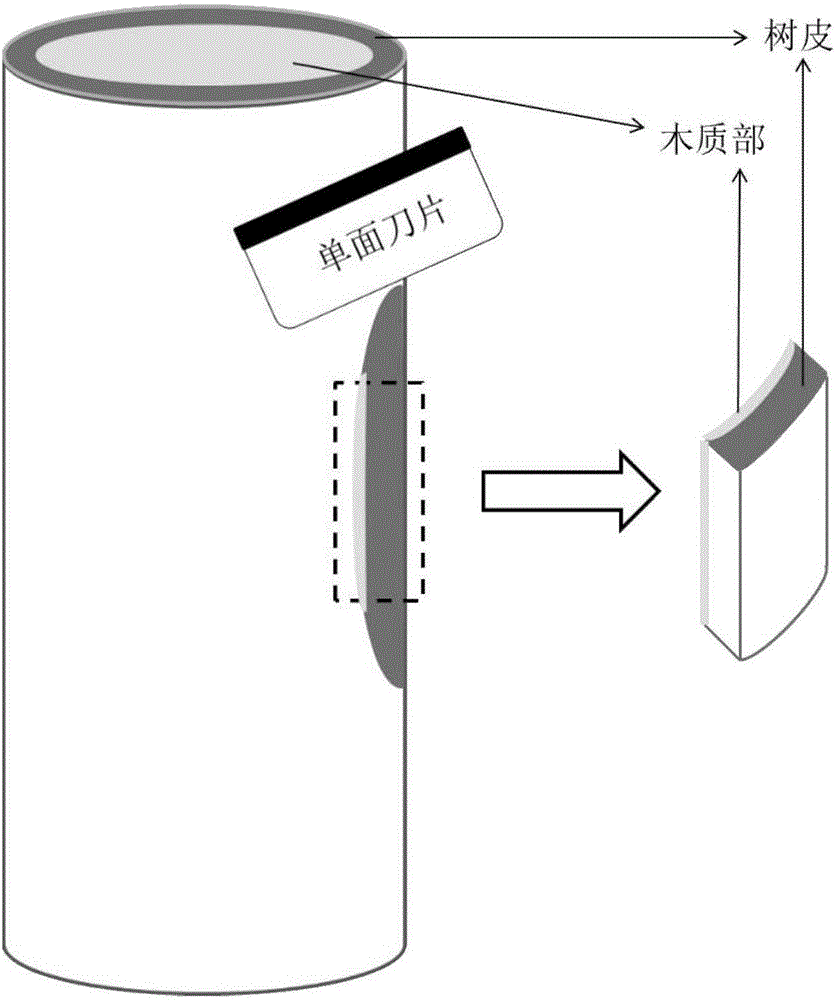
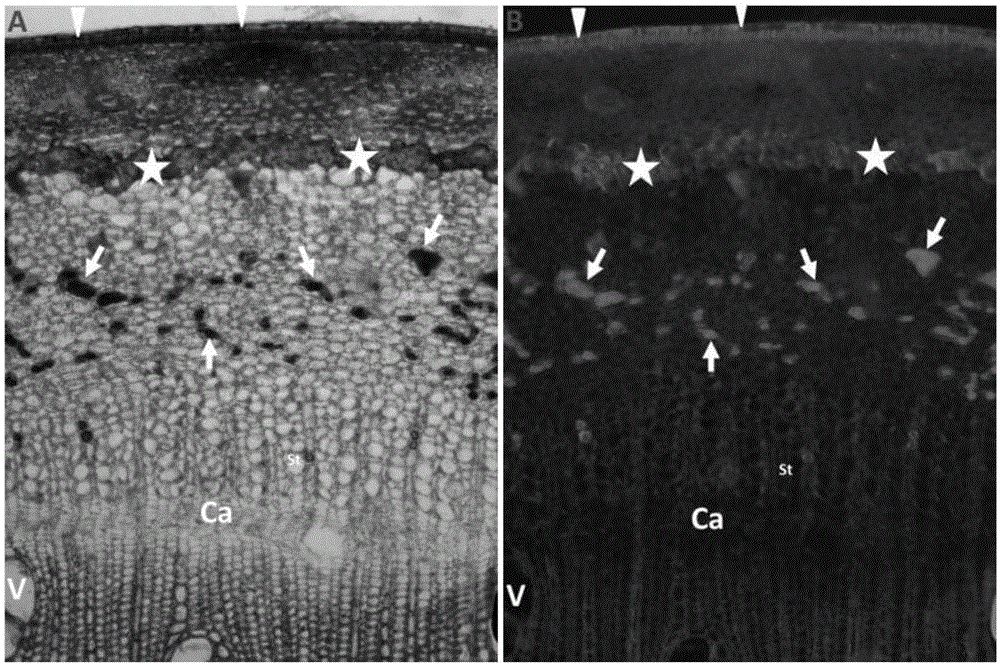
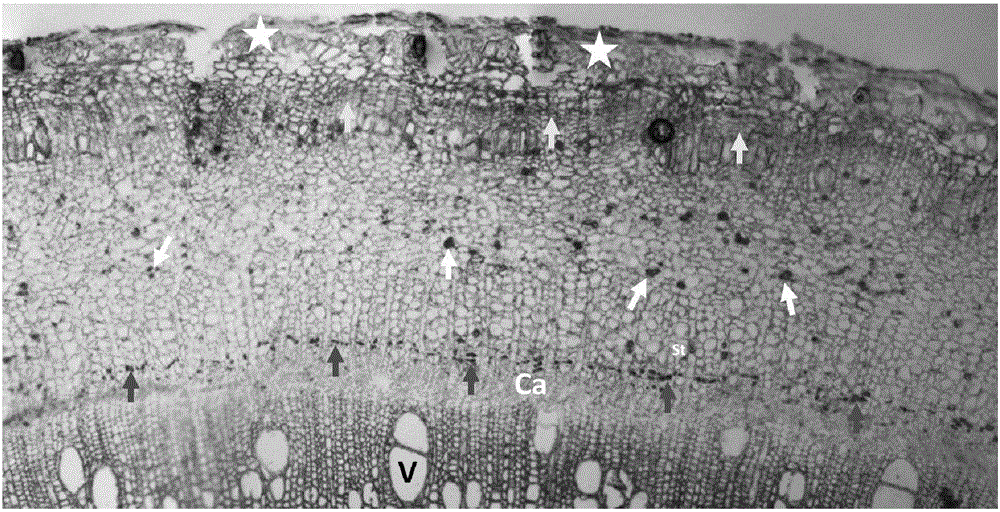
Histochemistry method capable of fast displaying latex vessel of bark of rubber tree
A rubber tree and bark technology, which is applied in the preparation of test samples, fluorescence/phosphorescence, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems that the slice quality is not easy to repeat, there are potential safety hazards, and it is easy to make mistakes in labels, etc. Universal batch screening, easy access to materials, and time-saving effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1, the primary milk duct histochemical display of bark under the natural state of annual saplings
[0031] In this embodiment, the bark of the young bark of the rubber tree variety CATAS7-33-97 in a natural state is used for histochemical display of the primary laticiferous ducts of the bark.
[0032]1. Experimental conditions: the bark of the new saplings of the rubber tree variety CATAS7-33-97 in the stable period was trimmed and cut into sliced tissue pieces of 0.5cm × 0.5cm wide, and placed in 3ml of 4wt% paraformaldehyde and 2.5wt % glutaraldehyde in 0.01M phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) fixative solution, pump air for 2min, replace with new fixative solution, and fix at room temperature for 5h; soak 3 times with 0.01M phosphate buffer solution (pH 7.2), 30 minutes each time; into the protective agent with different concentration gradients, the sucrose concentration of the protective agent is 2wt%-6wt%-10wt%-12wt%-14wt%-16wt%, and the time for each level is ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2, primary laticifer and secondary laticifer histochemical display of annual sapling bark after mechanical injury and jasmonic acid treatment
[0035] In this embodiment, the bark of the sapling bark of rubber tree variety CATAS7-33-97 was mechanically injured and treated with jasmonic acid for 7 days to perform histochemical display of laticiferous ducts.
[0036] 1. Experimental conditions: select the saplings of the rubber tree variety CATAS7-33-97 in the stable stage, scrape off the epidermis and part of the cortex (length 1cm × width 1cm) at a place about 2cm above the base of the new shoot, and expose the injured part directly to the air After 7 days of exposure, cut the bark at the scratched part as bark material for mechanical damage treatment; apply lanolin containing 3mM methyl jasmonate to the injured part, and then cover it with a black plastic film. After 7 days of treatment, cut the bark at the scratched part as Jasmonate-treated bark material. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com