Agrobacterium and transgenic plant manufacturing method using such agrobacterium
An Agrobacterium, nuclear transfer technology, applied in the fields of botany equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, plant products, etc., can solve the problems of uncontrollable target gene copy number, inconsistent gene expression level, target gene insertion, etc. The effect of improving gene targeting efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] [Example 1] Preparation of the gene disruption strain of Agrobacterium
[0080] Agrobacterium A208 strain (C58 chromosome, nopaline (nopaline) type T37pTi) gene disruption The strain was prepared using the "method based on the principle of site-specific insertion by homologous recombination mechanism and shedding by second-stage homologous recombination" described in JP-A-2007-259708.
[0081] The primers used for the preparation of the gene-disrupted strain of Agrobacterium are as follows.
[0082]
[0083]
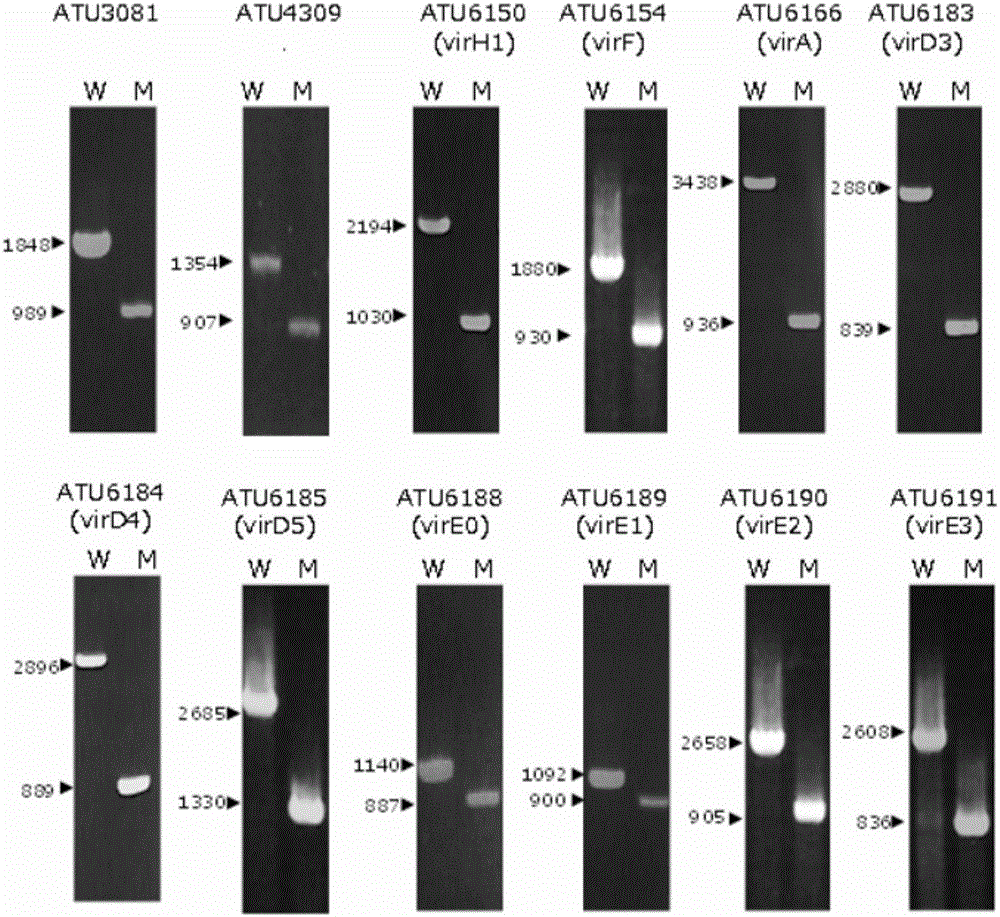
[0084] In addition, confirmation of gene disruption was carried out by genomic PCR of the prepared Agrobacterium strain. The PCR reaction conditions are shown in Table 2 below.
[0085] Table 2
[0086]
[0087] In addition, the following primers were used for genomic PCR for confirmation of gene disruption.
[0088]
[0089]
[0090] According to the result of genomic PCR, it was confirmed that the target gene had been destroyed in the gene dis...
Embodiment 2
[0091] [Example 2] Confirmation of Pathogenicity (T-DNA Chromosomal Insertion Ability) and T-DNA Nuclear Transfer Ability of Agrobacterium Gene Disruption Strain
[0092] The pathogenicity (T-DNA chromosomal insertion ability) of the Agrobacterium gene-disrupted strain was carried out by the following method. The Agrobacterium gene disruption strain prepared in [Example 1] was inoculated into the leaves of Kalanchoe daigre montiana plants with the bacterium obtained after cultivating the Agrobacterium gene disruption strain at 25° C. for 48 hours with LB solid medium (Difco company). . The presence or absence of pathogenicity (T-DNA chromosomal insertion ability) was judged by the presence or absence of tumor (crown gall) formation at the inoculation site 3 weeks after inoculation. In addition, the strength of pathogenicity was evaluated by comparing the tumor size with that of the Agrobacterium wild strain.
