N<15> stable isotope labeling method for biological protein quantifying and tracing
A technology of stable isotope and labeling method, which is applied in the field of N15 stable isotope labeling of biological protein quantification and tracing, can solve the problems of low labeling efficiency of primary cell culture, expensive SILAC reagents, and high test cost, and achieves short test period and high cost. The effect of practical value and low test cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
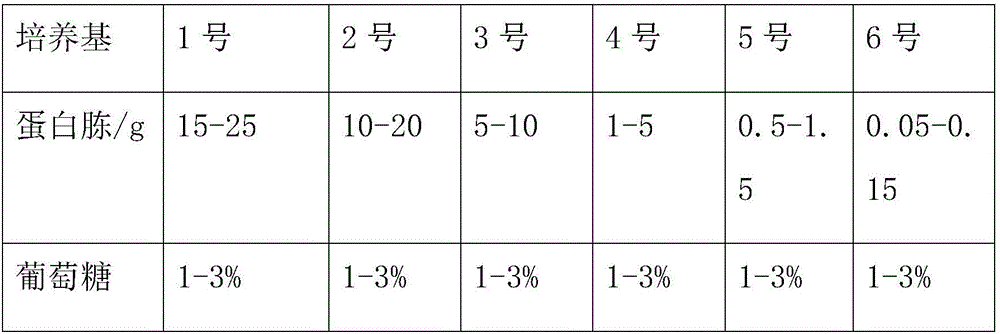
[0055] Embodiment 1 (N 15 Preparation of bacterial culture medium)
[0056] N for quantification and tracking of biological proteins described in this example 15 Stable isotope labeling method, specifically N 15 The preparation method of stable isotope labeling medium, comprises the following steps:
[0057] 1) Use only N 15 (excluding N 14 ) of the inorganic medium to cultivate the yeast;
[0058] Here, Pichia pastoris x-33 and basal salt medium (M9 mother liquor) are used;
[0059] 2) using the glass bead breaking method to lyse the yeast cells;
[0060] 3) Using protein semihydrolysis (acid hydrolysis) for N 15 Crude extraction of yeast protein;
[0061] 4)N 15 The preparation of bacterial culture medium, promptly will step 3) the N that produces after rough extraction 15 Peptone is used as the basic raw material of the medium, replacing the conventional N 14 Peptone is used for cultivation, and then adding inorganic salt substances without N to make the final N ...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Embodiment 2 (N 15 Preparation of fungal culture medium)
[0072] The difference from Example 1 is that step 1) of this example uses Cystogenic yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and basal salt medium (M9 mother liquor), and step 2) uses liquid nitrogen grinding method to lyse yeast cells, and step 3 ) using the yeast autolysis method (using its own enzymatic hydrolysis protein) to carry out N 15 The crude extraction of yeast protein, final step 4) makes N 15 Fungal culture medium.
[0073] N 15 Preparation of fungal culture medium
[0074]
[0075] Note: ① FeSO4.7H2O, Cacl2.2H2O, MgSO4.7H2O are made into high-concentration mother liquor, and added to the medium according to the amount after sterilization;
[0076] ②Glucose is made into mother liquor, and added to the medium according to the amount after sterilization.
[0077] The type of inorganic salt can adjust its composition and proportion according to the difference of specific fungal species. This impleme...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Embodiment 3 (N 15 Preparation of plant medium)
[0079] Different from embodiment 1 is the step 4) of present embodiment finally makes N 15 Plant medium, the specific steps are as follows:
[0080] 1) Use only N1 5 (excluding N 14 )'s inorganic medium to cultivate the yeast; Pichia x-33 and basal salt medium (M9 mother liquor) can be used here;
[0081] 2) using the glass bead breaking method to lyse the yeast cells;
[0082] 3) Using protein semihydrolysis (acid hydrolysis) for N 15 Crude extraction of yeast protein;
[0083] 4)N 15 Preparation of plant medium: the peptone of the following medium comes from step 3) in N 15 Crude extraction of yeast protein.
[0084] N 15 Preparation of plant medium:
[0085]
[0086] Note: ①FeSO 4 .7H 2 O. Cacl 2 .2H 2 O. KH 2 PO 4 , Na—EDTA, MgSO 4 .7H 2 O is made into a high-concentration mother solution, which is added to the medium according to the amount after sterilization.
[0087] ②Glucose is made into m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com