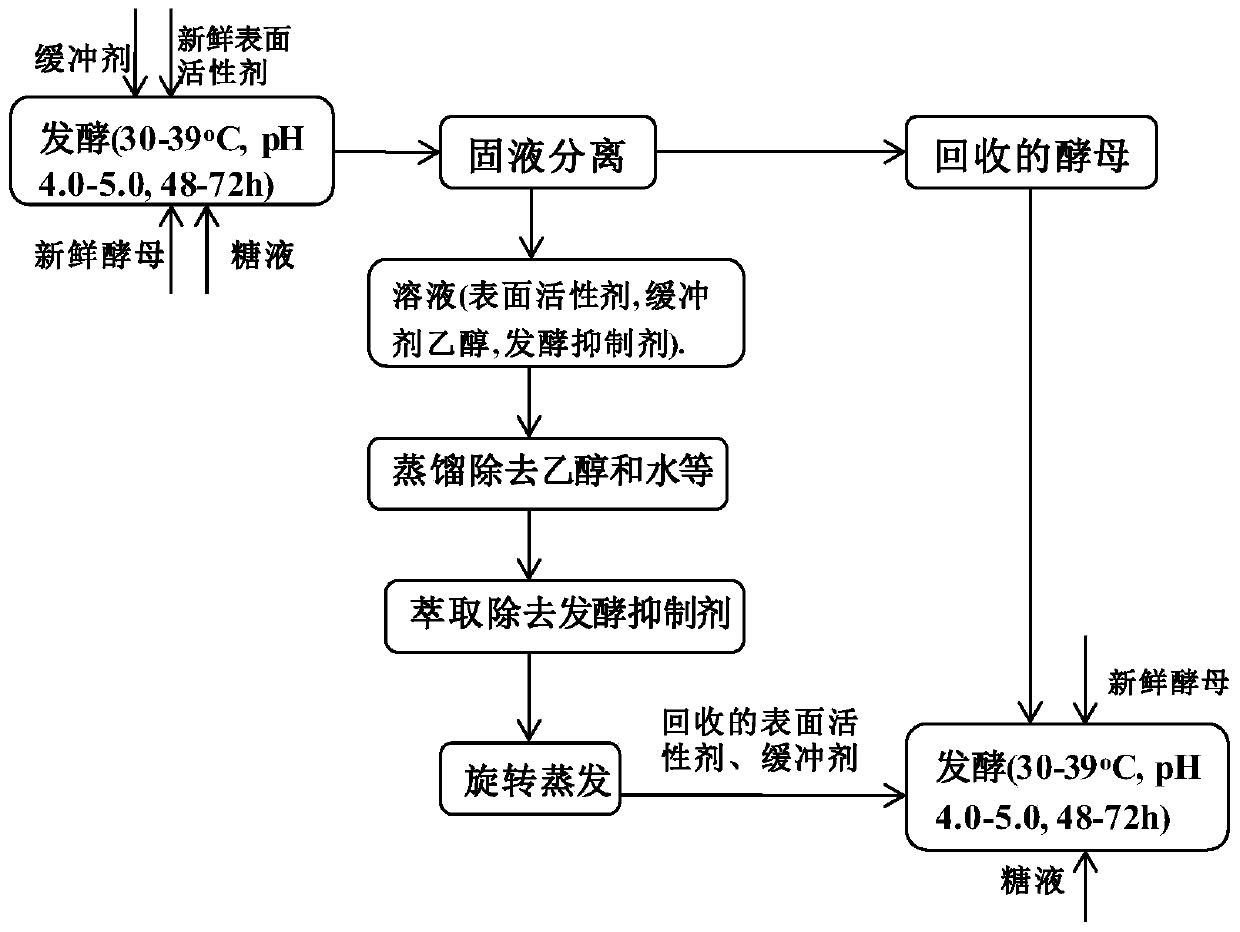
Surfactant recovery technology in lignocellulose hydrolyzate fermentation process
A technology of surfactant and lignocellulose is applied in the field of biomass raw material degradation to produce fuel ethanol through fermentation process, which can solve the problems of complex process, high equipment investment cost, sugar loss, etc., achieve wide application prospects and improve atom utilization rate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
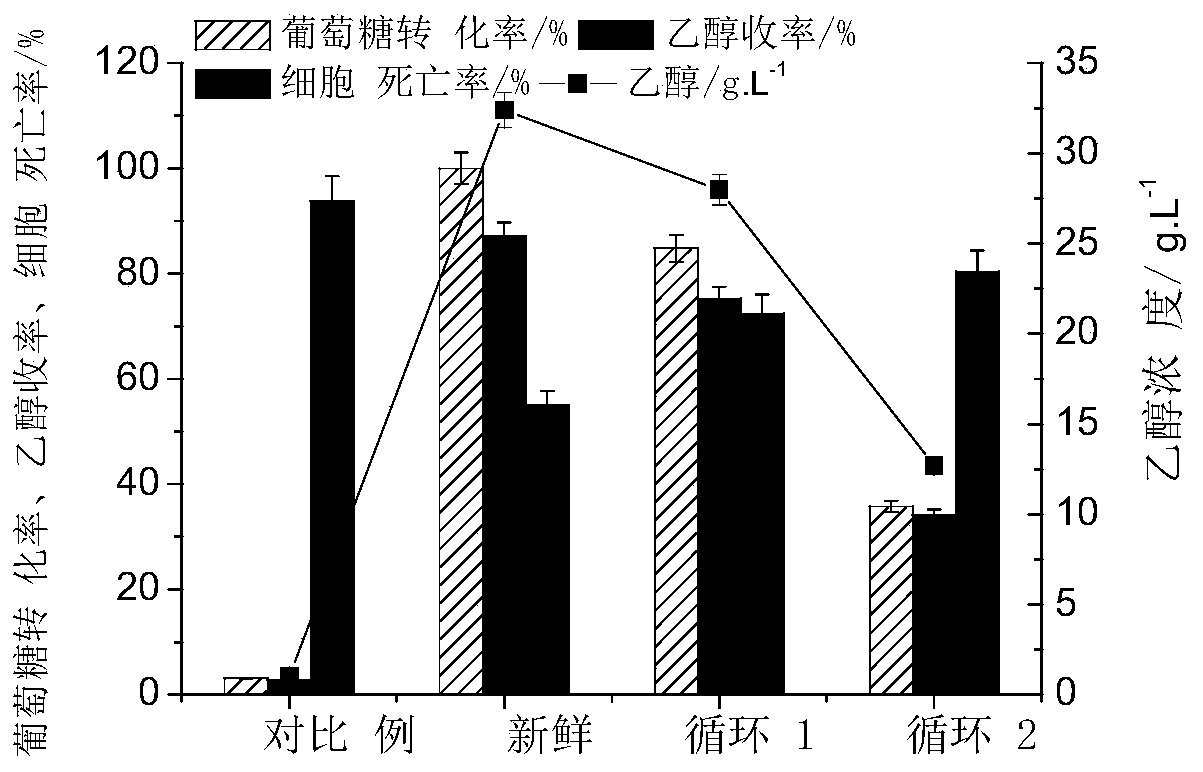
[0031] Lignocellulose hydrolyzate model substance 20mL, containing glucose concentration 71g.L -1 , mixed inhibitors (phenol, guaiacol, vanillin, HMF, furfural, levulinic acid mixture) (2.0g.L -1 ), add 0.2g.mL -1 PEG-400 (no PEG added in the comparative example), adding yeast cell concentration 0.8*10 8 ~0.96*10 8 per mL, the pH value was adjusted to 4.3, placed in a shaker for shaking, and fermented at 33°C for 48 hours. Solid-liquid separation is carried out after fermentation, and the recovered yeast cells are directly used for the next fermentation. Glucose conversion rate and ethanol concentration were as figure 2 shown. It can be seen from the comparative data in the figure that when PEG is not added to the fermentation system, the glucose is hardly converted, and the yeast cells are almost completely dead, which cannot be recycled and reused. However, when PEG was added to the fermentation system, the glucose was completely converted 100% and obtained 32g.L -1 ...