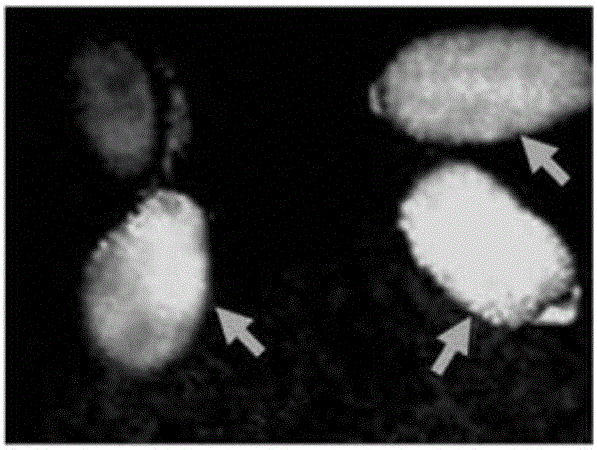
[0093] In addition, confirmation of T-DNA nuclear transfer abilit...
Embodiment 3
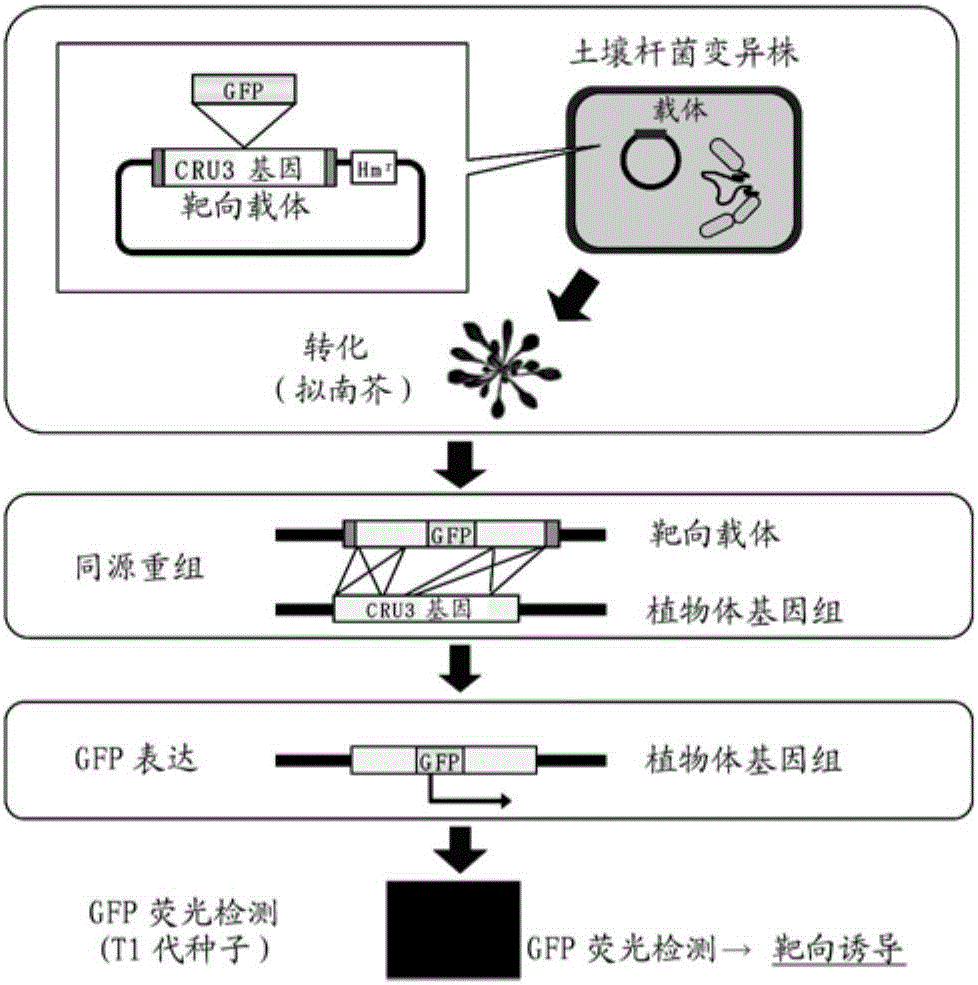
[0105] [Example 3] Construction of a gene targeting (homologous recombination) evaluation system using Arabidopsis
[0106]A targeted reporter gene using cruciferin 3 (hereinafter CRU3), which is a seed storage protein of Arabidopsis thaliana, was produced, and a gene targeting evaluation system in dicot Arabidopsis was constructed ( figure 2 ). For the targeting vector used, it can be considered that due to the insertion of GFP fluorescent protein (GFP) inside the CRU3 gene, when the gene targeting is successful, the endosperm, which is the expression site of the CRU3 gene, will emit specific GFP fluorescence.
[0107] In addition, the following primers and PCR reaction conditions in Table 4 were used to confirm the presence or absence of targeting by genomic PCR.
[0108] Forward primer ctacgcgcatgaagatcaag (SEQ ID NO: 82)
[0109] Reverse primer tcctcgcccttgctcaccat (SEQ ID NO: 83)
[0110] Table 4
[0111]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com