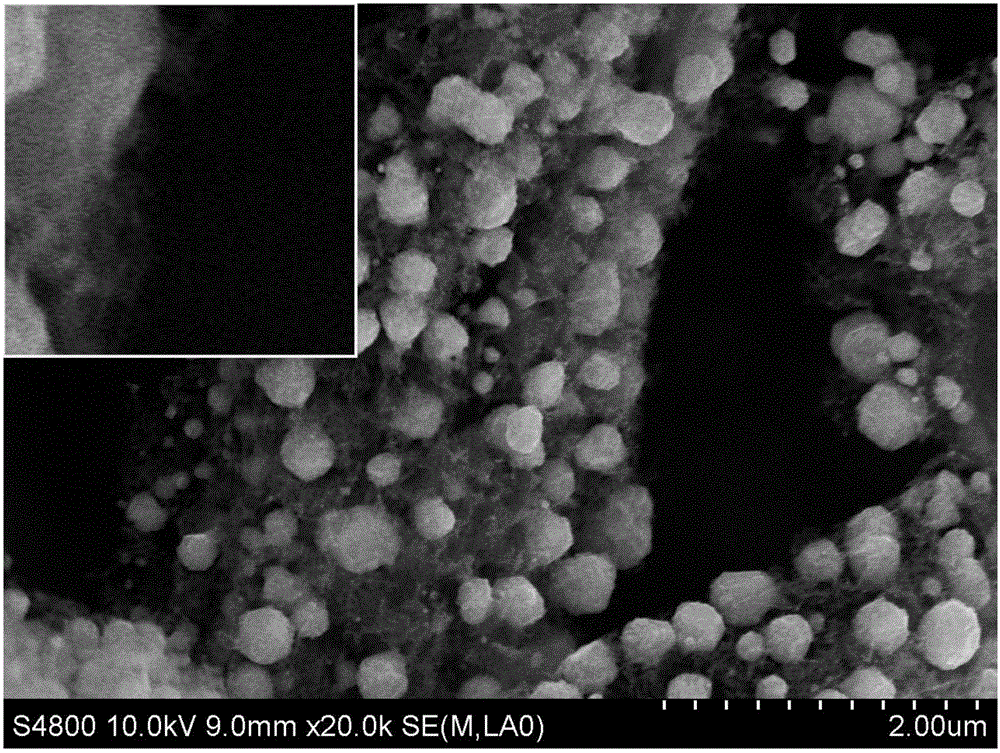
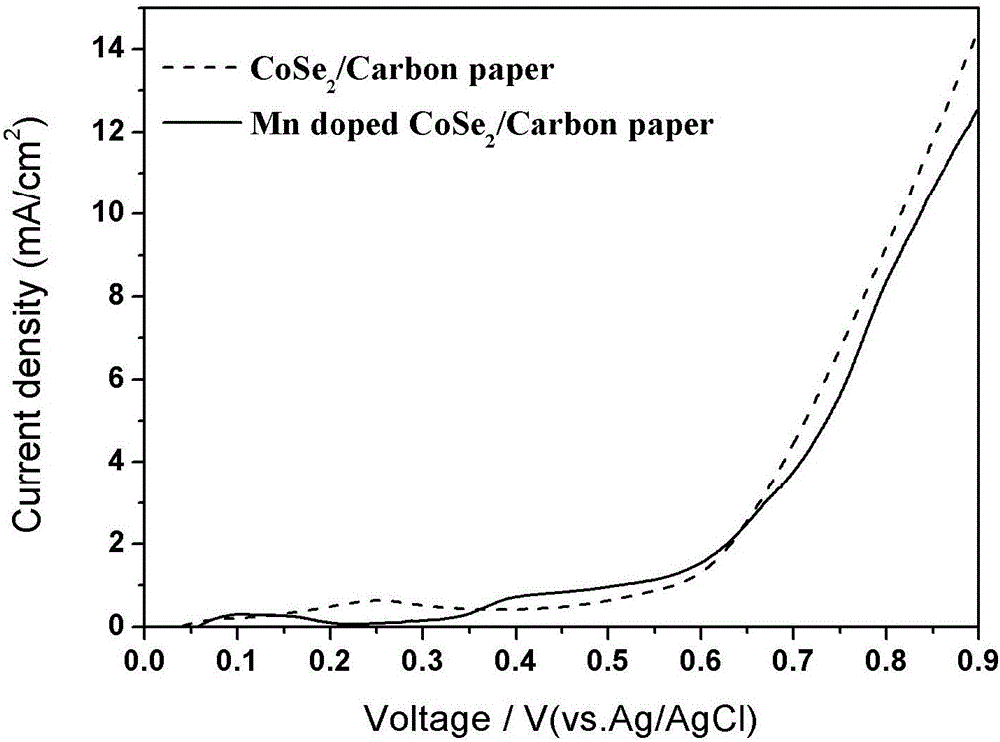
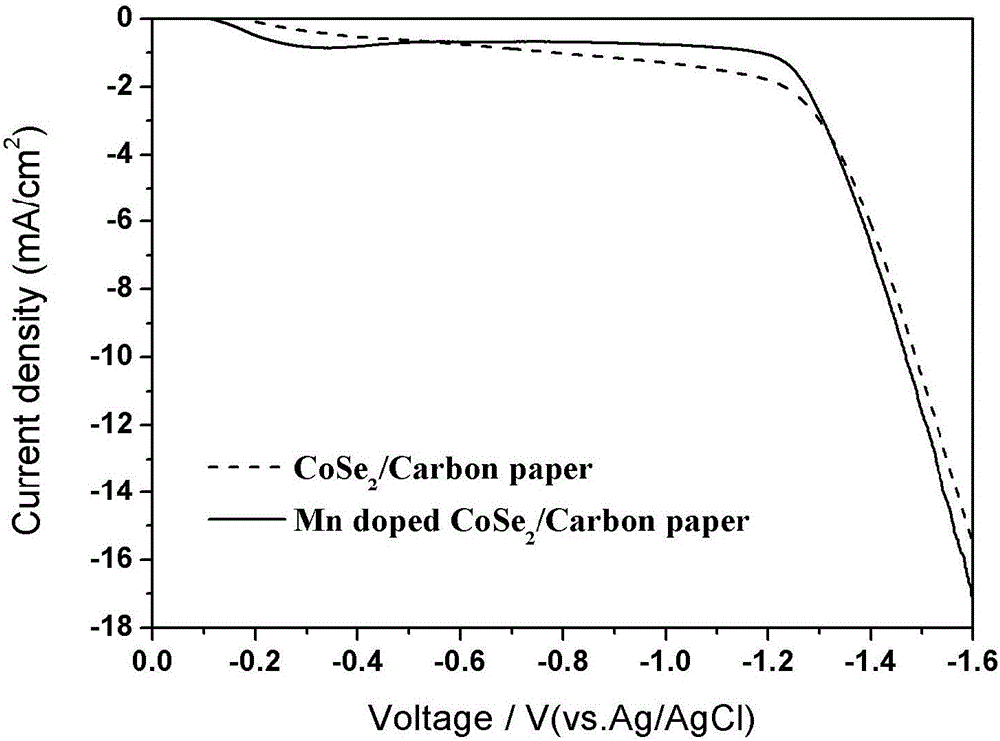
Process for preparing cobalt selenide composite carbon paper
A technology of cobalt selenide and composite carbon, applied in special paper, paper, papermaking and other directions, can solve the problems of being unsuitable for large-area electrodes and large-scale production, and achieve the effects of avoiding catalyst loss, reducing degradation, and being easy to degrade.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Add 0.5 mmol of sodium selenite to 28 mL of cellulose aqueous dispersion with a solid content of 1% to dissolve to obtain a solution A. 0.5 mmol of cobalt acetate was added into 56 mL of diethylenetriamine and dissolved to obtain B solution. Add solution B dropwise into solution A, mix and dissolve, and stir for 30 minutes. The mixture was transferred to a 100mL hydrothermal reaction kettle and sealed. The reaction kettle was placed in an oven, and the temperature was raised to 180° C. at a constant temperature of 16 hours at a heating rate of 3° C. / min, and then cooled down to room temperature naturally.
[0030] The mixed pulp obtained by diluting the reaction mixture with deionized water twice, adopts the method of wet papermaking, and uses a filter screen to directly make paper sheets with a size of 5cm×5cm, and then dry or hot press. Put the copied paper (cut and folded into any shape) into an inert atmosphere furnace, and under the protection of an inert gas (ar...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Add 0.5 mmol of sodium selenite to 28 mL of cellulose aqueous dispersion with a solid content of 1% to dissolve to obtain a solution A. 0.475mmol of cobalt acetate and 0.025mmol of manganese acetate were added into 56mL of diethylenetriamine