In-vivo platelet instant label-free detection system and detection method
A detection system and detection method technology, applied in the directions of diagnostic recording/measurement, blood characterization device, medical science, etc., can solve the problem that real-time, full-time and instant detection cannot be realized, and achieve the effect of avoiding waiting time and convenient detection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
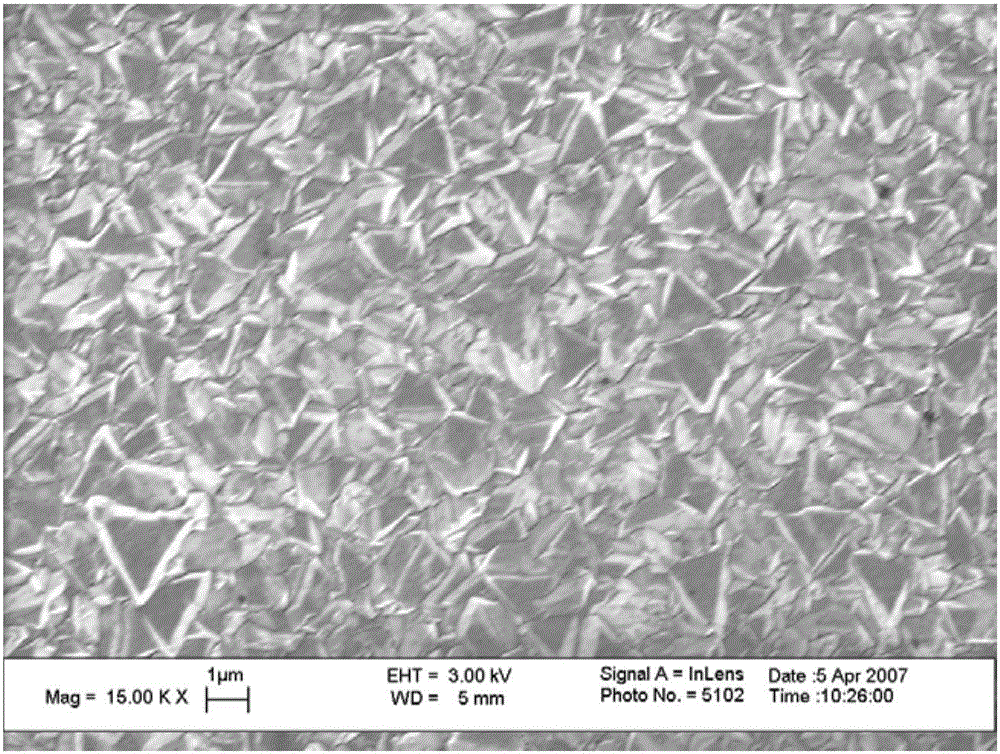
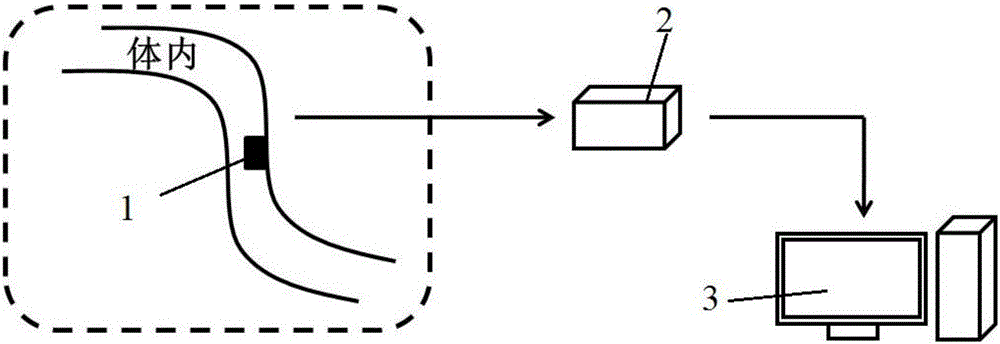
[0063] Taking the surface of an artificial heart assist device made of a titanium-based alloy as an example, a diamond film deposition process is used on the surface to form a diamond MEMS sensor on the surface of a titanium-based alloy, and to optimize its geometric distribution design on the surface of the artificial heart.
