Method and device for Fourier domain iterative splicing super-resolution microscopy based on surface wave illumination
A super-resolution and surface wave technology, applied in measurement devices, material analysis, material analysis by optical means, etc., can solve problems such as complex manipulation, and achieve the effect of fast imaging speed and simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
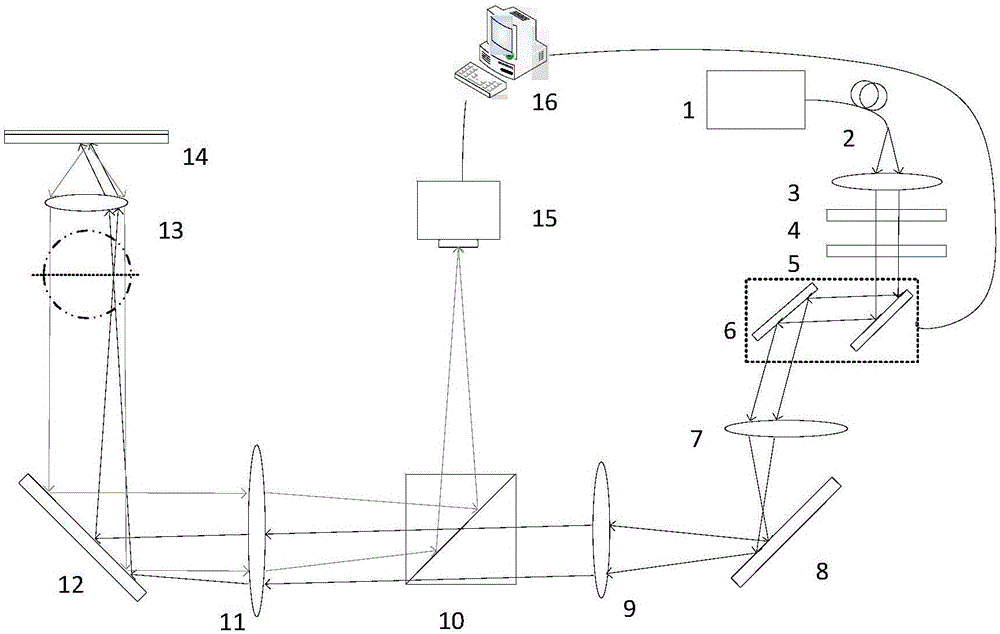
[0063] Such as figure 1 As shown, a Fourier domain iterative splicing super-resolution microscopic imaging device based on surface wave illumination propagating in different directions generated by a two-dimensional scanning galvanometer, including a laser 1, an optical fiber 2, a first lens 3, and a polarizer 4 , a half-wave plate 5, a two-dimensional scanning mirror 6, a scanning lens 7, a first mirror 8, a second lens 9, a dichroic prism 10, a field lens 11, a second mirror 12, an objective lens 13, and a sample 14 , CCD 15, computer 16.
[0064] use figure 1 The frequency-shifting super-resolution microscopy method realized by the shown device, its process is as follows:
[0065] (1) The laser 1 emits an illumination beam, which is collimated by the fiber coupling 2 and the first lens 3 to obtain a collimated beam; the collimated beam is modulated into a parallel linearly polarized light by a polarizer 4, and the parallel linearly polarized light is 1 / 2 After the wave...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Such as Figure 7 As shown, a Fourier domain iterative splicing super-resolution microscopic imaging device based on surface wave illumination that propagates in different directions through a digital micromirror (DMD), including a laser 1, an optical fiber 2, a first lens 3, and a polarizer 4. Half-wave plate 5, scan lens 6, second lens 7, digital micromirror (DMD) 17, third lens 9, beam splitter prism 10, field lens 11, second mirror 12, objective lens 13, sample 14, CCD 15, computer 16.
[0077] use Figure 7 The frequency-shifting super-resolution microscopy method realized by the shown device, its process is as follows:
[0078] (1) The laser 1 emits an illumination beam, which is collimated by the fiber coupling 2 and the first lens 3 to obtain a collimated beam; the collimated beam is modulated into a parallel linearly polarized light by a polarizer 4, and the parallel linearly polarized light is 1 / 2 After the wave plate 5 is the parallel linearly polarized li...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com