Ex vivo antibody production
An in vitro, anti-apoptotic technology, applied in the fields of molecular biology, immunology, and medicine, it can solve the problem that antibodies cannot be produced in advance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
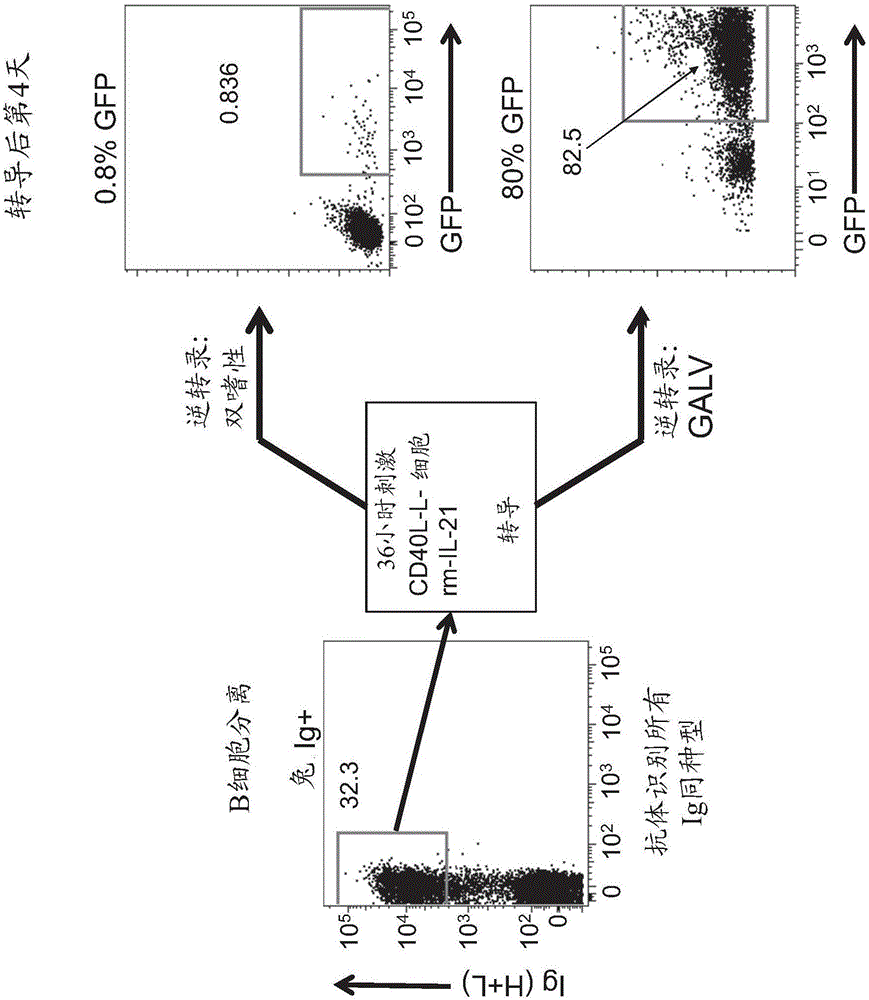
[0111] Transduction of B cells
[0112] Gene transfer into lymphocytes by traditional methods, such as calcium phosphate precipitation, liposome formation, or electroporation, is inefficient but, more importantly, often lacks stable gene integration. However, if an appropriate viral envelope is selected, viral transduction leads directly to the stable integration of the gene into the genome of the target cell, and with very high efficiency. Both retroviral and lentiviral transduction are suitable for efficient gene transfer. While retroviral integration is dependent on cell division, lentiviral transduction can also be used in cells that do not divide, such as plasma B cells. Large-scale production of recombinant retroviruses can be readily achieved using stable producer cell lines such as the Phoenix expression platform (Kinsella and Nolan, 1996). Production of high-titer lentiviruses tends to be more tedious, mainly because of the toxicity of the expressed viral proteins a...
