6 0.5mg / L, niacin 5.0mg / L, adenine 22.5mg / L, proline 2.0mg / L, folic acid 0.4mg / L , Biotin 0.1mg / L;
[0053] Inorganic additives: activated carbon 9g / L, N-methyl-nitrosourea 27.5mg / L;
[0054] Plant growth regulator: 2,4-D 1.0mg / L, KT 1.7mg / L;
[0055] Physiologically active substances: Lycium barbarum root extract 12.5g / L;
[0056] Coagulant and other additives: plant gel 5.75g / L, sorbitol 22.5g / L, hydrolyzed protein 1.0g / L.
[0057] Se...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Prepare the medium with the following formula (optimized screening of coagulants):
[0061] Macroelements: KNO 3 950mg / L, NH 4 NO 3 825mg / L, KH 2 PO 4 675mg / L, MgSO 4 ∙7H 2 O 1500mg / L, Glutamine 390mg / L, CaCl 2 ∙2H 2 O 220mg / L;
[0062] Trace elements: MnSO 4 ∙4H 2 O 18mg / L, ZnSO 4 ∙7H 2 O 27.5mg / L, H 3 BO 3 6.25mg / L, KI 0.8mg / L;
[0063] Iron salt and complexing agent: FeSO 4 ∙7H 2 O 42.5mg / L, Na 2 -EDTA∙2H 2 O 56mg / L;
[0064] Organic ingredients: inositol 50mg / L, vitamin B1 0.4mg / L, vitamin B6 0.5mg / L, niacin 5.0mg / L, adenine 22.5mg / L, proline 2.0mg / L, folic acid 0.4mg / L , Biotin 0.1mg / L;
[0065] Inorganic additives: activated carbon 9g / L, N-methyl-nitrosourea 27.5mg / L;
[0066] Plant growth regulator: 2,4-D 1.0mg / L, KT 1.7mg / L;
[0067] Physiologically active substances: Lycium barbarum root extract 12.5g / L;
[0068] Carbon source: sucrose 27.5g / L, fructose 13.5g / L;
[0069] Other additives: sorbitol 22.5g / L, hydrolyzed protein 1.0g / L. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com