Frozen section method for plant tissues and organs
A plant tissue and frozen section technology, applied in the preparation of test samples, sampling devices, etc., can solve the problems of complex operation process, difficulty in obtaining high-quality slices, and different slice conditions, and achieve simple operation and convenient microscopy Observation and analysis, the effect of low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
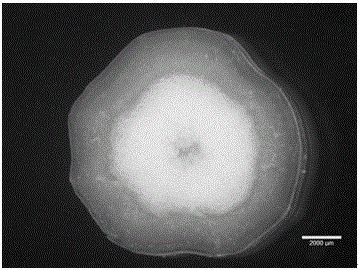
[0020] Example 1 Preparation, staining and observation of young Brassica napus stem slices
[0021] 1. Preparation of slices
[0022] (1) Sample embedding: Turn on the Leica CM1850 cryostat, lower the temperature of the case to -20°C, and after the temperature stabilizes, use a blade to cut out the young inflorescence stems of Brassica napus at the budding stage (fresh weight water content is 85% Above), use absorbent paper to dry the incision tissue fluid and surface moisture of the sample material, and then apply a layer of frozen embedding solution on the sample holder, put the sample on the sample holder and adjust the sample before the frozen embedding solution solidifies. Angle and orientation, and then use the frozen embedding solution to further embed the sample. When embedding the sample, no air bubbles can form around the sample.
[0023] (2) Slicing: Raise the temperature of the cryostat to -8°C and keep it for more than 30 minutes, then fix the sample holder on th...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2 Preparation, staining and observation of middle and lower stem slices of Brassica napus at the final flowering stage
[0029] 1. Preparation of slices
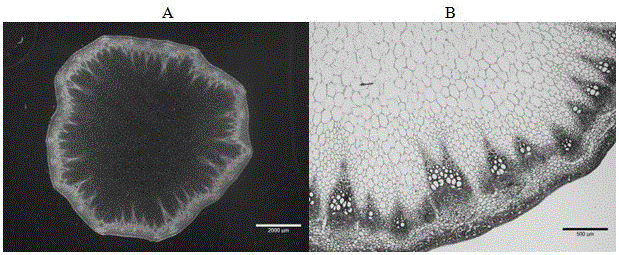
[0030] (1) Material pretreatment: The middle and lower stem materials of Brassica napus at the final flowering stage (the cross-section of which is as follows figure 2 As shown, it can be seen that the degree of lignification among the section tissues is not uniform and the spongy tissue contained in the pith exceeds one-half of the cross-sectional area of the stalk) soak in an ice-water bath for 2-3 days, and keep ice in the ice-water bath.
[0031] (2) Sample embedding: Turn on the Leica CM1850 cryostat, lower the temperature of the case to -20°C, and after the temperature stabilizes, cut off the pretreated stalk with a blade of 3-8mm, and use absorbent paper to dry the incision tissue fluid of the sample material and the moisture on the surface, and then apply a layer of frozen embedding solution on the...
Embodiment 3
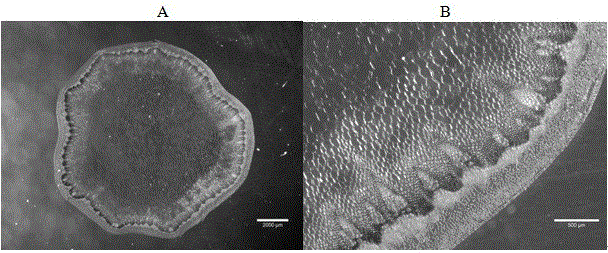
[0037] Example 3 Preparation, staining and observation of anther slices in mid-stage flower buds of Brassica napus
[0038] 1. Preparation of slices
[0039](1) Sample embedding: Turn on the Leica CM1850 cryostat and lower the temperature of the case to -20°C. After the temperature stabilizes, apply a layer of frozen embedding solution on the sample holder, and remove it before the frozen embedding solution solidifies. Calyx Brassica napus mid-term flower bud samples (fresh weight water content above 85%) are placed on the sample holder and the angle and orientation of the sample are adjusted, and then the sample is further embedded with frozen embedding fluid. Bubbles form around the sample.
[0040] (2) Slicing: Raise the temperature of the cryostat to -10°C and keep it for more than 30 minutes, then fix the sample holder on the positionable sample head of the microtome, and slice according to the operation manual of the microtome. In the machine box, use the pre-cooled tw...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com