Hemostatic material and preparation method thereof
A hemostatic material and solution technology, applied in the field of hemostatic material and its preparation, can solve the problems of not being suitable for hemostasis, hemostatic starch is not fast enough to stop bleeding, etc., and achieve excellent hemostatic effect, strong water absorption, hemostatic performance and improved water absorption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
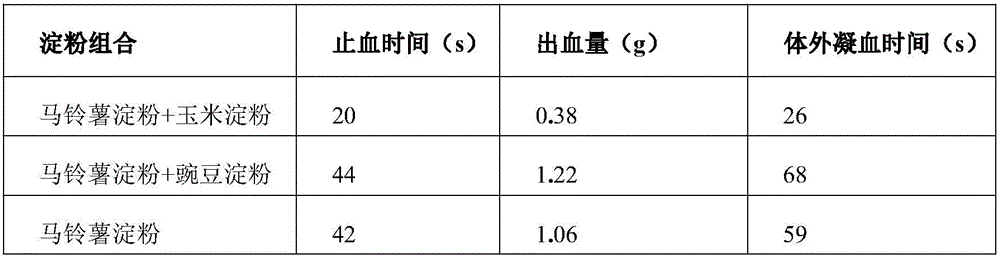
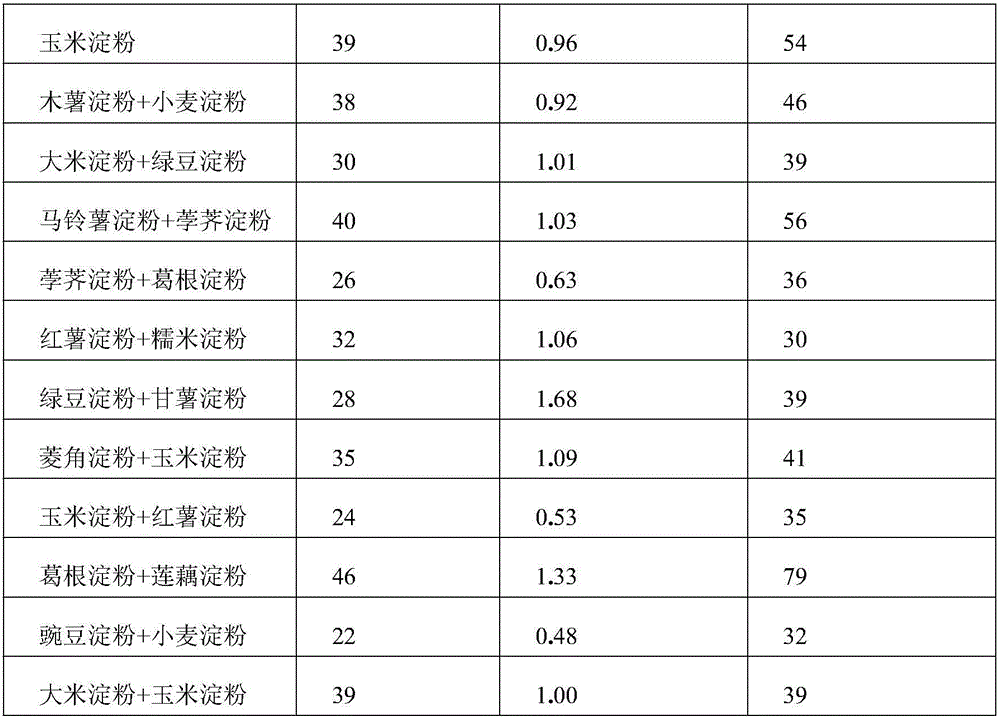
[0036] Example 1. Effect of the combination of different starch raw materials on the hemostatic performance of the hemostatic material
[0037] 1. Materials and methods
[0038] 1.1 Experimental animals: 90 healthy adult SD rats, male or female, weighing 210-240 g; 8 healthy adult New Zealand rabbits, male or female, weighing 1.9-2.1 kg, all provided by Guangdong Medical Experimental Animal Center.
[0039] 1.2 Test method
[0040]1.2.1 Determination of hemostasis time and bleeding volume 90 rats were randomly divided into 15 groups with 6 rats in each group according to the hemostatic materials prepared from the combinations of 15 kinds of starches in Table 1 below. All animals were fasted (without water) for 12 hours before the operation, anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 3% pentobarbital sodium 40 mg / kg body weight, and a longitudinal incision about 2 cm long was made under the costal arch along the midline of the abdomen, and the abdomen was cut along the midli...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2, a kind of hemostatic material
[0050] The hemostatic material described in Example 2 of the present invention is prepared by the following steps:
[0051] A) Acid hydrolysis: mix starch with 10% hydrochloric acid solution at a ratio of 1:5, stir to obtain a starch polysaccharide solution, place the above starch polysaccharide solution in a constant temperature water bath at 50°C for 15 hours, and keep stirring during the reaction. Speed is 600rpm, obtains the starch polysaccharide solution after the acid hydrolysis;
[0052] B) Cross-linking: Add soybean oil, sodium hydroxide solution, emulsifier and epichlorohydrin to the starch polysaccharide solution after the above-mentioned acid hydrolysis treatment, and stir and mix; wherein, soybean oil, sodium hydroxide solution, emulsifier and cyclic The weight ratio of oxychloropropane is 2:1:0.06:0.1, and the reaction is 36h;
[0053] C) Anionization reaction: Add ethanol solution, monochloroacetic acid, so...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Embodiment 3, a kind of hemostatic material
[0056] The hemostatic material described in Example 3 of the present invention is prepared by the following steps:
[0057] A) Acid hydrolysis: mix starch with 38% hydrochloric acid solution at a ratio of 1:1, stir to obtain a starch polysaccharide solution, place the above starch polysaccharide solution in a constant temperature water bath at 30°C for 1 hour, and continue stirring during the reaction. The speed is 200rpm, and the starch polysaccharide solution after acid hydrolysis is obtained;
[0058] B) Cross-linking: Add soybean oil, sodium hydroxide solution, emulsifier and epichlorohydrin to the starch polysaccharide solution after the above-mentioned acid hydrolysis treatment, and stir and mix; wherein, soybean oil, sodium hydroxide solution, emulsifier and cyclic The weight ratio of oxychloropropane is 1:1:0.1:0.1, and the reaction is 36h;
[0059] C) Anionization reaction: add ethanol solution, monochloroacetic a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com