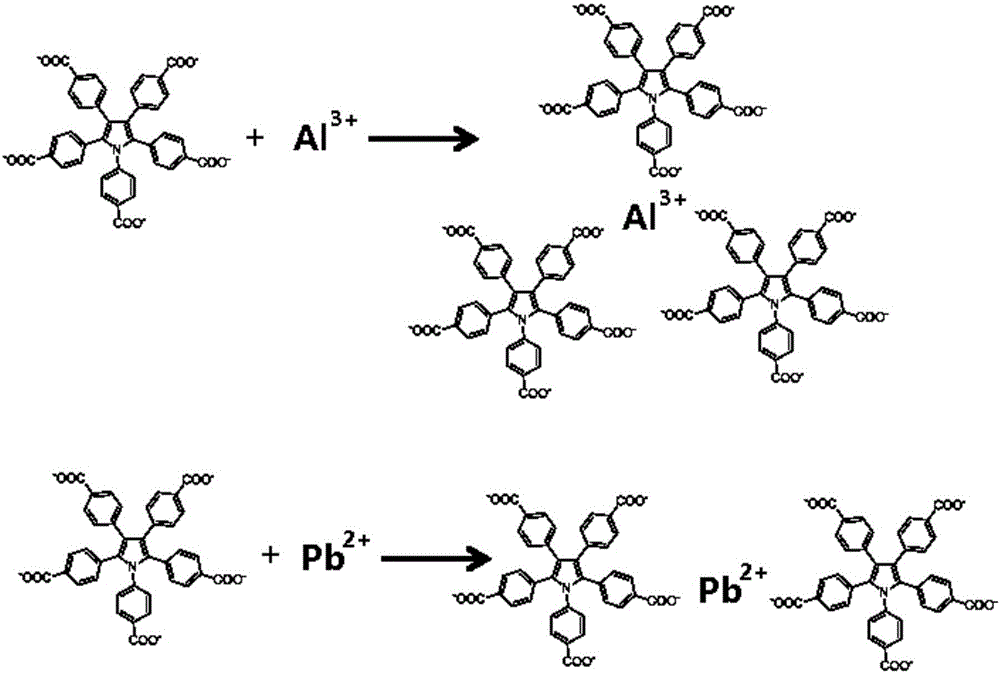
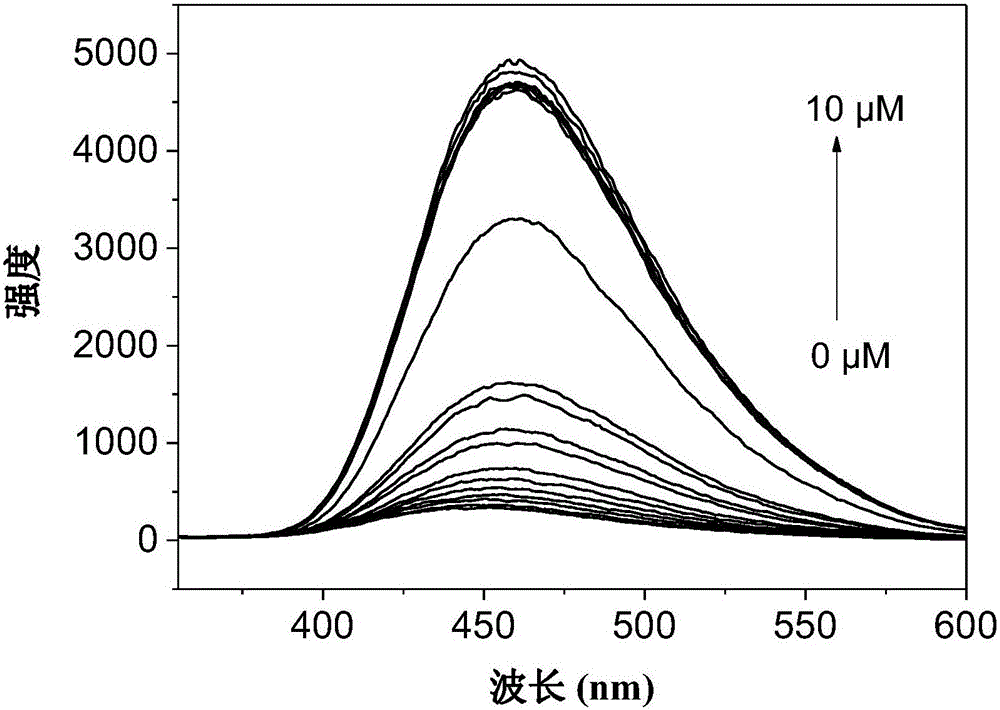
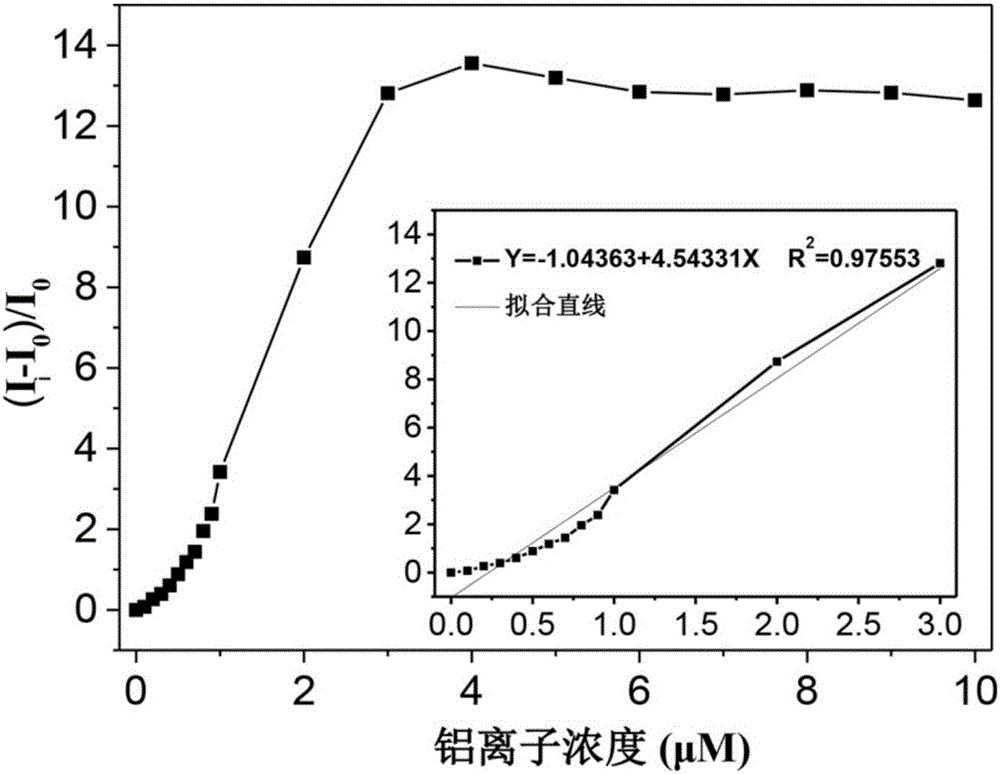
Fluorescent reagent for laddered detection of trace trivalent aluminium ions and divalent lead ions and preparation of fluorescent reagent
A fluorescent reagent, aluminum ion technology, applied in the field of fluorescent chemical sensors, to achieve the effect of fast detection, high selectivity, and enhanced fluorescence intensity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] A method for preparing a fluorescent reagent for stepwise detection of trace amounts of trivalent aluminum ions and divalent lead ions, the specific steps of the method are as follows:
[0062] (1) Preparation of PPP
[0063] Dissolve 100mg of 3,4-dibromo-1,2,5-tris(methoxycarbonylphenyl)pyrrole in 10mL of ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, add 282mg of 4-methoxycarbonylphenylboronic acid, 18mg of tetrakis(tri Phenylphosphine) palladium and 225mg cesium carbonate reacted for 18 hours at 70° C. to obtain a white solid powder; through nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer and mass spectrometer, it can be known that the white solid powder is PPP, and its proton nuclear magnetic spectrum, mass spectrum and infrared Data are as follows:
[0064] 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ(ppm):8.05(m,2H),7.85(m,8H),7.51(m,5H),6.98(m,5H),3.89(m,15H); MS(MALDI-TOF):calcd. for C 44 h 35 NO 10 ,737.2; found, 737.2; FTIR: 2950cm -1 (carbon-hydrogen single bond) 1728cm -1 (carbonyl double ...
Embodiment 2
[0071] A method for preparing a fluorescent reagent for stepwise detection of trace amounts of trivalent aluminum ions and divalent lead ions, the specific steps of the method are as follows:
[0072] (1) Preparation of PPP
