Method for recycling well flushing waste water in in-situ leaching uranium exploration
A technology of wastewater circulation and in-situ leaching for uranium production, which is applied in wellbore flushing, earthwork drilling, wellbore/well components, etc. It can solve the problem that the method cannot meet the needs of production, the amount of well-washing wastewater is large, and uranium cannot be effectively recovered. Recycling and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
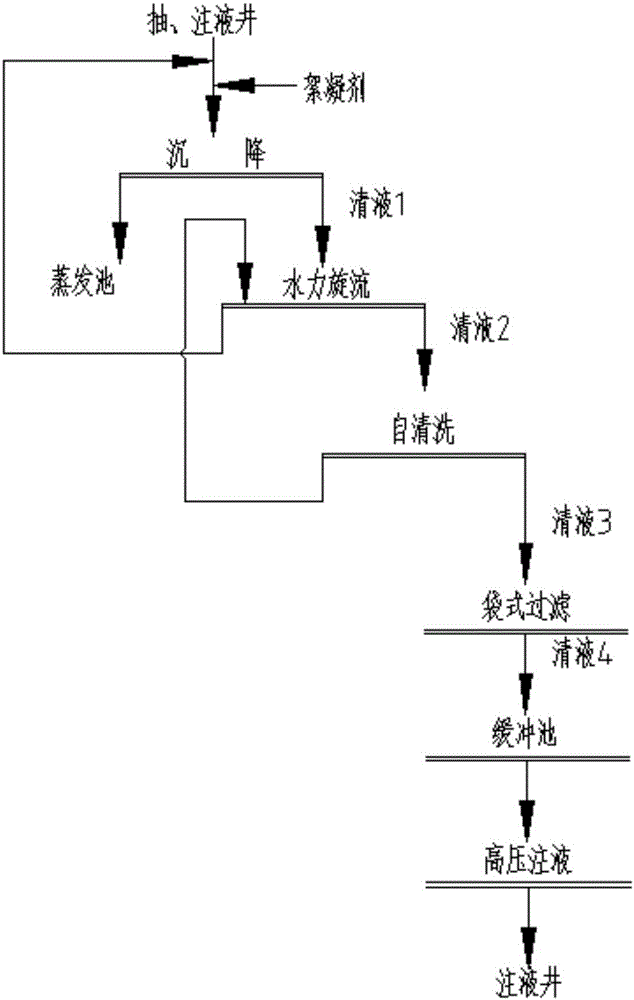
[0021] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of method for recycling waste water from uranium mining by in-situ leaching of the present invention, it comprises the following steps:
[0022] (a) Lifting the well-washing wastewater of the pumping and injection wells for uranium mining by in-situ leaching to the surface, and then settling through the settling tank, the bottom flow slurry of the settling tank is discharged into the evaporation pool, and the supernatant 1 of the settling tank enters step (b);
[0023] After being clarified by the settling tank, the silt (sand) content of the clear liquid 1 is less than 5.3%, and the particle size distribution is greater than 50 μm, accounting for 90%.
[0024] (b) The supernatant liquid 1 is sent into the hydrocyclone, and the clear liquid 2 coming out of the hydrocyclone enters step (c); the sand-containing solution coming out of the hydrocyclone is returned to the settling tank, and a closed-circuit circulation process is carried out; ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of method for recycling waste water from uranium mining by in-situ leaching of the present invention, it comprises the following steps:
[0033] (a) Lifting the well-washing wastewater of the pumping and injection wells for uranium mining by in-situ leaching to the surface, and then settling through the settling tank, the bottom flow slurry of the settling tank is discharged into the evaporation pool, and the supernatant 1 of the settling tank enters step (b);
[0034] After being clarified in the settling tank, the mud (sand) content of the clear liquid 1 is less than 4.2%, and the particle size distribution is greater than 50 μm, accounting for 75%.
[0035] (b) The supernatant liquid 1 is sent into the hydrocyclone, and the clear liquid 2 coming out of the hydrocyclone enters step (c); the sand-containing solution coming out of the hydrocyclone is returned to the settling tank, and a closed-circuit circulation process is carried out;
...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of method for recycling waste water from uranium mining by in-situ leaching of the present invention, it comprises the following steps:
[0044] (a) Lifting the well-washing wastewater of the pumping and injection wells for uranium mining by in-situ leaching to the surface, and then settling through the settling tank, the bottom flow slurry of the settling tank is discharged into the evaporation pool, and the supernatant 1 of the settling tank enters step (b);
[0045] After being clarified by the settling tank, the mud (sand) content of the clear liquid 1 is less than 4.8%, and the particle size distribution is greater than 50 μm, accounting for 85%.
[0046] (b) The supernatant liquid 1 is sent into the hydrocyclone, and the clear liquid 2 coming out of the hydrocyclone enters step (c); the sand-containing solution coming out of the hydrocyclone is returned to the settling tank, and a closed-circuit circulation process is carried out;
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com