Modification method for Y type molecular sieve
A molecular sieve and modification technology, applied in octahedral crystalline aluminosilicate zeolite, crystalline aluminosilicate zeolite, etc., can solve the problems of industrial application limitations, poor thermal and hydrothermal stability of mesoporous materials, poor hydrothermal stability, etc. , to achieve the effect of improving environmental protection efficiency, simple preparation process and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Mix deionized water, sodium hydroxide, dimethyloctadecyl[3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl]ammonium chloride, polyacrylamide with a molecular weight of 30,000 and molecular sieves, and the proportioning ratio is: Molecular sieve (gram): dimethyloctadecyl [3-(trimethoxysilyl) propyl] ammonium chloride (gram): polyacrylamide (gram): sodium hydroxide (mol): water (gram) =10:2.7:6:0.1:90. Put this mixture into a stainless steel sealed reaction kettle, and place it at a constant temperature of 105°C for 10 hours, then filter the mixture, wash with water, and dry it at 110°C for 3 hours, and then roast it at 550°C for 5 hours to obtain a molecular sieve The sample is denoted as MY-1.
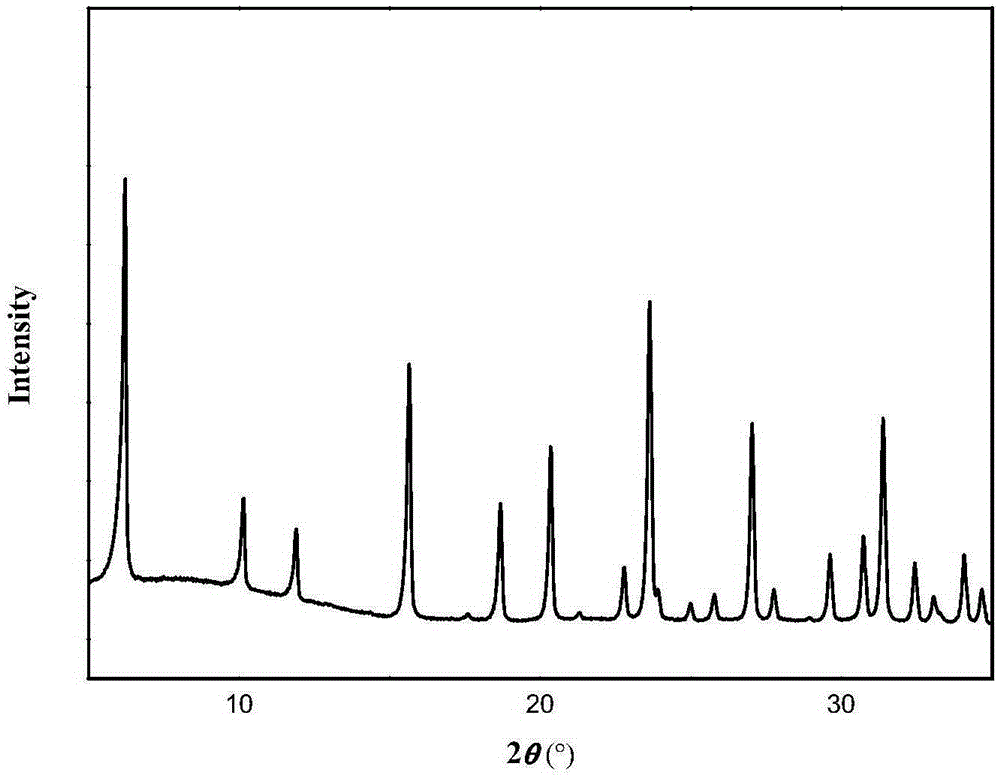
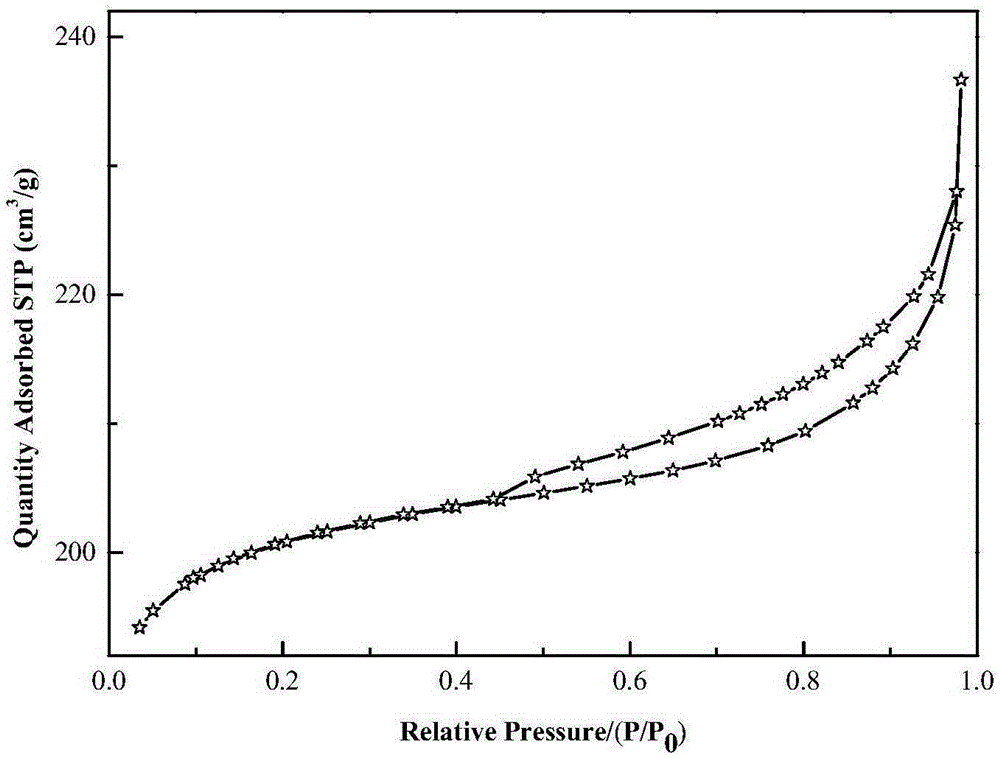
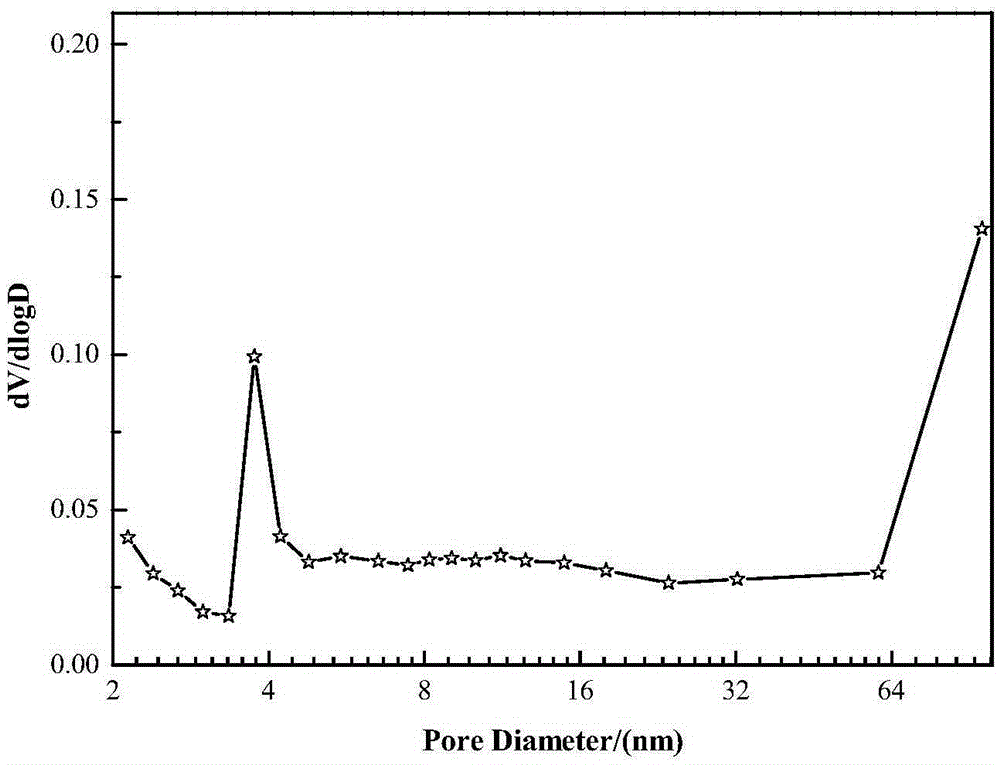
[0031] The XRD spectrum of MY-1 is shown in figure 1 . The low temperature nitrogen physical adsorption-desorption curve is shown in figure 2 . The pore size distribution curve calculated according to the BJH model is shown in image 3 .
Embodiment 2