Embodiment 2
[0118] cell culture
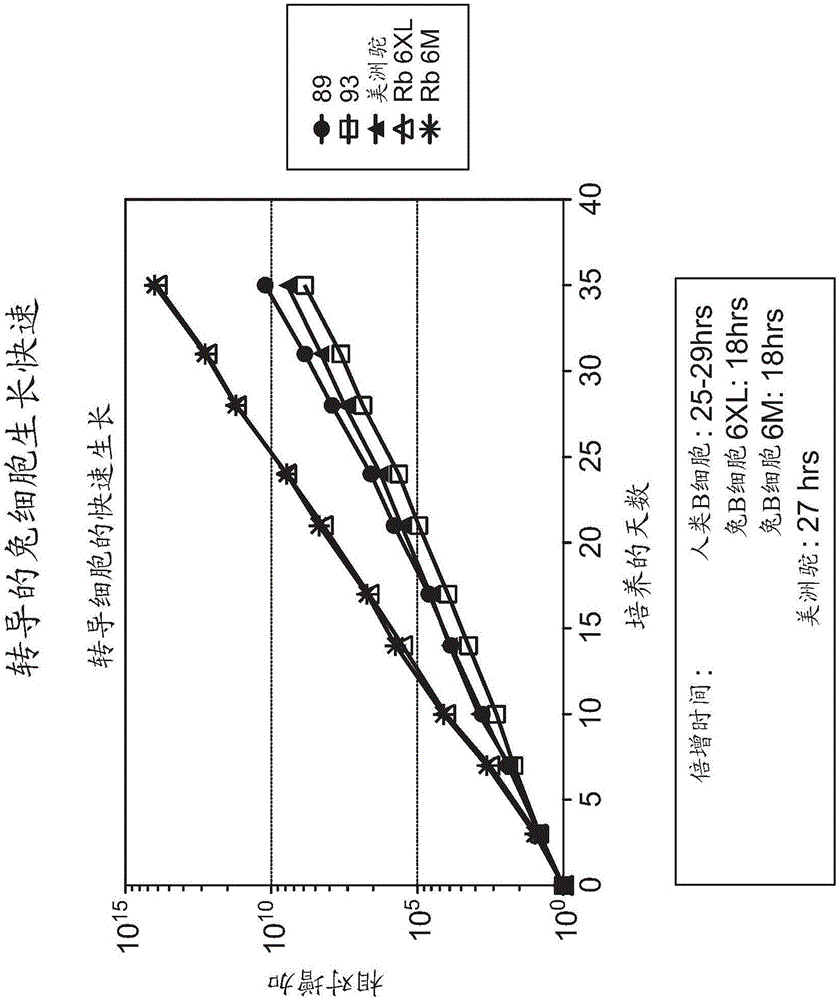
[0119] We will B cells (2 × 10 5Cells / ml) were maintained in Iscove's modified Dulbecco's medium (Iscove's modified Dulbecco's medium, Gibco), and they were cultured in γ-irradiated (50Gy) mouse L cell fibroblasts stably expressing CD40L (CD40L-L cells, 10 5 cells / ml). To determine the doubling time of cells, cells were cultured in 24-well plates at a density of 50-100.000 cells / well together with CD40L-L cells and IL-21. Cells were counted every 3-4 days and 50-100.000 cells were transferred to new wells. figure 2 In , B cells from two human donors (89 and 93), a sample of rhea B cells (Rhinosaurus), and a sample of rabbit B cells transduced with a GALV-type retrovirus (Rb 6XL) are shown. Growth curve, the GALV-type retrovirus carries nucleic acid molecules containing human Bcl-6 sequence and human Bcl-xL. In addition, a growth curve of a rabbit sample (Rb6M) transduced with a GALV-type retrovirus carrying a nucleic acid molecule containing the seq...
Embodiment 3
[0121] Expression of B cell receptors and antigen-specific staining
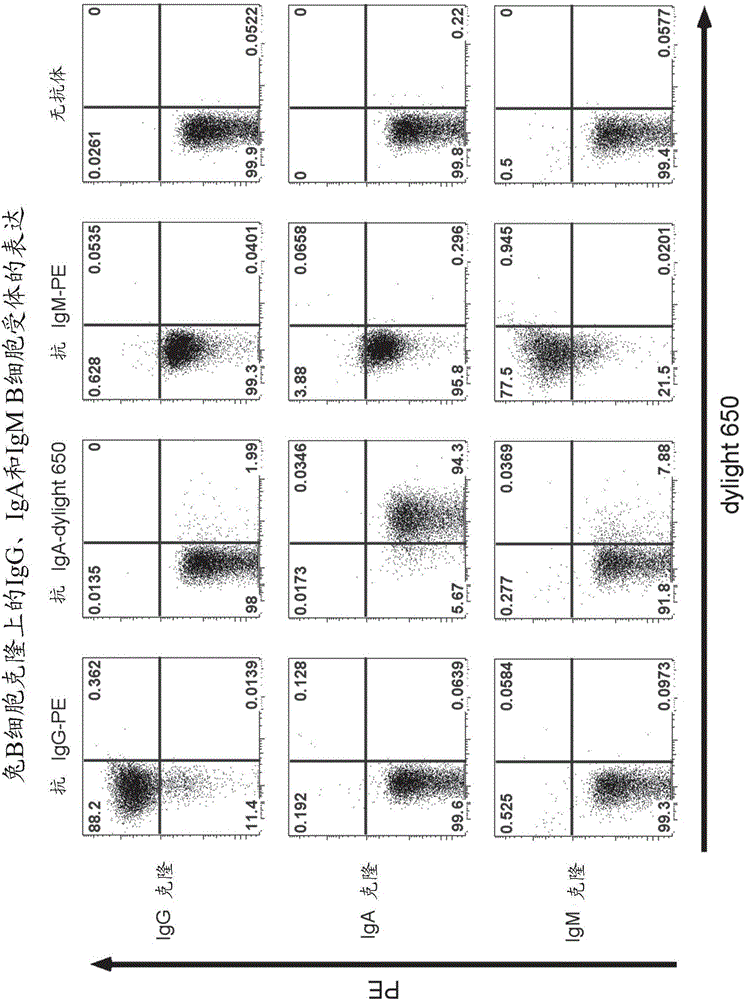
[0122] Immortalized human B cells express the B cell receptor. This property enables antigen-specific staining and sorting of B cells. To determine whether B cell receptors are also expressed on transduced rabbit B cells, B cell clones were stained with fluorescently labeled antibodies that react specifically with rabbit IgG, rabbit IgM, or rabbit IgA. B cells were washed in cold (4°C) cell culture medium and incubated on ice in the dark with immunofluorescence-conjugated antibodies against rabbit IgG, IgM, IgA or markers The antigen is specific. Afterwards, excess labeled antibody or antigen was washed away, and B cell receptor expression was analyzed on a FACS analyzer (Guava easycyte (Millipore) or FACS Aria3 (BD)).
[0123] image 3 In , three different B cell clones of different isotypes were stained using fluorescently-labeled antibodies that specifically recognize rabbit antibody isotypes IgG, IgA...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com