Clay-based hydrogel matrix for three-dimensional printing and preparation method application thereof
A three-dimensional printing and hydrogel technology, applied in medical science, prosthesis, additive processing, etc., can solve the problems of inability to print, reduce material selectivity, and high gel slurry, achieve simple process and improve three-dimensional printing. Efficiency, suitable viscosity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0080] A method for preparing a clay-based three-dimensional gel support, comprising the steps of:
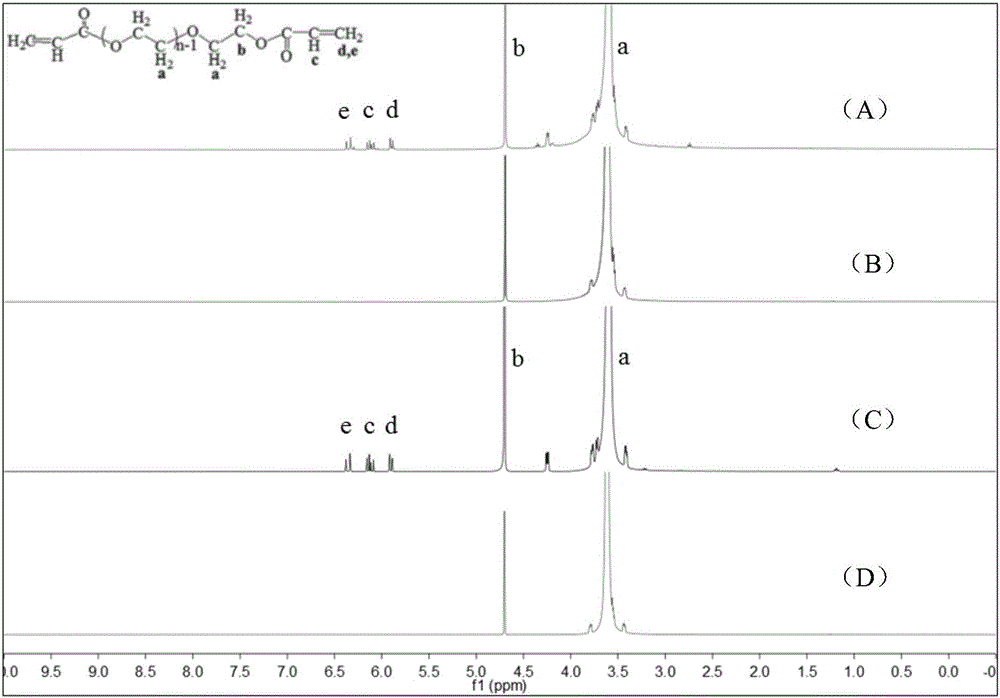
[0081] A. Preparation of double bond modified polyethylene glycol (Mn=4000) macromolecular cross-linking agent
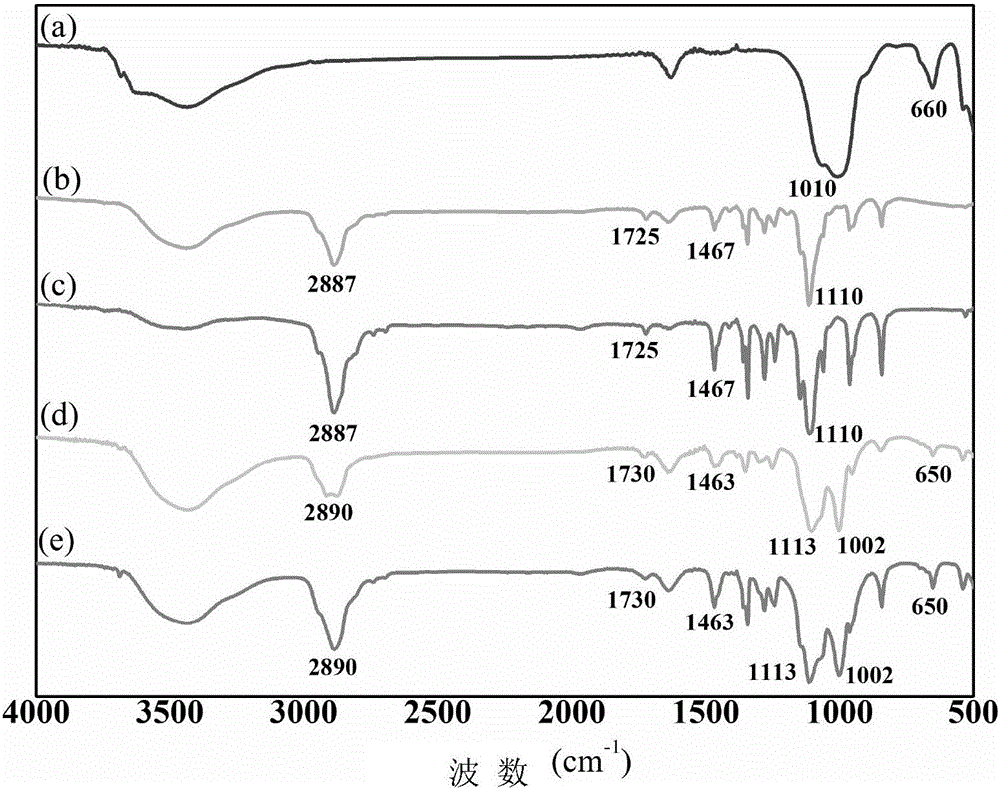
[0082] First, 1.2 ml of acryloyl chloride was dissolved in 10 ml of dichloromethane to prepare an acryloyl chloride solution. Subsequently, 10 g of polyethylene glycol (Mn=4000) was placed in a 50 ml three-neck flask, 20 ml of dichloromethane was added to dissolve, and the mixture was stirred evenly at room temperature. Under ice-water bath conditions, 2.1 ml of triethylamine solution was slowly added. Subsequently, under the condition of an ice-water bath, the acryloyl chloride solution prepared in advance was added dropwise. The temperature of the system was controlled to zero until all the acryloyl chloride was added dropwise, and the reaction was carried out at room temperature for 24 hours under the protection of nitrogen. After the reaction, the triethylamin...