[0064] Then, the in vitro simulation experiment was carried out, and the artificial heart was connected with the dynamic blood flow simulator to simulate the flow field after the artificial heart intervention. The experiment uses donor blood for testing, and the output results are compared in two stages, the first is to compare with the computational fluid dynamics simulation results with the thrombus prediction module, and the second is to compare the monitoring results at different time points with the fluorescence microscope observation The microthrombosis distribution on the surface was compared. This checks the sensitivity of the sensor surface and...
Embodiment 2
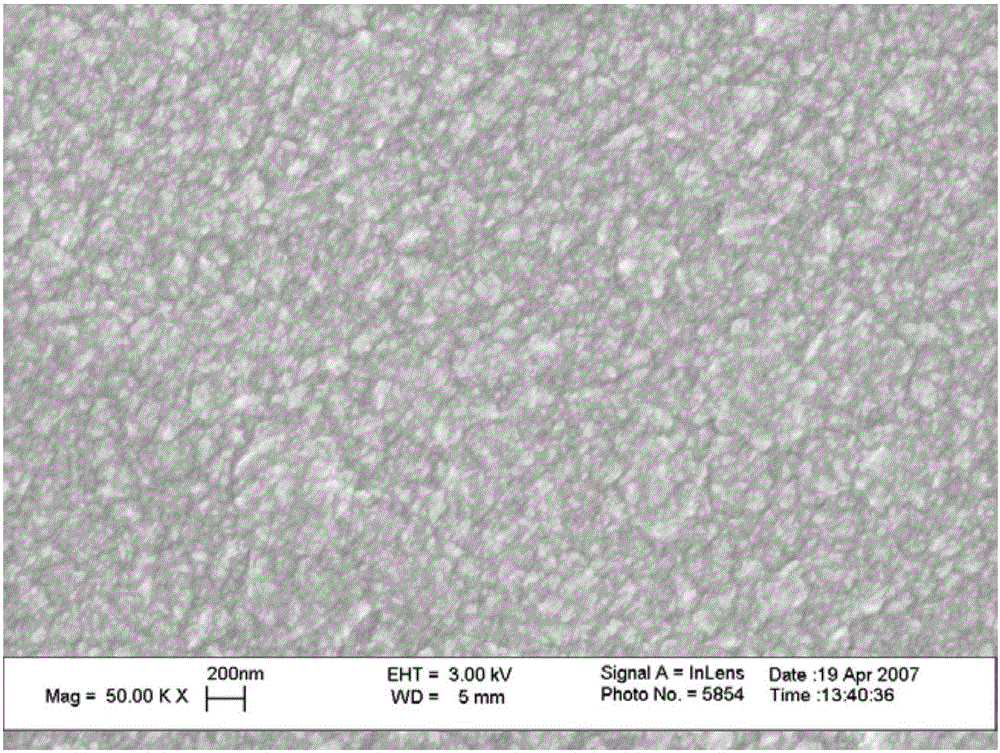
[0067] In this embodiment, the diamond MEMS sensor is prepared on the surface of the vascular stent or the artificial blood vessel, and is used to detect the surface blood flow velocity.
[0068] The MEMS electrodes form an electric field on the diamond surface, and the surface electric field will also change under different blood flow conditions, which will be fed back to the diamond MEMS sensor to obtain a change in the electrical signal. Such as Figure 6 Shown is the current density kinetic curve of the thrombus formation process in vivo (dots are data points). It can be seen that as time goes by, platelets gradually aggregate to form blood coagulation, and the current density gradually increases.
[0069] By analyzing the changes of electrical signals and the regional concentration information of red blood cells and plasma through a fixed algorithm, the blood flow velocity on the surface of the device can be obtained in real time, so as to obtain the space of the coagulat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com