[0033] Deionized water, sodium hydroxide, cyclopentyltrimethoxysilane, polymethacrylate with a molecular weight of 40,000 are mixed with molecular sieves, and the proportioning ratio is: molecular sieve (gram): cyclopentyltrimethoxysilane (gram ): Polymethacrylate (g): NH 4 OH (mole): water (gram) = 10:4:10:0.4:90. Put this mixture into a sealed stainless steel reaction kettle, and place it at a constant temperature of 100°C for 12 hours, then filter the mixture, wash with water, and dry it at 110°C for 3 hours, and then roast it at 550°C for 5 hours to obtain a molecular sieve The sample is denoted as MY-2.
[0034] See also the XRD spectrum of MY-2 figure 1 Characteristics. The low temperature nitrogen physical adsorption-desorption curve is the same as figure 2 Characteristics. The pore size distribution curve calculated according to the BJH model is the same as image 3 Characteristics.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Mix deionized water, sodium hydroxide, 3-(phenylamino)propyltrimethoxysilane, polyacrylamide with a molecular weight of 10,000, and molecular sieves. The ratio is: molecular sieve (g): dimethyl octadecadecane Alkyl[3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl]ammonium chloride (g): polyacrylamide (g): NH 4 OH (mole): water (gram) = 10:4:10:0.4:90. Put this mixture into a sealed stainless steel reaction kettle, and place it at a constant temperature of 100°C for 12 hours, then filter the mixture, wash with water, and dry it at 110°C for 3 hours, and then roast it at 550°C for 5 hours to obtain a molecular sieve The sample is denoted as MY-3.
[0037] See also the XRD spectrum of MY-3 figure 1 Characteristics. The low temperature nitrogen physical adsorption-desorption curve is the same as figure 2 Characteristics. The pore size distribution curve calculated according to the BJH model is the same as image 3 Characteristics.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| crystallinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com