Use of benzyloxycarbonyl-l-glutamic acid in the preparation of blys antagonists
A technology of benzyloxycarbonyl and glutamic acid, which is applied in anti-inflammatory agents, non-central analgesics, bone diseases, etc., and can solve problems such as benzyloxycarbonyl-L-glutamic acid that have not yet been developed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1: BLyS-related small molecule compounds were screened out using computer simulation screening technology.
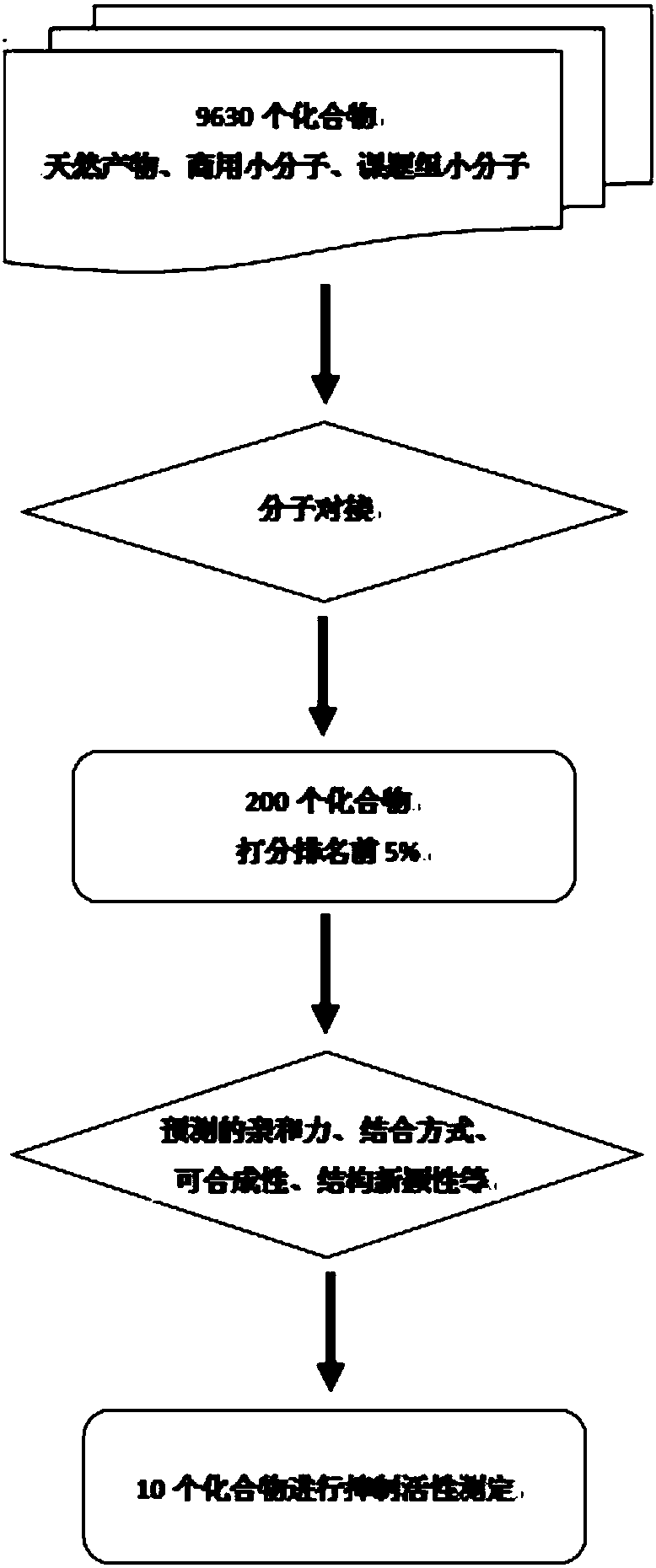
[0038] Acquisition of protein structure information: Download the BLyS protein structure (PDB ID: 1OQD and 1OQE) from the Protein Date Bank protein database (http: / / www.rcsb.org / pdb). Computational methods such as molecular dynamics were used to explore the interaction mechanism between BLyS and its natural receptors (BCMA, TACI, BR3) at the molecular level. According to the contribution of each amino acid residue to the binding energy, determine its key residues. figure 1 with figure 2 The key residues of the natural receptors of the BLyS target, and the binding pocket and key residues of the BLyS target are shown respectively.
[0039] Acquisition of Small Molecule Database: The small molecule database contains nearly 10,000 compounds with different structures, which mainly come from two ways: small molecules in the natural product database or commer...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Computer Analysis of Small Molecule Antagonists and BLyS Binding Mode.