Embodiment 2
[0094] A method for preparing a clay-based three-dimensional gel support, comprising the steps of:
[0095] (1) Using the same method as in Example 1, the polyethylene glycol with a molecular weight of 4000 is modified with a double bond to obtain the crosslinking agent polyethylene glycol diacrylate, CH 2 =CHCO-(OCH 2 CH 2 ) n OCOCH=CH 2 (n is 88);
[0096] (2) Adopt 2-hydroxyl-4'-(2-hydroxyethoxyl)-2-methyl propiophenone as ultraviolet photoinitiator, LaponiteXLG as inorganic clay, weigh crosslinking agent, inorganic Clay and ultraviolet photoinitiator were added to water and mixed evenly to obtain a clay-based hydrogel matrix with a viscosity of 170Pa·s. The above-mentioned raw materials were mixed according to the following mass percentages:
[0097] Cross-linking agent: 30%;
[0098]Inorganic clay: 8%;
[0099] UV photoinitiator: 0.05%;
[0100] Water: 61.95%;
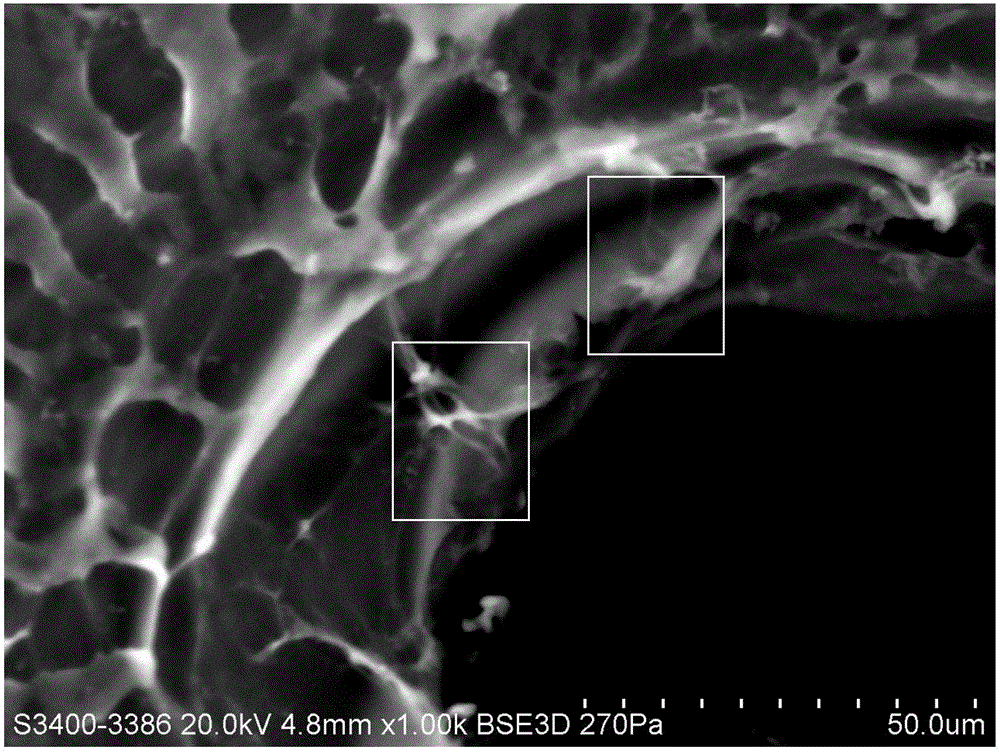
[0101] (3) Three-dimensionally print the above-mentioned clay-based hydrogel matrix at normal temperat...
Embodiment 3
[0103] A method for preparing a clay-based three-dimensional gel support, comprising the steps of:
[0104] (1) Using the same method as in Example 1, the polyethylene glycol with a molecular weight of 10000 is modified with a double bond to obtain the crosslinking agent polyethylene glycol diacrylate, CH 2 =CHCO-(OCH 2 CH 2 ) n OCOCH=CH 2 (n is 224);
[0105] (2) Adopt 2-hydroxyl-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1-propanone as ultraviolet photoinitiator, Laponite XLG as inorganic clay, weigh crosslinking agent, inorganic clay, ultraviolet light according to the following formula quantity Initiator, add water and mix evenly to obtain a clay-based hydrogel matrix with a viscosity of 150Pa·s, and the above-mentioned raw materials are mixed according to the following mass percentages:
[0106] Cross-linking agent: 20%;
[0107] Inorganic clay: 7%;
[0108] UV photoinitiator: 0.05%;
[0109] Water: 72.95%;
[0110] (3) Three-dimensionally print the above-mentioned clay-based hydrogel ma...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com