Human skin epidermal cell culture medium and application thereof
A technology of epidermal cells and medium, which is applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of expensive addition of factors, time cannot meet the treatment of burns and scalds, slow expansion of epidermal cells, etc., and achieve the effect of shortening the time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
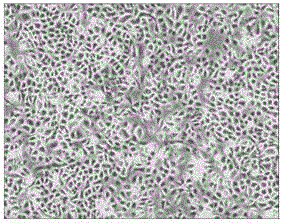
[0041] Example 1: Comparison of the morphology and cell quantity of the original epidermis cultured by the human skin epidermal cell culture medium of the present invention and the traditional serum-containing epidermis medium
[0042] Materials and methods:
[0043] Tissue source: discarded neonatal foreskin during hospital operation
[0044] Cell culture medium: traditional serum-containing epidermal medium, human skin epidermal medium of the present invention
[0045] a) The collected fresh tissue samples were disinfected with alcohol for three minutes, and then treated twice with PBS containing 2 times double antibody, each time for 3 minutes. The tissues were soaked in F12 medium containing 1 times double antibody and stored at 4°C for later use. Tissue storage time is not higher than 72 hours.
[0046] b) Take out the tissue in the soaking liquid, drain the excess liquid, weigh it and make a record, cut the tissue into long strips, spread it evenly in a 100mm petri di...
example 2
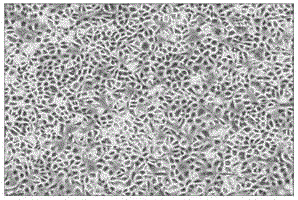
[0055] Example two: adopt human skin epidermal cell culture medium of the present invention and the comparison of the original epidermal cell morphology and cell quantity of traditional serum-free keratin medium (K-sfm) culture
[0056] Materials and methods:
[0057] Tissue source: discarded fetal scalp during hospital operation
[0058] Cell culture medium: K-sfm medium, human skin epidermis medium of the present invention
[0059] a) The collected fresh tissue samples were disinfected with alcohol for three minutes, and then treated twice with PBS containing 2 times double antibody, each time for 3 minutes. The tissues were soaked in F12 medium containing 1 times double antibody and stored at 4°C for later use. Tissue storage time is not higher than 72 hours.
[0060] b) Take out the tissue in the soaking liquid, drain the excess liquid, weigh it and make a record, cut the tissue into long strips, spread it evenly in a 100mm petri dish, and add 2.5mg / ml Neutral protease...
example 3
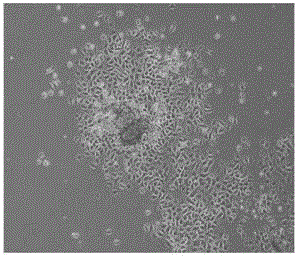
[0069] Example three: adopt human skin epidermis culture medium of the present invention and the comparison of the passage newborn's foreskin epidermal cell morphology and cell quantity that traditional serum-free keratin medium (K-sfm) cultivates
[0070] Materials and methods:
[0071] Cells: subcultured neonatal foreskin epidermal cells
[0072] Medium: K-sfm medium, human skin epidermis medium of the present invention
[0073] a) Remove the old culture medium in the culture bottle.
[0074] b) Wash each bottle once with 5-10ml PBS to remove residual serum.
[0075] c) Add 3 ml of 0.05% trypsin containing EDTA to T75flask and digest in a 37 degree incubator for 10 min.
[0076] d) Observe under the microscope, if the cells are all detached, add 10ml of DMEM containing 10% FBS to each bottle for neutralization (can be gently blown several times), and collect all the cells into a 50ml centrifuge tube.
[0077] e) Centrifuge at 1000 rpm for 5 minutes, and discard the super...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com