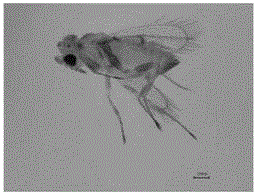
Molecular identification method for two kinds of leafhopper egg parasitic wasps in tea garden
A molecular identification and parasitic wasp technology, applied in the direction of determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient control of leafhopper population, difficulty in determining the morphological identification of parasitic wasp species, etc., and achieve accurate and rapid identification. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1 Collection of parasitoid eggs of tea leafhopper eggs
[0025] The high incidence period of the small green leafhopper in tea gardens in Zhejiang Province is from June to October, and its egg parasitoids have an obvious follow-up effect on leafhoppers, so the collection of parasitoids should follow the two peak periods of leafhoppers. Every few days in the tea garden, randomly cut one-bud five-leaf branches with obvious puncture marks on the tender stems, and bring them back to the laboratory and put them in water for cultivation. During this period, the epidermis of tea shoots and tender stems was girdled, and the eggs of small green leafhoppers were picked out and placed on filter paper soaked in distilled water for moisture observation. After the parasitoids emerged, the parasitoid eggs of leafhoppers were collected with glass finger tubes. The eclosion parasitoids were first photographed with a three-dimensional depth-of-field system for preliminary morphol...
Embodiment 2
[0026] The extraction of embodiment 2 genome DNA
[0027] Air-dry the preserved single parasitic wasp body of the green leafhopper, add 0.5 ml lysis buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, 5 mM EDTA, 0.5 % SDS, 200 mM NaCl, pH 8.0) and 1 steel ball, shake and crush, Add 5 ml of proteinase K (20 mg / ml) and digest in a water bath at 55°C for 5 hours. Use an equal volume of phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1) and chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1) to extract once, centrifuge at 12,000 r / min for 10 min at 4°C, and use the supernatant Add 2 times the volume of absolute ethanol and add 1 / 10 volume of NaAc (3 mol / L), precipitate at -20°C for 30 min, centrifuge at 12,000 r / min at 4°C for 10 min, wash the DNA pellet with 70% ethanol, and ultra-clean Add 100 ml of sterile deionized water after the workbench is air-dried, and store in a -20°C refrigerator.
Embodiment 3
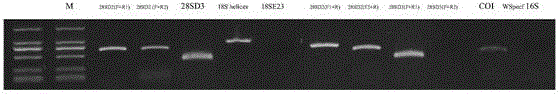
[0028] Example 3 Molecular Identification Marker Gene Screening
[0029] A series of primers including 28S, 18S, COI and 16sRNA were designed and synthesized according to the marker genes used in the study of the evolution of Hymenoptera insects. Using parasitoid DNA as a template, amplify each gene under the same conditions, and use a 20ml system for PCR reaction (template 1ml, 10×buffer 2.0ml, dNTP 1.6ml, forward and reverse primers 0.5ml, Taq enzyme 0.2ml, plus sterilized Double distilled water to 20ml), the PCR amplification procedure is as follows: first, pre-denature at 94°C for 3 minutes; then perform 35 cycles of 94°C for 30 s, 55°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 1 min; finally, extend at 72°C for 10 min. Take 10ml of the PCR product and test it by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis (for the test results, see figure 2 ). A total of 9 pairs of primer combinations produced products, which were sequenced to remove repetitive sequences. Considering their representativeness in the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com