Method for improving fermenting property of solventogenic clostridia
A technology of Solventogenic Clostridium and Clostridium acetobutylicum, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, fermentation, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems that have not been explored and increase fermentation costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
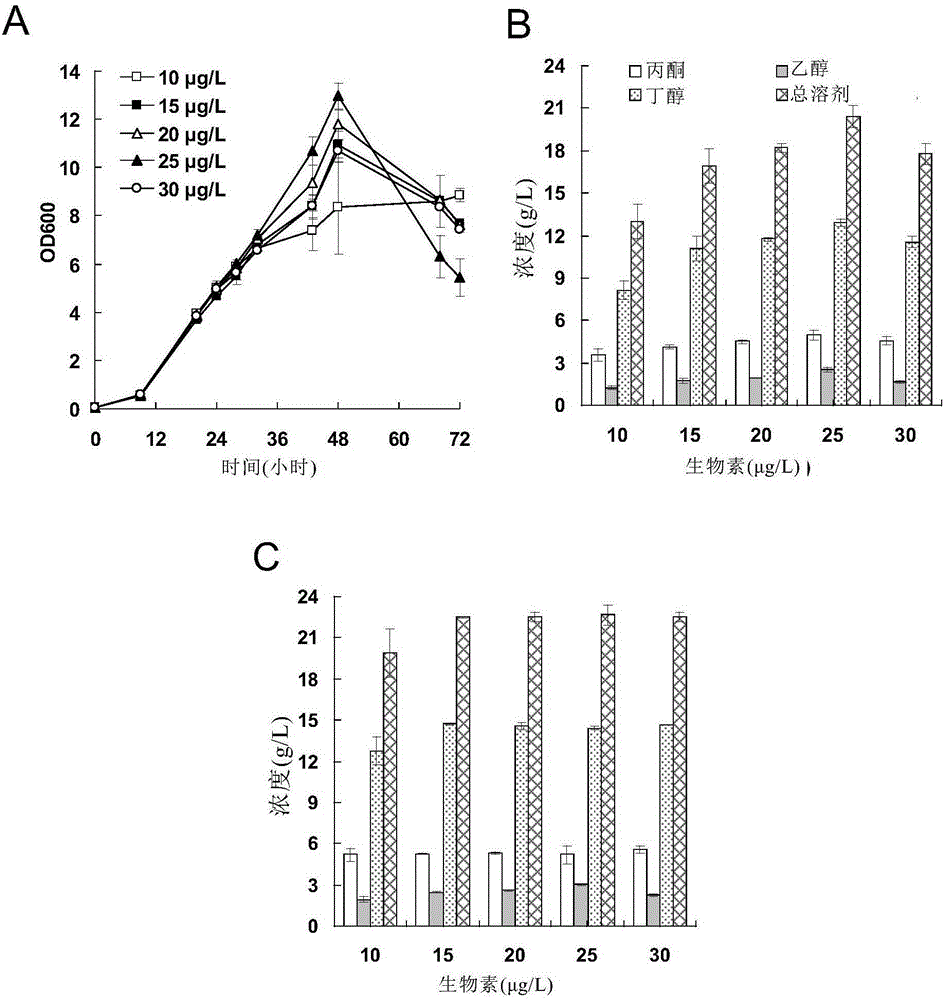
[0075] Embodiment 1: adding biotin can strengthen the fermentation performance of Clostridium acetobutylicum
[0076] experimental method:
[0077] The wild-type Clostridium acetobutylicum was fermented using the P2 medium supplemented with different concentrations of biotin to determine the effect of biotin on the fermentation of Clostridium acetobutylicum.
[0078] Experimental steps:
[0079] 1) Add different concentrations of biotin (biotin concentration: 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 μg / L) to the fermentation medium of Clostridium acetobutylicum (P2 medium without biotin) to construct different concentrations of biotin fermentation medium;
[0080] 2) Inoculate wild-type Clostridium acetobutylicum in the medium prepared in 1) at a ratio of 5% (v / v), and carry out static fermentation at 37°C in an anaerobic box; the specific fermentation conditions are as follows: P2 medium (30ml), 7% glucose (w / v), 5% inoculum size (v / v), biotin added concentrations: 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 μg / L...