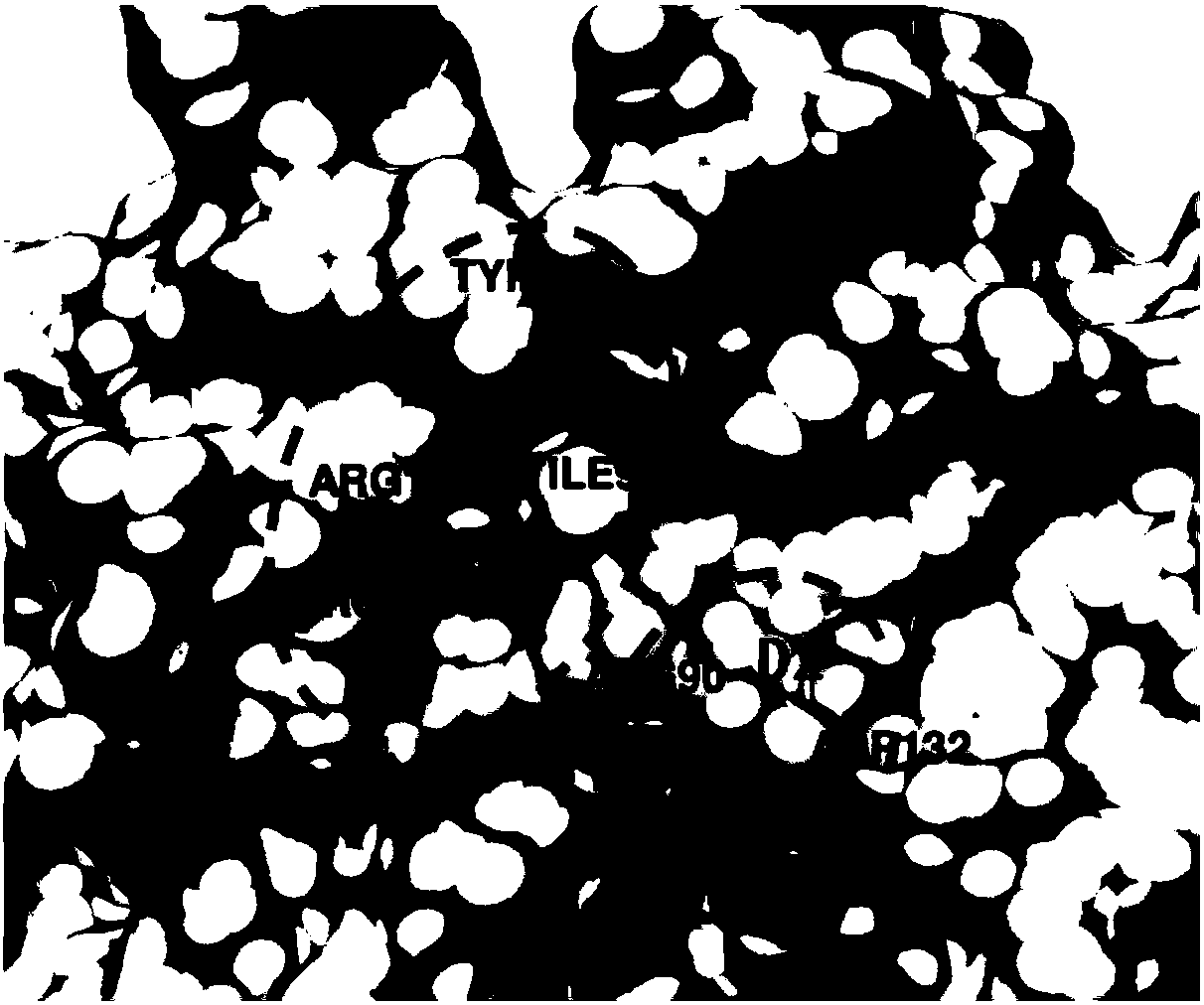
[0042] CBz-L-glutamic acid (structure see Figure 4 ) and the molecular mechanism of BLyS, and analyze the key amino acid residues and key interactions between it and BLyS ( Figure 5 ). It was found that a benzene ring of CBz-L-glutamic acid was inserted into the conserved hydrophobic pocket of BLyS, forming hydrophobic interactions with His69, Leu70 and Ile92, and forming π-cation interactions with the side chains of Arg124 and Arg90 residues, which jointly strengthened CBz -The combination of L-glutamic acid and BLyS; the carboxyl groups on the two side chains form a salt bridge with Arg90; the oxygen on the benzyloxycarbonyl group and the carbonyl oxygen in the amino acid carboxyl group form a hydrogen bond interaction with the key residue Arg124 of BLyS , the OH in the amino acid carboxyl group forms a hydrogen bond with Y65.
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3: Competition ELISA to analyze the inhibitory effect of compounds on BLyS binding to TACI / BCMA protein.
[0044] If the compound CBz-L-glutamic acid can compete with TACI / BCMA for binding to the active pocket of BLyS, the added compound CBz-L-glutamic acid will inhibit the binding of BLyS to TACI / BCMA; on the contrary, if the compound CBz-L-glutamic acid Without BLyS binding, there is no competition with TACI / BCMA. Then the addition of compound CBz-L-glutamic acid has no effect on the binding of BLyS to TACI / BCMA. Therefore, the effect of the small molecule CBz-L-glutamate on blocking the binding of BLyS to the receptors TACI and BCMA was tested by competitive inhibition ELISA experiments.
[0045] First, perform ELISA for the combination of BLyS and TACI-Fc / BCMA-Fc according to the conventional ELISA method. Determine the concentration of TACI-Fc / BCMA-Fc used in the competitive inhibition ELISA experiment. The final determined concentration was 10 μg / mL. T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com