One-step in-situ preparation method of graphene/polyaniline composite electrode
A composite electrode and in-situ preparation technology, which is applied to battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of poor uniformity and repeatability, low mechanical strength, and long preparation time, achieving controllable size, short time consumption, Simple operation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] The traditional graphite paper electrode was used as the carrier electrode, and the protonic acid / aniline electrolyte (H 2 SO 4 0.1M, aniline 0.05M) as the working medium, using a working electrode (traditional graphite paper electrode)-counter electrode (platinum wire electrode) double-electrode system, under the action of 10V DC voltage, process for 2min, wash in deionized water, and dry , that is, a graphene / polyaniline composite electrode is prepared in one step.
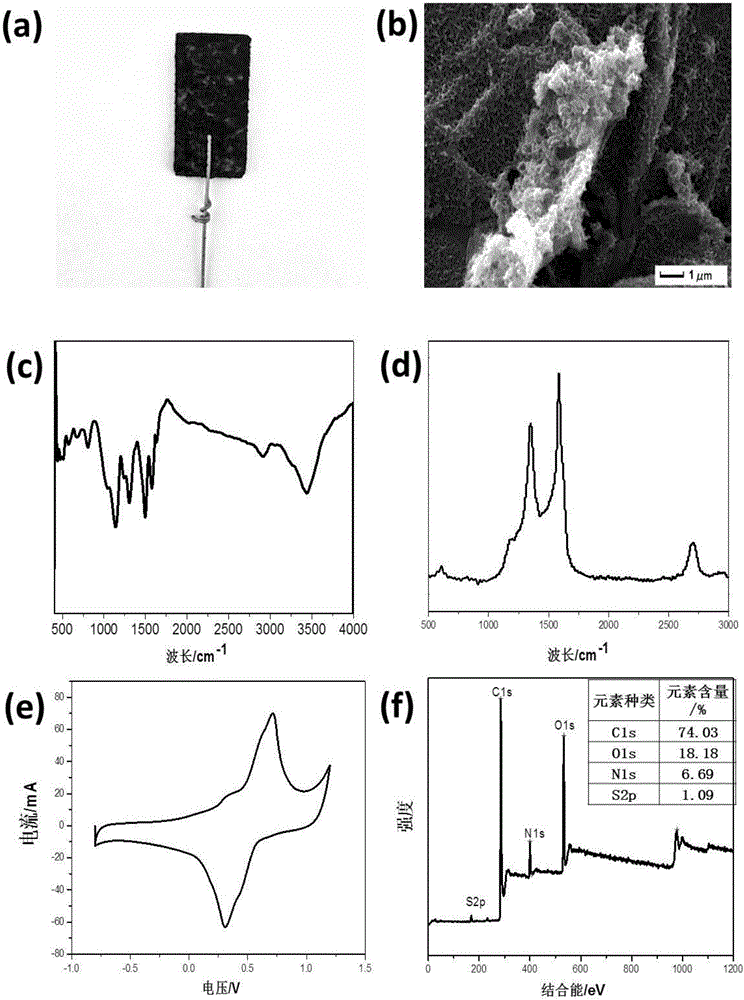
[0025] Such as figure 1 As shown, it can be seen from the SEM image that the graphene wrinkled structure is covered with fine particles of polyaniline; it can be seen from the RAMAN image that the composite material is at 1000-1750cm -1 It does have the D-G characteristic peaks of graphene and the broad characteristic peaks of polyaniline in the range; it can be seen from the FTIR diagram that the composite material not only has the characteristic absorption peaks of graphene functional groups such as ...
Embodiment 2
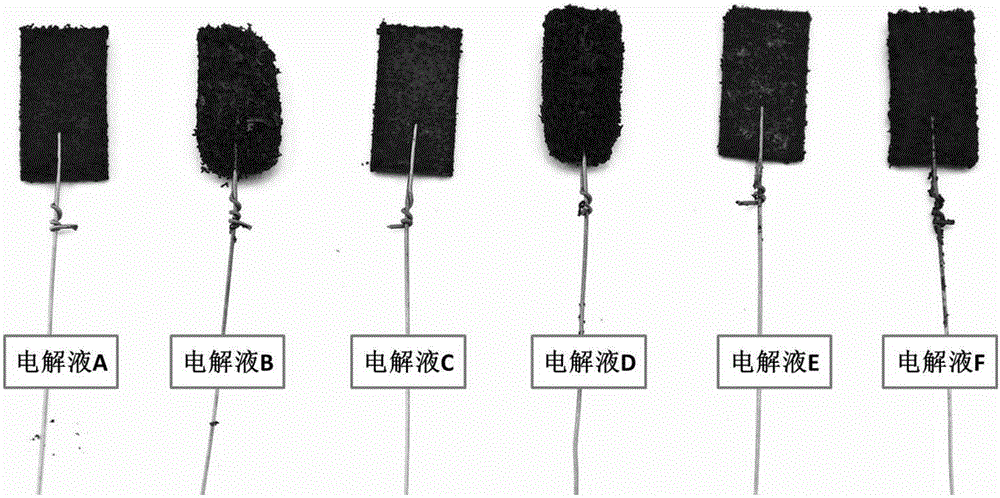
[0027] Basically the same as Example 1, but with the following changes: protonic acid / aniline electrolyte selection: electrolyte A (0.1MH 2 SO 4 / 0.05M aniline solution), electrolyte B (1M H 2 SO 4 / 0.05M aniline solution), electrolyte C (0.1M HClO 4 / 0.05M aniline solution), electrolyte D (1M HClO 4 / 0.05M aniline solution), electrolyte E (0.1M HCl / 0.05M aniline solution) and electrolyte F (1M HCl / 0.05M aniline solution), the obtained composite electrode is as follows figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
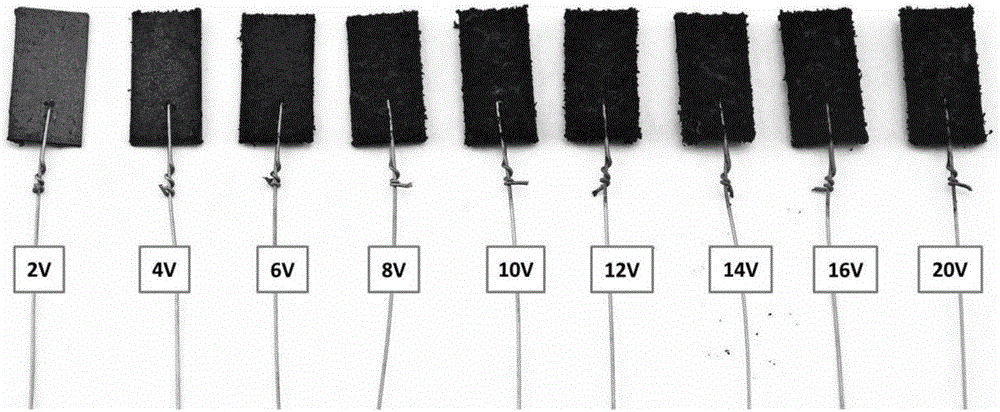
[0029] It is basically the same as Example 1, but with the following changes: the applied voltage provided by the DC stabilized power supply is 2V, 4V, 6V, 8V, 10V, 12V, 14V, 16V, 20V, and the resulting composite electrode is as follows: image 3 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com