Embodiment 2
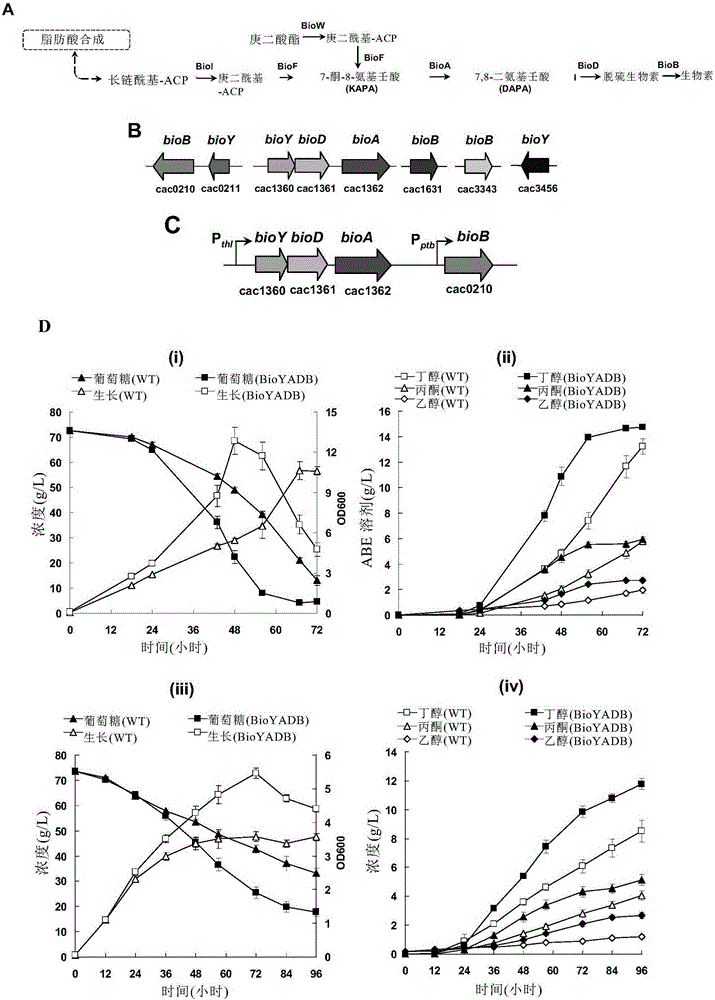
[0085] Example 2: Analysis and identification of biotin synthesis-related genes in Clostridium acetobutylicum and enhancement of their expression levels
[0086] experimental method:
[0087] Bioinformatics, comparative genomics and protein amino acid sequence homologous alignment were used to analyze and identify biotin synthesis genes in Clostridium acetobutylicum, and further improve the fermentation of Clostridium acetobutylicum by overexpressing biotin synthesis-related genes performance.
[0088] Experimental steps:
[0089] 1) According to the genome annotation in KEGG (http: / / www.genome.jp / kegg / ), the genes related to biotin synthesis in Clostridium acetobutylicum were analyzed;
[0090] 2) Using the amino acid sequence of biotin synthesis-related proteins in Bacillus subtilis as a template, search for potential biotin synthesis-related proteins in Clostridium acetobutylicum by using the amino acid sequence homologous alignment method (protein blast);
[0091] 3) En...
Embodiment 3
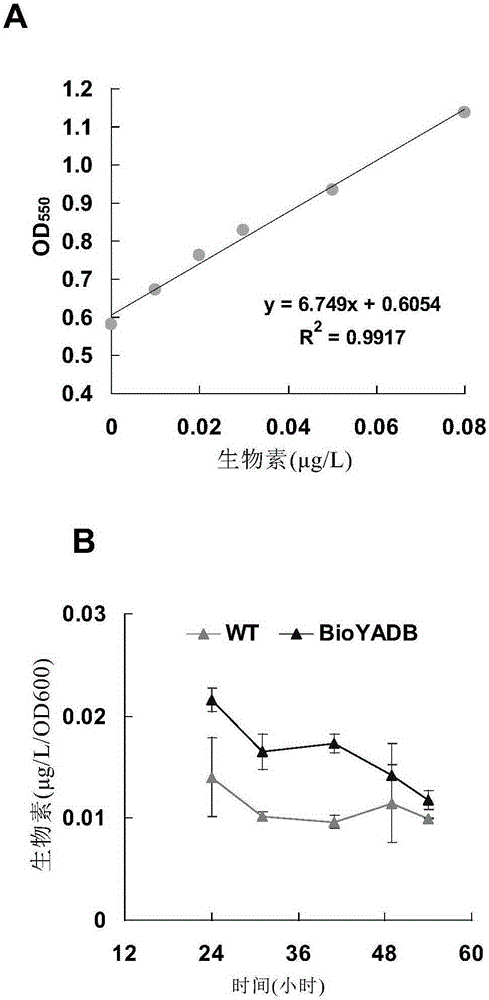
[0110] Embodiment 3: Determination of biotin content in BioYADB and EP strains
[0111] experimental method:
[0112] The content of biotin synthesized by Clostridium acetobutylicum was detected by biotin auxotrophic Lactobacillus plantarum E4.
[0113] Experimental steps:
[0114] 1) EP and BioYADB were anaerobically fermented in P2 medium without adding biotin, and samples were taken at 24h, 31h, 41h, 49h and 54h (4ml);
[0115] Fermentation conditions: P2 medium (400ml, no biotin added), 7% glucose (w / v), 5% inoculum size (v / v), erythromycin final concentration 10 μg / ml;
[0116] 2) Centrifuge the culture solution obtained in 1) to collect the bacteria, and collect the supernatant for determining the content of extracellular biotin;
[0117] 3) After washing the bacteria obtained in 2) three times with 0.9% NaCl (w / v), use 3M H 2 SO 4 Suspended bacteria were sterilized at 121°C for 1 hour to fully degrade the bacteria and release biotin in the body. After centrifugatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com