Plant pesticide for preventing vegetable grey mould and preparation method of plant pesticide
A botanical pesticide and Botrytis cinerea technology, applied in botanical equipment and methods, plant growth regulators, biocides, etc., can solve problems such as weak control effects, achieve thorough antibacterial and bactericidal effects, strong bactericidal effects, and improve active effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
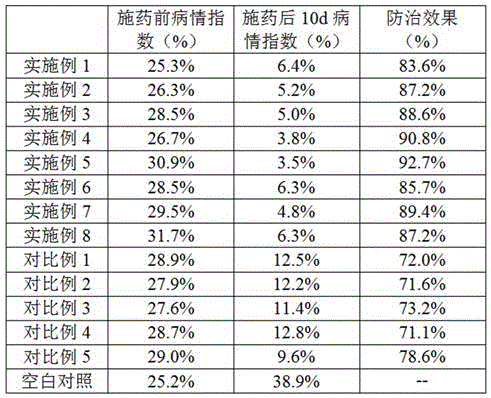
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A botanical pesticide for preventing and treating gray mold of vegetables, comprising the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20 parts of cocklebur, 30 parts of Scutellaria chinensis, 15 parts of philodendron bark, 15 parts of camphor leaves, 20 parts of cloves, and 4 parts of surfactant 6 parts, 6 parts of wetting agent, 80 parts of filler.
[0026] Wherein the surfactant is fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether.
[0027] The wetting agent is sodium lauryl sulfate.
[0028] The filler is kaolin.
[0029] A preparation method of a botanical pesticide for preventing and treating botrytis cinerea, comprising the following steps:
[0030] (1) Weigh Xanthium, Scutellaria and Cinnamomum bark, crush them to 80 mesh, add 6 times the total weight and volume fraction of Xanthium, Scutellaria and Cinnamomum bark in ethanol solution, and add the total Measure 0.1 times the weight of cellulase, soak for 2 hours, then ultrasonically extract twice, combine the filtrates, con...
Embodiment 2
[0035] A botanical pesticide for preventing and treating gray mold of vegetables, comprising the following raw materials in parts by weight: 22 parts of cocklebur, 28 parts of Scutellaria chinensis, 16 parts of camphora bark, 16 parts of camphor leaves, 19 parts of cloves, and 5 parts of surfactant 7 parts, 7 parts of wetting agent, 85 parts of filler.
[0036] Wherein the surfactant is alkylphenol polyoxyethylene ether.
[0037] Wherein the humectant is propylene glycol.
[0038] Wherein the filler is chitosan.
[0039] A preparation method of a botanical pesticide for preventing and treating botrytis cinerea, comprising the following steps:
[0040] (1) Weigh cocklebur, scutellaria and philodendron, crush them to 90 mesh, add 7 times the total weight and volume fraction of cocklebur, scutellaria and philodendron in ethanol solution, and add the total Measure 0.2 times the weight of cellulase, soak for 2.5 hours, then ultrasonically extract 3 times, combine the filtrates, ...
Embodiment 3
[0045]A botanical pesticide for preventing and treating botrytis cinerea, comprising the following raw materials in parts by weight: 24 parts of cocklebur, 26 parts of Scutellaria chinensis, 17 parts of philodendron bark, 17 parts of camphor leaves, 18 parts of cloves, and 6 parts of surfactant 8 parts, 8 parts of wetting agent, 90 parts of filler.
[0046] Wherein the surfactant is fatty acid polyoxyethylene ether.
[0047] Wherein the humectant is glycerin.
[0048] Wherein the filler is chitin.
[0049] A preparation method of a botanical pesticide for preventing and treating botrytis cinerea, comprising the following steps:
[0050] (1) Weigh Xanthium, Scutellaria and Cinnamomum bark, crush them to 100 meshes, add 8 times the total weight and volume fraction of Xanthium, Scutellaria and Cinnamomum bark in ethanol solution, and add the total Measure 0.15 times the weight of cellulase, soak for 3 hours, then ultrasonically extract twice, combine the filtrates, concentrate...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com