Method for detecting minimal residual disease in T cell leukemia based on high-throughput sequencing
A minimal residual disease, high-throughput technology, applied in the field of molecular biology detection, can solve problems such as false negatives, amplification of TCR genes and sequencing, and incomplete sequencing gene information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] A method for detecting T-cell leukemia minimal residual disease by high-throughput sequencing, comprising the steps of:
[0083] (1) Obtain 10mL of human blood samples in EDTA anticoagulant tubes;
[0084] (2) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were separated using the lymphocyte separation medium Ficoll-1077 (Sigma, USA #10771);
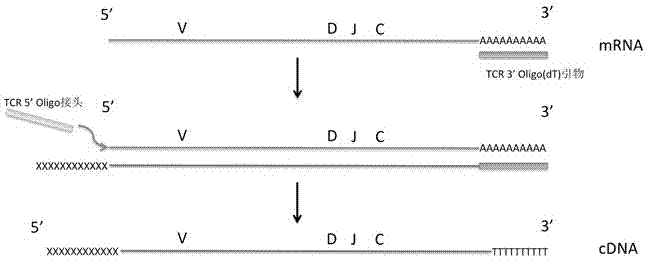
[0085] (3) Utilize the method of Trizol to extract the total RNA of PBMC, the reagent used is RNAzol RT (US MRC company #RN190);
[0086] (4) The RNA is reverse-transcribed into cDNA, and an adapter is added to the 5' end of the cDNA for the 5' end primer binding during subsequent PCR amplification,
[0087] Specific steps are as follows,
[0088] Reagents used:
[0089] ·TCR 3'Oligo(dT) primer (10μM)
[0090] 5X reverse transcription buffer (250mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.3), 375mM KCl, 15mM MgCl 2 )
[0091] Dithiothreitol, DTT (20mM) US Thermo Scientific #R0861
[0092] · dNTP Mix (10mM) US Invitrogen#18427088
[0093] ·RNAse Out (40...
Embodiment 2
[0162] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a method for preparing a T lymphocyte receptor (TCR) RNA sample, comprising the following steps:
[0163] 10 milliliters (mL) of fresh peripheral blood samples were collected and operated according to the instructions of Ficoll-1077 (Sigma Company #10771, USA) to obtain relatively pure peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC);
[0164] Adopt the method of Trizol to extract the total RNA of PBMC, reagent used is RNAzol RT (US MRC company #RN190), the total RNA obtained, utilize 2.0 Fluorometer (#Q32866 from Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA), with RNA HS Assay Kit kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA #Q32852) was used to measure the RNA concentration, and then the RNA was reverse transcribed;
Embodiment 3
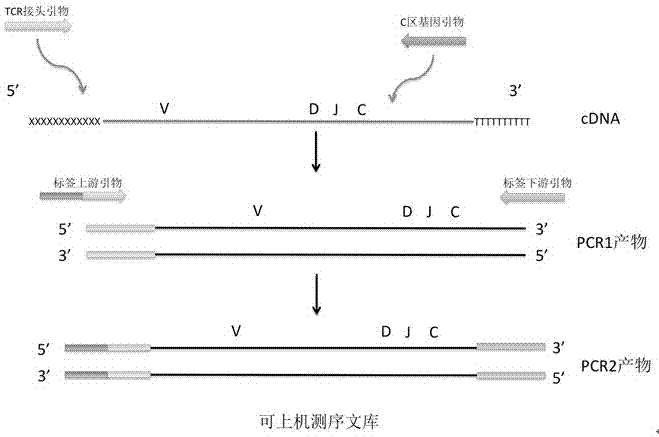
[0166] Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides a method for constructing a TCR high-throughput sequencing library for minimal residual disease of leukemia using a single pair of primers of the TCR library for minimal residual disease of leukemia, including the following steps:
[0167] Using the RNA obtained in Example 1 as a template for reverse transcription, the cDNA to which the TCR 5' end adapter was added was obtained according to the reagents and steps in the fourth part of the above "second aspect". Purify the products (libraries) of PCR 1, PCR 2 and PCR 2 according to the reagents and steps in the fifth, sixth and seventh parts of the above "second aspect".
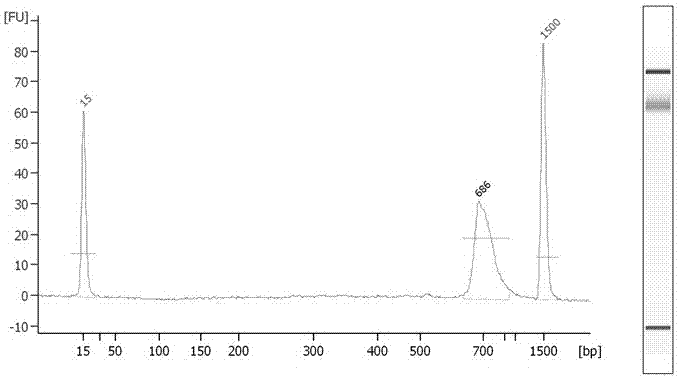
[0168] After the library was purified, use Agilent 2100Bioanalyzer (US Agilent #G2939AA) to detect the purity and size of the library. The kit used was Agilent DNA 1000Kit (US Agilent #5067-1504), and the test results were as follows: image 3 As shown, the size of the library is 686bp, and the purity of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com