Chardonnay grape seed extract
An extract and grape seed technology, applied in the field of Chardonnay grape seed extract, can solve problems such as less ideal and high temperature processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] method of extraction
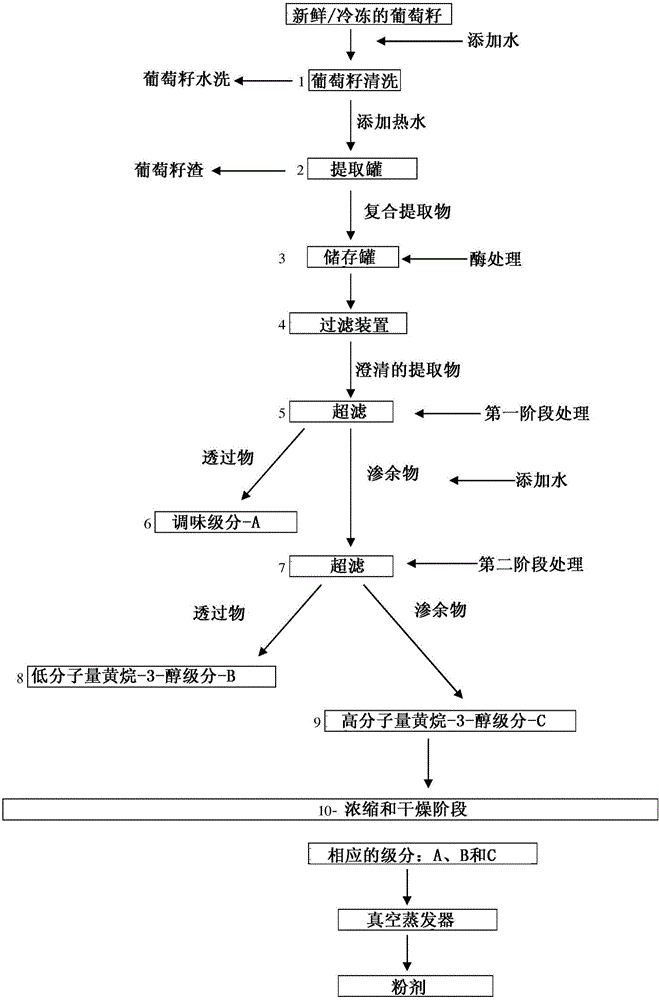
[0079] A specific non-limiting embodiment of the extraction process is shown in figure 1 middle. In step (1), Chardonnay grape seeds 1 (fresh, frozen or dried) are washed with drinking water at room temperature. Various weight ratios of water to grape seed can be used, such as a 2:1 to 10:1 ratio, but the example shown uses a 5:1 ratio of water to grape seed [weight:weight], which is obtained by Wash with continuous mixing for 15 minutes. This process is repeated at least two or more times, preferably three times and at most four times. In some examples, the water, eg, the water of the first wash, is neutralized by the addition of alkali to reduce the extraction of polyphenolic compounds into the wash water and simultaneously increase the extraction of sugars into the wash water. In a particular example, the water is neutralized by adding sodium bicarbonate, eg, 0.1% sodium bicarbonate, to the water. Each rinse water is discarded, which main...
