Fibrinolysin of fermented soya beans and culture method thereof
A technology of soybean fibrinolytic enzyme and culture, applied in the field of cultivation of fermented soybean fibrinolytic enzyme, can solve problems such as allergies, too expensive, bleeding, etc., and achieve the effect of stable thrombolytic properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1: Preparation of liquid fermentation culture
[0024] Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (Bacillus amyloliquefaciens) strain Jxnuwx-1 (preservation number: CCTCC M 2014638) was used as the culture strain to carry out slant culture, seed culture and liquid fermentation culture, and the liquid fermentation culture was obtained after 3 days of fermentation.
[0025] Wherein, culture medium and culture condition:
[0026] (1) Incline medium: beef extract 0.3%, peptone 1%, NaCl 0.5%, agar 2%, pH 7.0. The sterilization temperature of the culture medium is 121°C, and the sterilization time is 30min. The culture condition was 37°C, the culture time was 24h, and then the slant was preserved at 4°C.
[0027] (2) Seed medium: 5% yeast extract, 1% tryptone, 1% NaCl, pH 7.0. The sterilization temperature of the medium is 115°C, and the sterilization time is 30min. The culture conditions were shake flask culture, 170r / min, 12h, 37°C.
[0028] (3) Fermentation medium: 2% sucrose...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Embodiment 2: Separation and purification of tempeh fibrinolytic enzyme
[0030] The liquid fermentation culture obtained in Example 1 was subjected to 65% saturation ammonium sulfate salting out and precipitation, and was suspended with a phosphate buffer solution with a pH of 7.0 to obtain a crude enzyme solution, and then passed through:
[0031] a. Use a dialysis bag to perform dialysis and desalination while performing buffer exchange. The dialysis buffer is Tris-HCl buffer with a pH of 8.5 and a concentration of 20 mM.
[0032] b. Put the desalted solution containing plasmin on the DEAE-sepHarose FF column, use 0-0.5moL / L NaCl and Tris-HCl buffer solution with a pH of 8.5, and the concentration is 20mM to elute, and collect the fibrinolytic active group point.
[0033] c. Then perform gel chromatography with Superdex 75 column, elute with phosphate buffer solution with pH 7.0, the eluent contains 0.3moL / L NaCl, collect fibrinolytic active ingredients, and obtain ...
Embodiment 3
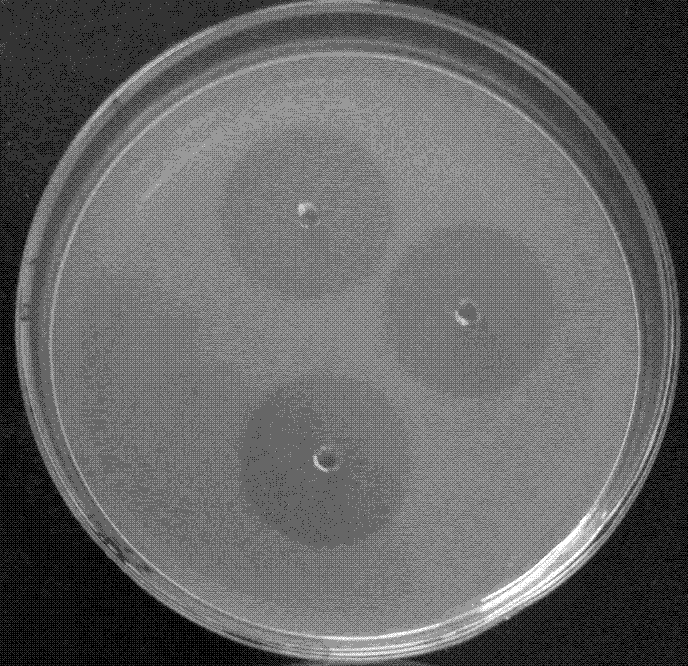
[0034] Embodiment 3: Determining the properties of the fermented soya bean fibrinolytic enzyme after separation and purification
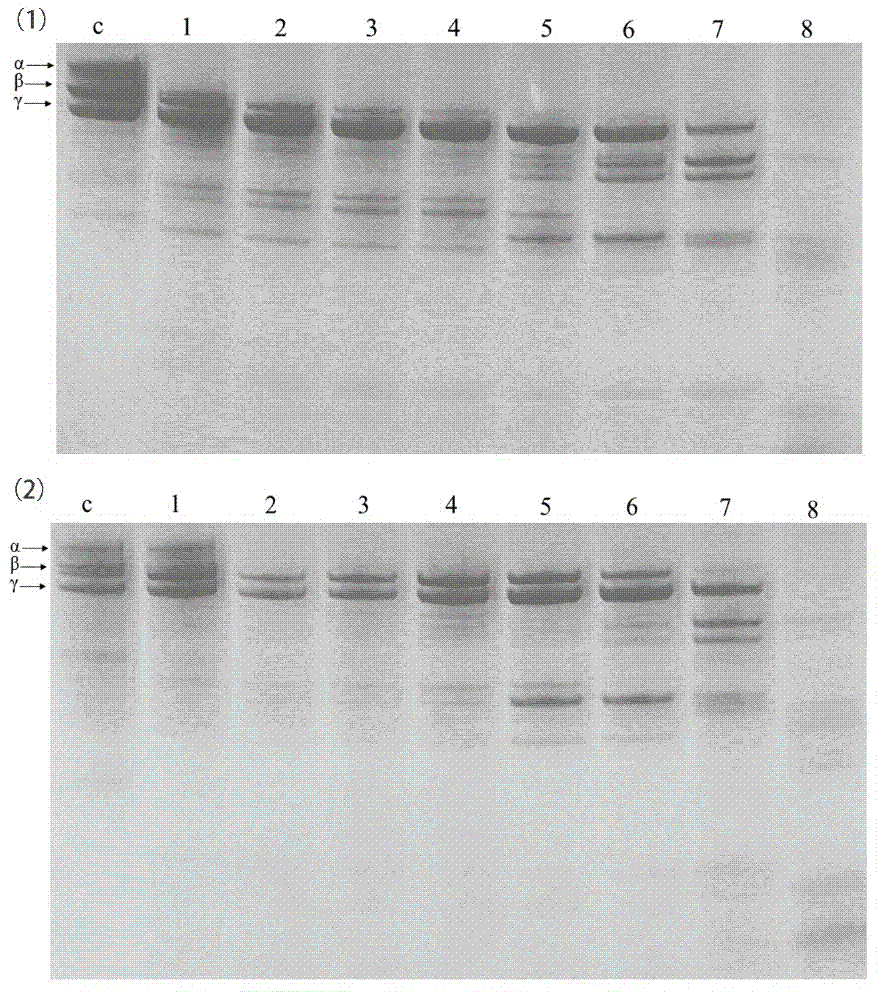
[0035] Using the SDS-PAGE method to determine the relative molecular mass of the fermented soybean fibrinolytic enzyme obtained in Example 2 is 29kDa, and the optimum temperature and optimum pH are respectively 41°C and 7.6. , Fe 3+ , Fe 2+ Inhibited, the tempeh plasmin can rapidly degrade the Aα subunit of fibrin (ogen), followed by the Bβ and Cγ subunits, the tempeh plasmin can not only directly degrade fibrin (ogen) but also act as a The original activator, while the tempeh plasmin can also degrade thrombin.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Relative molecular mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com