Method for preparing polymer microspheres by taking ferric hydroxide colloid as emulsion-method water phase
A technology for the preparation of ferric hydroxide and water phase, applied in the direction of inorganic non-active ingredients, can solve the problems of carcinogenesis and immune response, and achieve the effect of promoting proliferation and good cell compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] (1) Weigh 0.5 g PLGA (LA / GA =85 / 15, M w =100 kDa) into 5 ml of dichloromethane, stirred at 300 rpm for 30 min to obtain an oil phase solution of PLGA;
[0040] (2) Take 60 ml FeCl with a mass fraction of 3% 3 Add the solution to 240 ml of boiling deionized water and continue heating for 2 minutes to make a ferric hydroxide colloid solution as the water phase of the emulsion;
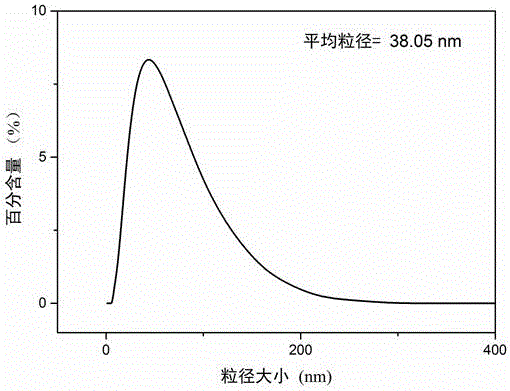
[0041] figure 1 Fe(OH) in water phase 3 The particle size distribution diagram of colloidal nanoparticles, by figure 1 It can be seen that most Fe(OH) 3 The particle size distribution of colloidal nanoparticles is between 0 and 200nm, with an average particle size of 38.05nm;
[0042] (3) Add the oil phase solution of PLGA to the colloidal solution of ferric hydroxide dropwise under the stirring condition of 300 rpm to obtain an oil-in-water single emulsion;
[0043](4) Continuously stirred the single emulsion for 5 h, volatilized and removed the organic solvent, and obtained PLGA microspher...
Embodiment 2
[0048] (1) Weigh 0.5 g PLGA (LA / GA =85 / 15, M w =100 kDa) into 5 ml of dichloromethane, stirred at 300 rpm for 30 min to obtain PLGA oil phase solution;
[0049] (2) Weigh 1.50 g of PVA and add it to 250 ml of deionized water at 90°C, continue heating for 60 minutes to fully dissolve the PVA, and obtain an aqueous solution of PVA after cooling;
[0050] (3) Add the oil phase solution of PLGA to the PVA water phase solution dropwise under the stirring condition of 300 rpm to obtain an oil-in-water single emulsion;
[0051] (4) Stir the single emulsion continuously for 5 h, volatilize and remove the organic solvent, and obtain PLGA microspheres without iron on the surface; collect the solidified PLGA microspheres, wash with deionized water for 3 times, freeze-dry, and mark as PVA-PLGA Microspheres.
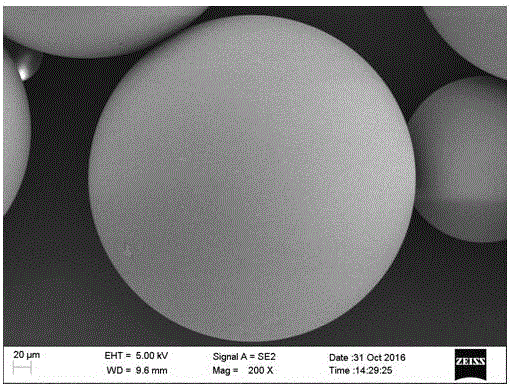
[0052] Figure 5 The overall morphology of the prepared PVA-PLGA microspheres is shown by Figure 5 It can be seen that the surface of the PVA-PLGA microspheres prepared by the t...
Embodiment 3
[0055] (1) Weigh 0.5 g PLLA (M w =50 kDa) into 5 ml of dichloromethane, stirred at 300 rpm for 30 min to obtain an oil phase solution of PLLA;
[0056] (2) Take 60 ml FeCl with a mass fraction of 3% 3 Add the solution to 240 ml of boiling deionized water and continue heating for 2 minutes to make a ferric hydroxide colloid solution as the water phase of the emulsion;
[0057] (3) Add the oil phase solution of PLLA to the colloidal solution of ferric hydroxide dropwise under the stirring condition of 300 rpm to obtain an oil-in-water single emulsion;
[0058] (4) Stir the single emulsion continuously for 5 h, volatilize and remove the organic solvent, and obtain PLLA microspheres with iron elements on the surface; collect the solidified PLLA microspheres, wash with deionized water for 3 times, freeze-dry, and mark as Fe(OH) 3 - PLLA microspheres.
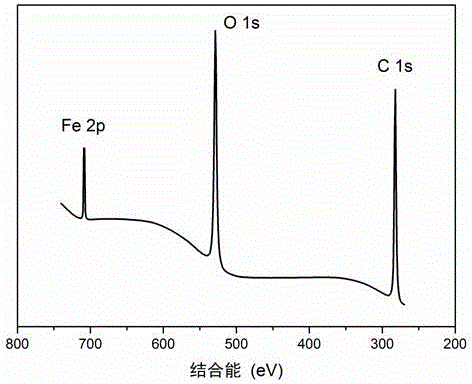
[0059] Figure 7 For the preparation of Fe(OH) 3 - Overall topography of PLLA microspheres, Figure 7 Shows successful prepar...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com