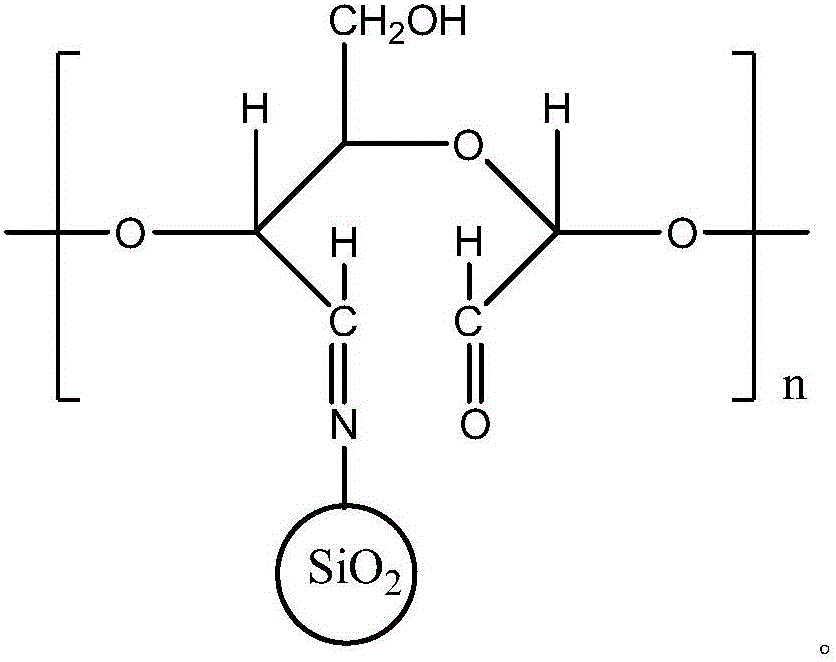
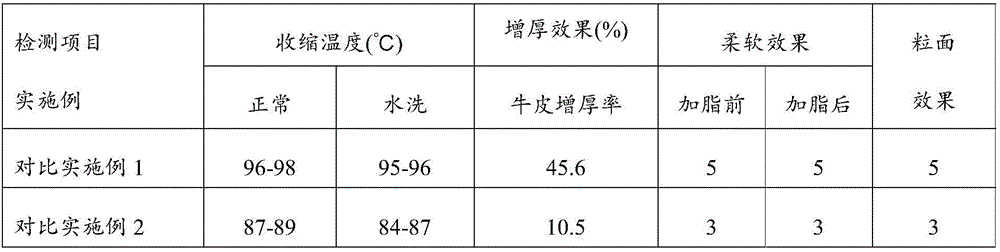
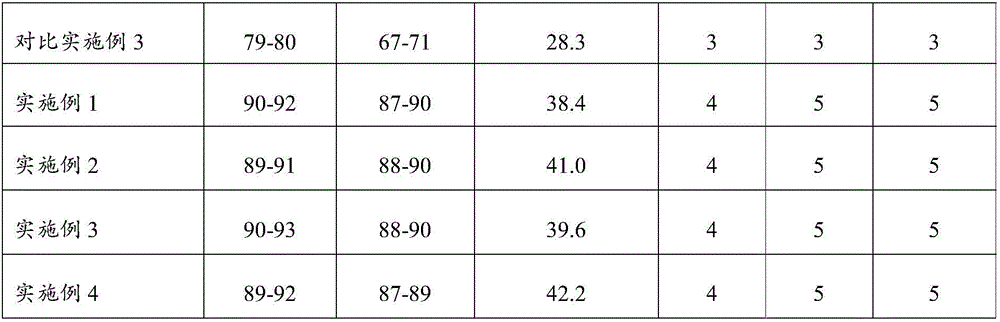
Leather tanning agent based on cellulose and nanometer SiO2 hybridization and preparation method
A cellulose, dialdehyde cellulose technology, applied in small raw hide/large raw hide/leather/fur treatment, small raw hide/large raw hide/leather hide/fur chemical treatment, tanning treatment, etc., can solve the shrinkage of vegetable tanned leather Low temperature, unsuitable production of soft leather, environmental pollution and other problems, to improve the washing resistance, avoid surface over-tanning phenomenon, avoid the effect of rough surface phenomenon
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] (1) Weigh 5 g of cellulose and dissolve it in 100 mL of hydrochloric acid solution with a concentration of 5 mol / L, stir, hydrolyze for 12 hours, centrifuge and take the precipitate. The precipitated substance is washed and soaked with deionized water, and the precipitate is suspended in deionized water; sodium periodate is added to the solution under stirring until the precipitated substance is evenly dispersed. The reaction was carried out in a light-proof environment, and the pH value of the solution was kept at 4 during the process, and the temperature was 40°C. After the reaction, add tert-butanol to the solution, and centrifuge to obtain dialdehyde cellulose.
[0029] (2) Add 10mL tetraethylsiloxane to 50mL ethanol-water solution, mix well, then add 0.5mL glacial acetic acid, heat up to 75°C, after 15 minutes, add N-aminoethyl-γ-aminopropanol dropwise Trimethoxysilane until a gel appears. The gel was vacuum dried to obtain SiO 2 -NH 2 .
[0030] (3) The diald...
Embodiment 2
[0033] (1) Weigh 5 g of cellulose and dissolve it in 100 mL of hydrochloric acid solution with a concentration of 5 mol / L, stir, hydrolyze for 12 hours, centrifuge and take the precipitate. The precipitated substance is washed and soaked with deionized water, and the precipitate is suspended in deionized water; sodium periodate is added to the solution under stirring until the precipitated substance is evenly dispersed. The reaction was carried out in a dark environment, and the pH value of the solution was kept at 3 during the process, and the temperature was 35°C. After the reaction, add tert-butanol to the solution, and centrifuge to obtain dialdehyde cellulose.
[0034] (2) Add 10mL butyl orthosilicate to 50mL ethanol-water solution, mix well, then add 0.5mL glacial acetic acid, heat up to 70°C, after 20 minutes, add N-aminoethyl-γ-aminopropyl dropwise trimethoxysilane until a gel appears. The gel was vacuum dried to obtain SiO 2 -NH 2 .
[0035] (3) The dialdehyde ce...
Embodiment 3
[0038] (1) Weigh 5 g of cellulose and dissolve it in 100 mL of hydrochloric acid solution with a concentration of 5 mol / L, stir, hydrolyze for 12 hours, centrifuge and take the precipitate. The precipitated substance is washed and soaked with deionized water, and the precipitate is suspended in deionized water; sodium periodate is added to the solution under stirring until the precipitated substance is evenly dispersed. The reaction was carried out in a dark environment, the pH value of the solution was kept at 5, and the temperature was 50°C during the process. After the reaction, add tert-butanol to the solution, and centrifuge to obtain dialdehyde cellulose.
[0039] (2) Add 10mL of butyl orthosilicate to 50mL of ethanol-water solution, mix well, then add 0.5mL of glacial acetic acid, heat up to 80°C, after 10 minutes, add N-aminoethyl-γ-aminopropyl dropwise trimethoxysilane until a gel appears. The gel was vacuum dried to obtain SiO 2 -NH 2 .
[0040] (3) The dialdehy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com