Fluorescence in-situ hybridization method for asparagus fern medium-term chromosomes
A fluorescence in situ hybridization and chromosome technology, applied in the field of molecular cytogenetics, can solve the problems such as the application of fluorescence in situ hybridization technology, the failure of chromosome production, the expansion and deformation of chromosomes, etc., to achieve clear signal points, high labeling efficiency, full effect of denaturation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
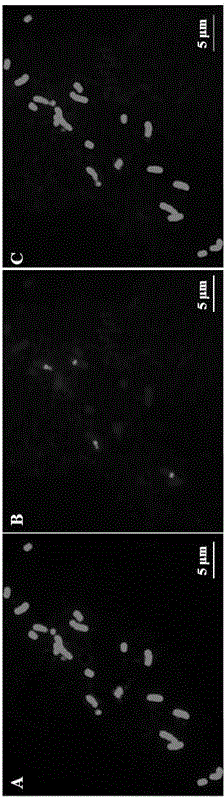
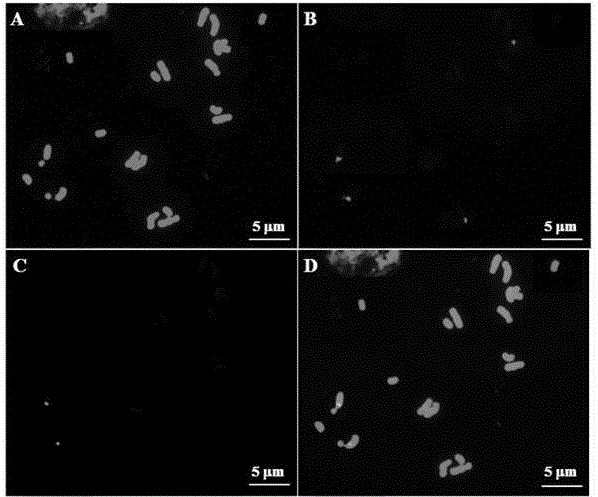
[0025] (1) Preparation of chromosomal slide specimens. Control the water of potted asparagus bamboo for three days, and then water it. Take the root tip at 9:00-10:00 the next morning after watering, and use N 2 After O treatment for 2 hours, acetic acid with a mass percentage of 90% was fixed on ice for 10 min, and after fixation, it was washed with deionized water on ice for 10 min. Enzyme hydrolyze in a mixture of 2% cellulase at 37°C for 2 hours, wash the root tip twice with 70% ethanol by volume after enzymatic hydrolysis, then mash the root tip in 40 μL ethanol with a dissecting needle, and vortex to suspend Cells, centrifuge to retain the precipitate and add 30 μL of anhydrous acetic acid, mix well, absorb 5-8 μL droplet, place at room temperature for 5 minutes, and then perform microscopic examination. The microscopically well-examined slides are placed in a UV cross-linking instrument and passed through 120-125mJ / cm 2 Process for 2 minutes to fix the chromosomes to ob...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com