Embodiment 2
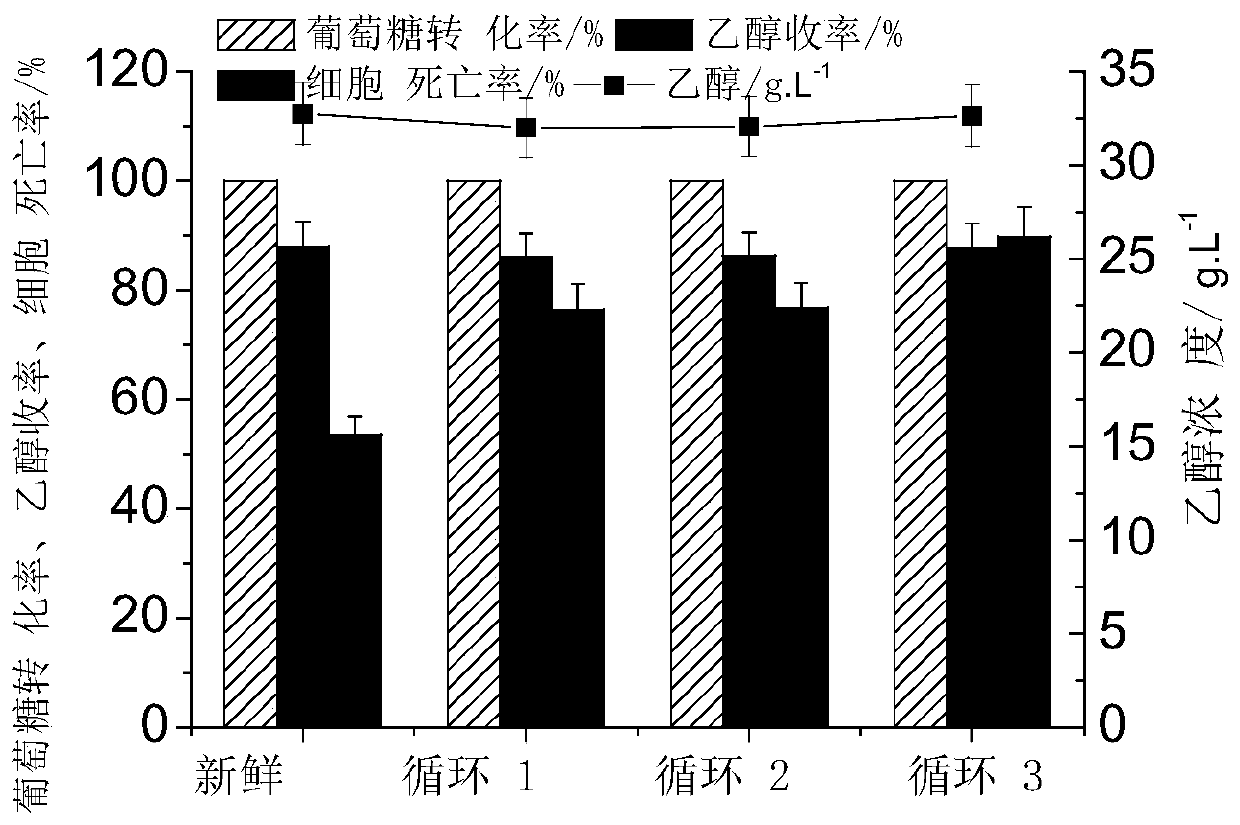
[0033] Lignocellulose hydrolyzate model substance 20mL, containing glucose concentration 71g.L -1 , mixed inhibitors (phenol, guaiacol, vanillin, HMF, furfural, levulinic acid mixture) (2.0g.L -1 ), add 0.2g.mL -1 PEG-1000, add yeast cell concentration 0.8*10 8 ~0.96*108 per mL, the pH value was adjusted to 4.3 with sulfuric acid solution, placed in a shaker for shaking, and fermented at 33°C for 48 hours. After fermentation, solid-liquid separation is carried out, and the upper liquid is distilled, extracted, and re-distilled, and the remaining liquid is surfactant, buffer, and the recovered yeast can be directly used in the next fermentation process (such as figure 1 ), add some new yeast. PEG-1000 and the recovered yeast were recycled 3 times and the results were as follows: image 3 shown. It can be seen from the figure that PEG-1000 can be recycled and reused, and the glucose conversion rate and ethanol concentration remain basically unchanged.
Embodiment 3
[0035] The experimental procedure is the same as in Example 2, except that 0.2g.mL is added -1 PEG-200, glucose conversion rate, ethanol yield and concentration data are shown in Table 1. It can be seen from the table that PEG-200 can be recycled and reused. After three cycles, the glucose is completely converted, and the ethanol concentration remains basically unchanged.
[0036] Table 1 Glucose conversion rate and ethanol concentration data
[0037]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com