Embodiment 2
[0088] analysis results
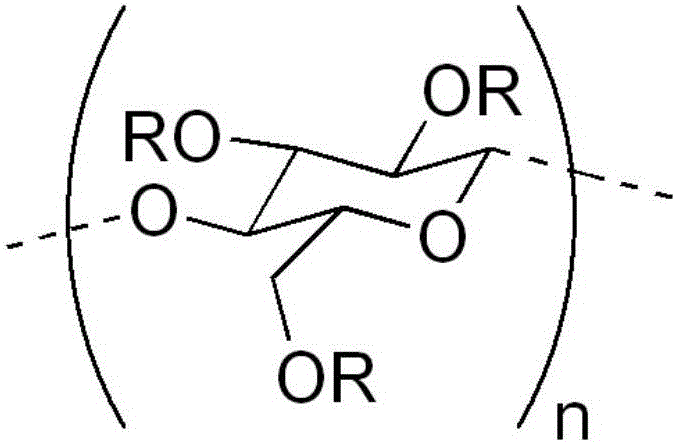
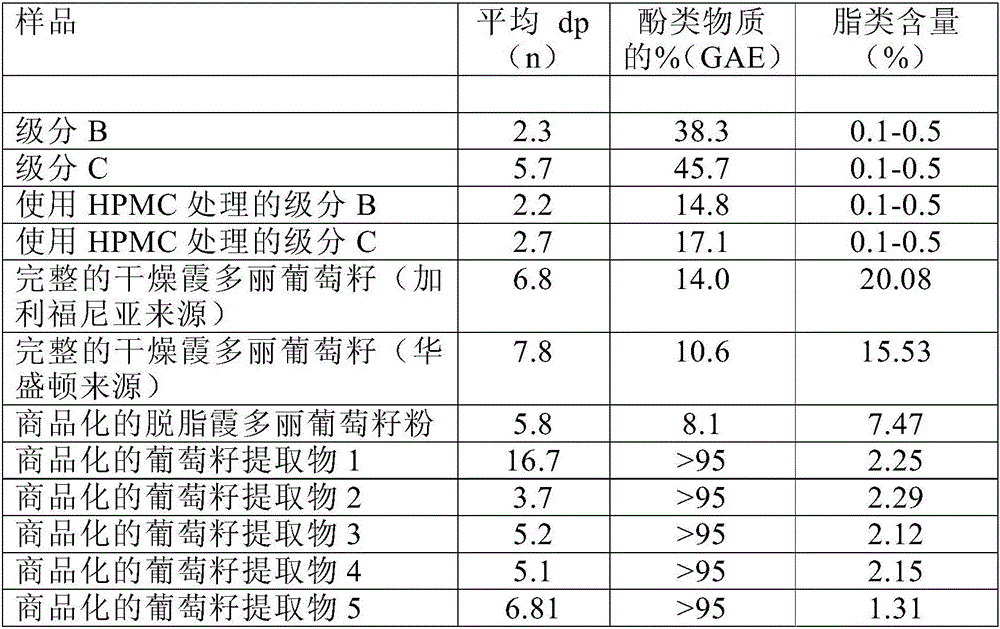
[0089]Intact Chardonnay grape seeds (fresh grape seeds typically contain 40-50% water) and Fraction A were analyzed by the modified Folin-Ciocalteu method (Singleton and Rossi, Am J Enol Vitic 16:144-158, 1965) , B and C (produced for the first time using an ultrafiltration membrane with a maximum cut-off of 5 kD and for the second time with an ultrafiltration membrane with a maximum cut-off of 500 kD as described in Example 1) and polyphenols compound (gallic acid equivalent [GAE]). As shown in Table 1, Fraction A is almost entirely sugars, 90% of which is fructose and glucose. Fraction B mainly comprised low molecular weight polyphenolic compounds such as monomeric and dimeric flavanols (see Tables 2 and 3 below) and a small amount of fiber. Fraction C contained flavanol oligomers and polymers (tannins) as described in Tables 2 and 3 below and was rich in fiber. Importantly, Fractions B and C contained very low levels of lipids (<1%), compared to...
Embodiment 3
[0100] cleaning steps
[0101] This example illustrates the beneficial effect of seed washing prior to ultrafiltration on polyphenol yield. Although seed washing was shown to increase phenolic recovery at lower extraction temperatures, the washing step was not an essential component of the method disclosed in Example 1. In contrast, the washing step provides additional benefits to the separation method described separately in Example 1 and thus should not be considered a requirement of the method.
[0102] Although the main purpose of the disclosed extraction process is to separate the different components of grape seeds for use in different applications, improving yield efficiency (both by weight and polyphenolic compounds) contributes to better commercial viability. sex. As noted above, existing processes often include harsh solvents and / or high extraction temperatures to maximize extraction yields, but these conditions are undesirable for a variety of reasons. Especially...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com