and dissolved to obtain solution B. Add solution B dropwise into solution A, mix and dissolve, and stir for 30 minutes. The mixture was transferred to a 100mL hydrothermal reaction kettle and sealed. The reaction kettle was placed in an oven, and the temperature was raised to 180° C. at a constant temperature of 16 hours at a heating rate of 3° C. / min, and then cooled down to room temperature naturally.
[0034] The mixed pulp obtained by diluting the reaction mixture with deionized water twice, adopts the method of wet papermaking, and uses a filter screen to directly make paper sheets with a size of 5cm×5cm, and then dry or hot press. Put the copied paper (or folded into any shape) into an inert atmosphere furnace, and under the...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Add 0.2 mmol of sodium selenite to 28 mL of cellulose aqueous dispersion with a solid content of 2% to dissolve to obtain a solution A. 0.2mmol of cobalt acetate was added into 56mL of diethylenetriamine and dissolved to obtain B solution. Add solution B dropwise into solution A, mix and dissolve, and stir for 30 minutes. The mixture was transferred to a 100mL hydrothermal reaction kettle and sealed. The reaction kettle was placed in an oven, and the temperature was raised to 180° C. at a constant temperature of 16 hours at a heating rate of 3° C. / min, and then cooled down to room temperature naturally.
[0038] The mixed pulp obtained by diluting the reaction mixture twice with deionized water is wet papermaking, and is directly made into 8cm×8cm paper sheets with a filter screen, and dried or hot pressed. Put the copied paper (or folded into any shape) into an inert atmosphere furnace, and under the protection of an inert gas (argon or nitrogen, etc.), raise the tem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com