Method for preparing magnetic porous carbon spheres through microfluidic method
A porous carbon and microfluidic technology, which is applied in the preparation/purification of carbon, the oxide of ferrous iron, the manufacture of inductors/transformers/magnets, etc. Uniformity, harsh preparation conditions, etc., to achieve the effect of novel and unique method, easy post-processing, and uniform particle size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
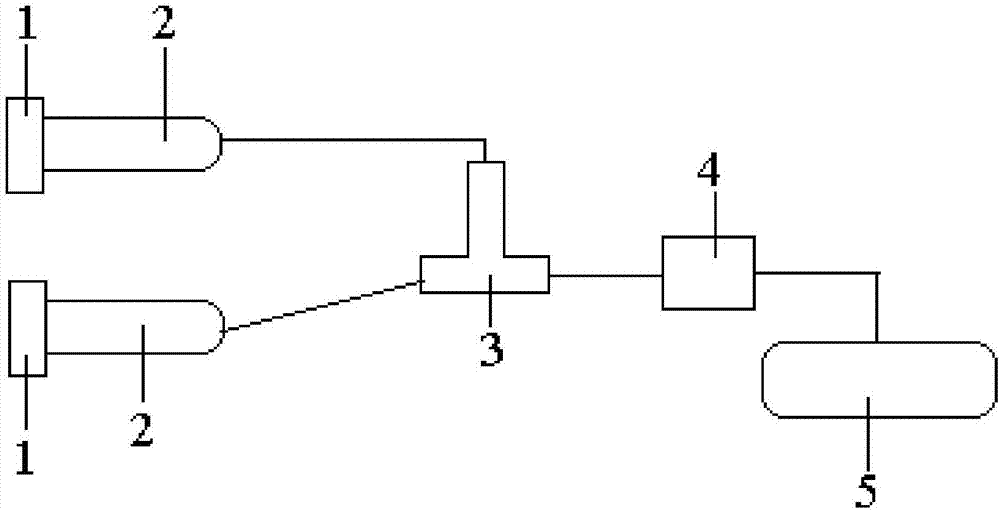
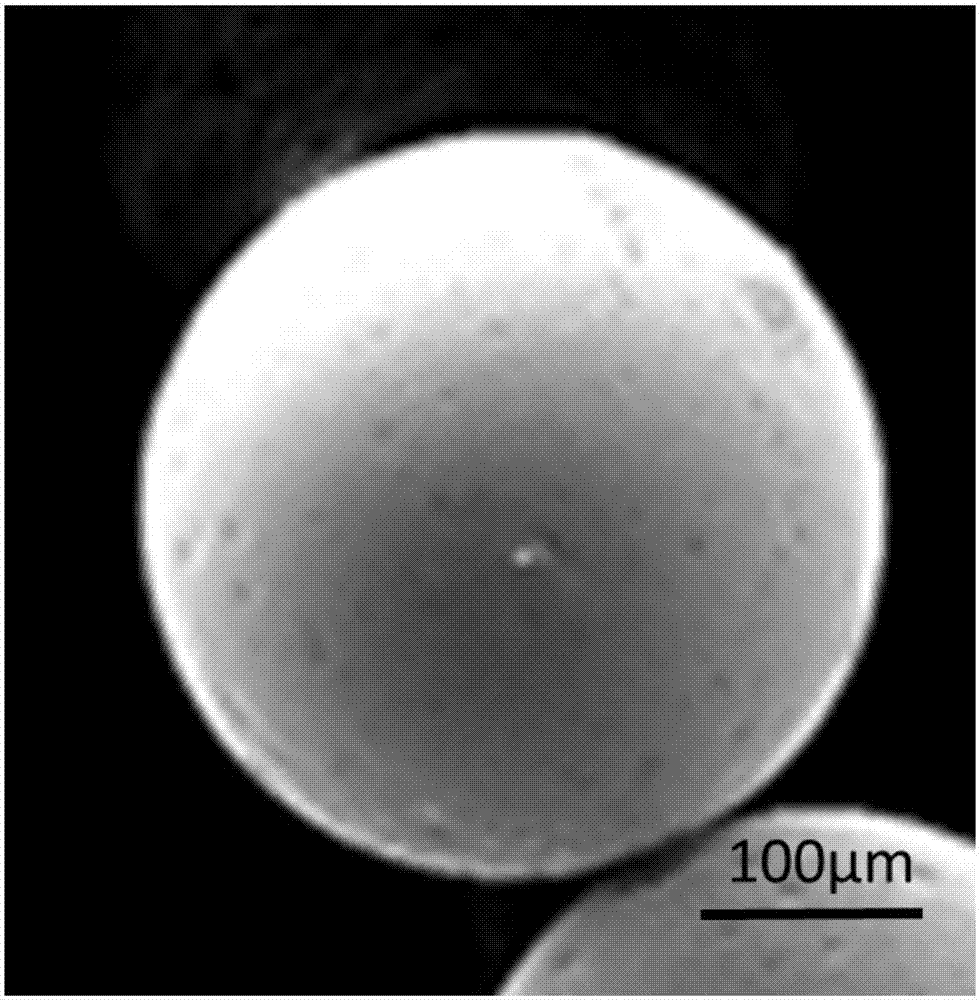
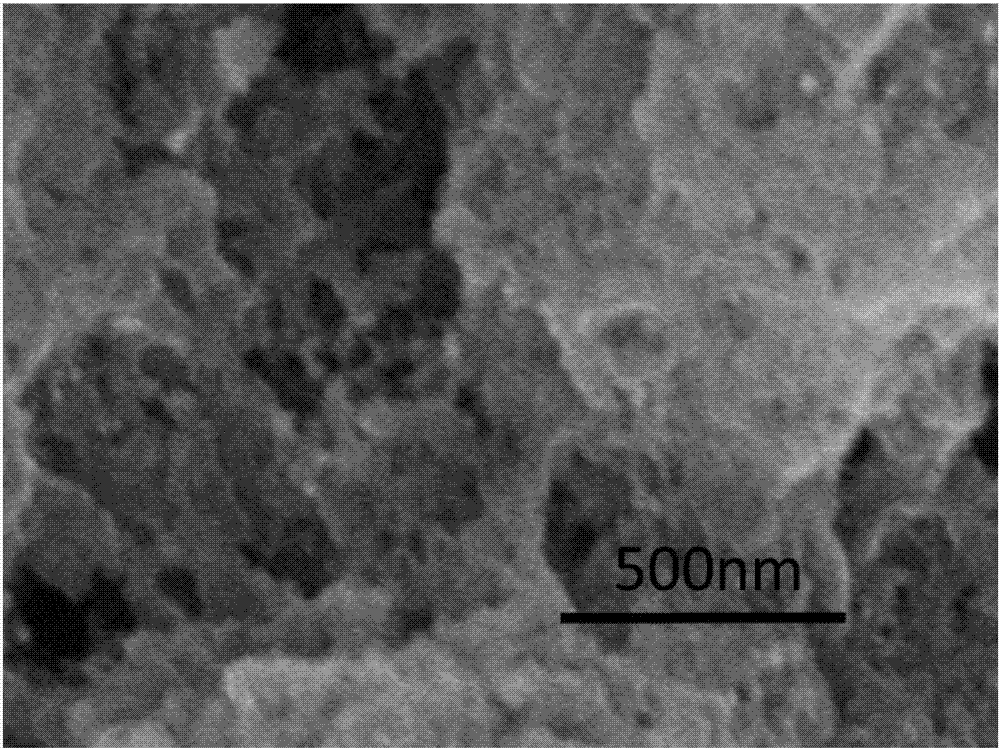
[0017] Embodiment 1: This embodiment is a method for preparing magnetic porous carbon spheres by a microfluidic method, specifically as follows:
[0018] 1. Prepare the dispersed phase: dissolve polyvinylpyrrolidone in water, then add polystyrene microspheres and Fe 3 o 4 The magnetic particles are uniformly stirred into a dispersed solution to obtain a dispersed phase; the mass ratio of the polyvinylpyrrolidone to water is (1~15):100; the mass ratio of the polystyrene microspheres to water is (1~15): 4): 20; said Fe 3 o 4 The mass ratio of magnetic particles to water is (1~5):100;
[0019] 2. Preparation of microbeads: Put the mobile phase and the dispersed phase prepared in step 1 into two syringes respectively, use two jet pumps to control the propulsion speed of the two syringes, and the outlets of the two syringes are respectively connected to the two outlets of a three-way The two inlets are connected, the outlet of the three-way is connected to the polypropylene rec...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0021] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the preparation method of the polystyrene microsphere described in step one is as follows:
[0022] Two ports in the three-necked flask were respectively equipped with a reflux condenser and a mechanical stirring paddle, and 500 mL of deionized water, 50 mL of styrene, and 5 mL of methacrylic acid were added to the three-necked flask, and the remaining one port was sealed, and the rotating speed was 300 rpm. Stir at a temperature of 80°C. After the reaction system refluxes and stabilizes, add 0.5 g of potassium persulfate and continue to stir for 2 hours at a speed of 300 rpm and a temperature of 80°C. The product is centrifuged to obtain a solid , the solid was washed and dried to obtain polystyrene microspheres. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0023] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the polystyrene microspheres described in step 1 are non-crosslinked polystyrene microspheres with a particle size of 50 nm to 500 nm. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com