[0073] Dissolve 100 mg of 3,4-dibromo-1,2,5-tris(methoxycarbonylphenyl)pyrrole in 30 mL of ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, add 548 mg of 4-methoxycarbonylphenylboronic acid, 55 mg of tetrakis(tris) Phenylphosphine) palladium and 364mg cesium carbonate reacted for 30 hours at 70° C. to obtain a white solid powder; through nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer and mass spectrometer, it can be seen that the white solid powder is PPP, and its proton nuclear magnetic spectrum, mass spectrum and infrared Data are as follows:
[0074] 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ(ppm):8.05(m,2H),7.85(m,8H),7.51(m,5H),6.98(m,5H),3.89(m,15H).MS(MALDI-TOF):calcd. for C 44 h 35 NO 10 , 737.2; found, 737.2.FTIR: 2950cm -1 (carbon-hydrogen single bond) 1728cm -1 (carbonyl dou...
Embodiment 3
[0081] A method for preparing a fluorescent reagent for stepwise detection of trace amounts of trivalent aluminum ions and divalent lead ions, the specific steps of the method are as follows:
[0082] (1) Preparation of PPP
[0083] Dissolve 100 mg of 3,4-dibromo-1,2,5-tris(methoxycarbonylphenyl)pyrrole in 20 mL of ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, add 300 mg of 4-methoxycarbonylphenylboronic acid, 40 mg of tetrakis(tris) Phenylphosphine) palladium and 280mg cesium carbonate reacted for 24 hours at 70° C. to obtain a white solid powder; through nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer and mass spectrometer, it can be seen that the white solid powder is PPP, and its proton nuclear magnetic spectrum, mass spectrum and infrared Data are as follows:
[0084] 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ(ppm):8.05(m,2H),7.85(m,8H),7.51(m,5H),6.98(m,5H),3.89(m,15H).MS(MALDI-TOF):calcd. for C 44 h 35 NO 10 , 737.2; found, 737.2.FTIR: 2950cm -1 (carbon-hydrogen single bond) 1728cm -1 (carbonyl dou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com