Method for detecting semiconductor polish wafer surface scratches
A detection method and semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurement, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as corrosion, complex detection process, SiC wafer contamination, etc., and achieve low cost and small damage effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
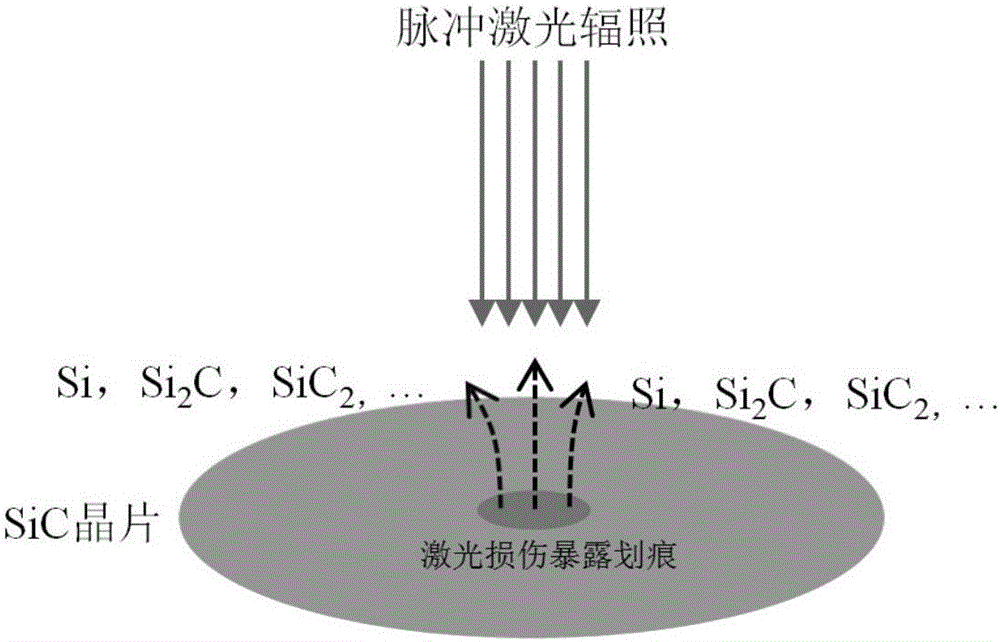
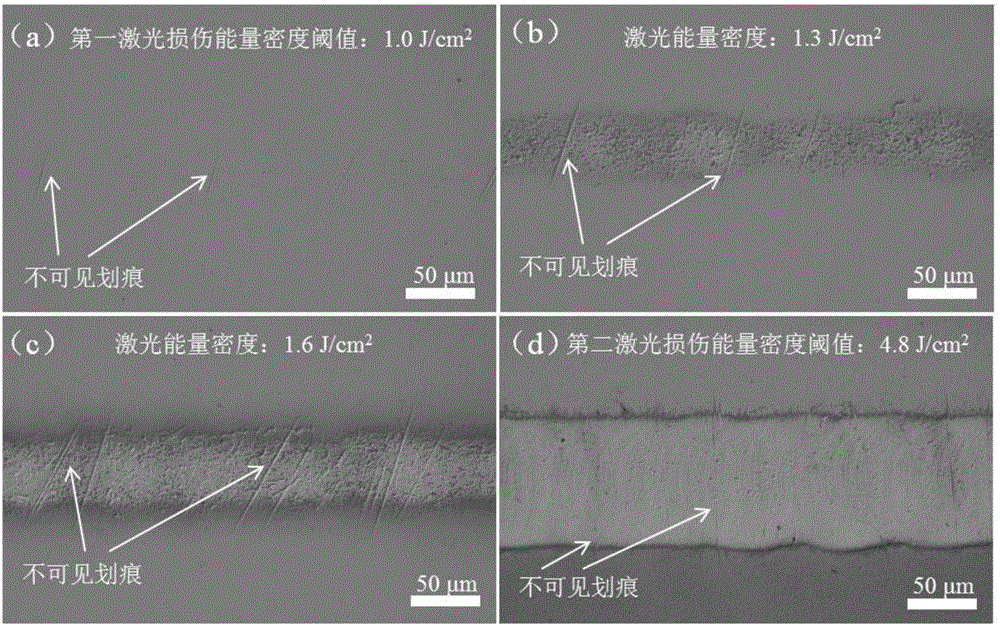
[0029] In this embodiment, a conductive 6H-SiC wafer doped with nitrogen (N) is taken as an example for illustration. figure 1 The atomic force microscope morphology of the nitrogen-doped 6H-SiC polished wafer surface after chemical mechanical polishing is shown. It can be seen that the scratches on the surface of the nitrogen-doped 6H-SiC polished wafer cannot be observed by the expensive atomic force microscope. The present embodiment provides a kind of detection method of the scratch on the conductive 6H-SiC polishing wafer surface of a kind of N doping, refer to below figure 2 and image 3 The method is described in detail. figure 2 A schematic diagram showing the detection method of SiC polished wafer surface scratches provided by the present invention, image 3 The optical microscope topography of the nitrogen-doped 6H-SiC polished wafer surface in the irradiated area is shown for different total laser irradiation energy densities. image 3 (a)-(d) corresponding to...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The present embodiment provides a kind of detection method of scratches on the surface of semi-insulating 4H-SiC wafer doped with vanadium (V), refer to below Figure 4 The method is described in detail. Figure 4 The optical microscope topography of vanadium-doped 4H-SiC polished wafer surface in the irradiated area is shown for different total laser irradiation energy densities. Figure 4 (a)-(d) corresponding to the total laser irradiation energy density is 1.6J / cm 2 、2.1J / cm 2 , 2.5J / cm 2 and 5.3J / cm 2 . The detection method of the vanadium-doped 4H-SiC polished wafer surface scratch of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0037] 1) The size to be detected is 1×1cm 2 The vanadium-doped semi-insulating 4H-SiC wafer was ultrasonically cleaned with acetone, absolute ethanol and deionized water in sequence, and finally the cleaned silicon carbide wafer was blown dry with nitrogen.
[0038] 2) Irradiating the cleaned vanadium-doped 4H-SiC wafer ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com