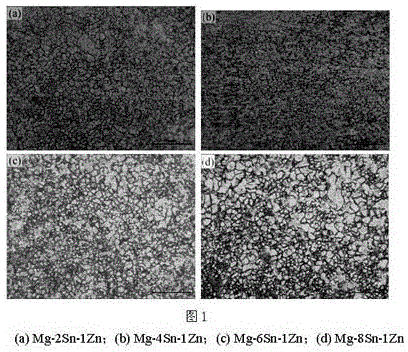
Biological medical Mg-Sn-Zn alloy and rolling method thereof
A biomedical, mg-sn-zn technology, applied in metal rolling and other directions, can solve the problems that degradation products easily cause inflammation and swelling, are not biodegradable biomedical materials, and have low mechanical properties of magnesium alloys, and achieve excellent bearing capacity. and biocompatibility, excellent comprehensive mechanical properties, casting defect elimination effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] A biomedical Mg-Sn-Zn alloy with a slab size of 120×100×20mm 3 , its rolling method comprises the following steps:
[0023] The Mg-Sn-Zn alloy ingot is kept at 300°C for 12 minutes, and then the Mg-Sn-Zn alloy slab is subjected to single-pass 15% hot rolling pre-deformation at 300°C, and then continues to be heated at 300°C Carry out a single pass of 80% large-reduction rolling forming, and then carry out water-cooling treatment to room temperature. The alloy slab after water-cooling treatment is subjected to aging treatment at 150°C for 4 hours, and finally water-quenched.
[0024] The biomedical Mg-Sn-Zn alloy is composed of the following components: Sn 2.0%, Zn 0.8%, Mg 97.2%.
[0025] The casting molding of described Mg-Sn-Zn alloy billet comprises the following steps:
[0026] Melt Mg, Sn, and Zn at 740°C and cast them into Mg-Sn-Zn alloy ingots. The smelting process is protected by argon gas; then it is subjected to homogenization annealing treatment, the anneal...
Embodiment 2
[0029] The biomedical Mg-Sn-Zn alloy of the present invention has a slab size of 140×110×35mm 3 , its rolling method comprises the steps:
[0030] The Mg-Sn-Zn alloy ingot is kept at 315°C for 35 minutes, and then the Mg-Sn-Zn alloy slab is subjected to single-pass 16% hot rolling pre-deformation at 317°C, and then continues to be heated at 317°C Carry out a single pass of 86% large-reduction rolling forming, and then carry out water-cooling treatment to room temperature. The alloy slab after water-cooling treatment is subjected to aging treatment at 165°C for 6 hours, and finally water-quenched.
[0031] The biomedical Mg-Sn-Zn alloy is composed of the following components: Sn 4.0%, Zn 1.0%, Mg 95%.
[0032] The casting molding of described Mg-Sn-Zn alloy billet comprises the following steps:
[0033] Melt Mg, Sn, and Zn at 752°C and cast them into Mg-Sn-Zn alloy ingots. The smelting process is protected by argon; then it is subjected to homogenization annealing treatment, ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] A biomedical Mg-Sn-Zn alloy with a slab size of 170×135×50mm 3 , its rolling method comprises the steps:
[0037] The Mg-Sn-Zn alloy ingot was kept at 342°C for 80 minutes, and then the Mg-Sn-Zn alloy slab was subjected to single-pass 18% hot-rolling pre-deformation at 335°C, and then continued at 335°C Carry out single-pass 90% large-reduction rolling forming, and then carry out water-cooling treatment to room temperature. The alloy slab after water-cooling treatment is subjected to aging treatment at 180°C for 8 hours, and finally water-quenched.
[0038] The biomedical Mg-Sn-Zn alloy is composed of the following components: Sn 6.0%, Zn 1.2%, Mg 92.8%.
[0039] The casting molding of described Mg-Sn-Zn alloy billet comprises the following steps:
[0040] Melt Mg, Sn, and Zn at 764°C and cast them into Mg-Sn-Zn alloy ingots. The smelting process is protected by argon; then it is homogenized and annealed. The annealing temperature is 430°C and the annealing time is 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com