Application of traditional Chinese medicine monomer toosendanin as STAT3 inhibitor in preparation of osteosarcoma resisting drug
A technology of toosendanin and osteosarcoma, applied in the field of medicine, can solve problems such as unclear molecular targets of Chinese herbal medicine monomers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
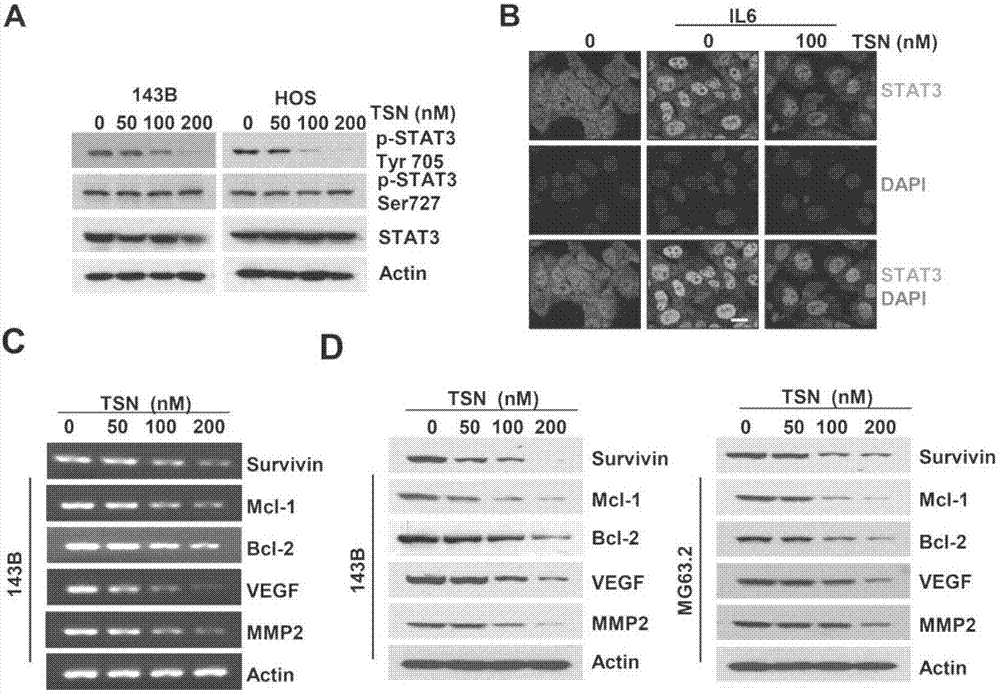
[0037] Embodiment 1: toosendanin (TSN) suppresses the activity of STAT3
[0038] 1. Technical method
[0039] 1. Western Blot experiment
[0040] After the cells were treated with different concentrations of drugs for 48 hours, the cells were lysed with the lysate to extract the protein, and the protein samples separated by polyacrylamide gel PAGE electrophoresis after boiling and denaturation were transferred to PVDF, incubated overnight with the corresponding primary antibody, and washed three times with PBST , 10 minutes each time. Incubate with HPR-labeled secondary antibody for 1 hour, and then wash with PBST three times, 10 minutes each time. ECL color development.
[0041]2. Immunofluorescence
[0042] 143B cells were inoculated on the pre-coated cell "climbing sheet". After 24 hours, basic medium containing different concentrations of toosendanin was added. After 24 hours, they were stimulated with 50ng / mL IL6 for 30 minutes. Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldeh...
Embodiment 2
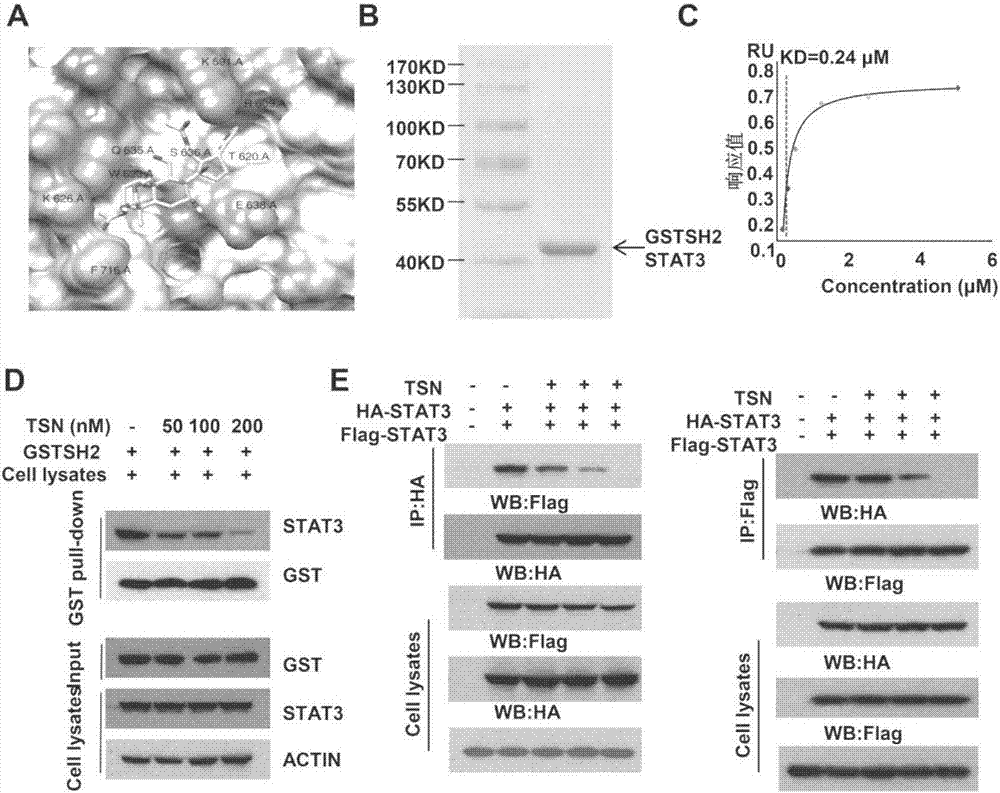
[0047] Example 2: Toosendanin (TSN) and STAT3-SH2 domain binding
[0048] 1. Technical method
[0049] 1. Molecular docking experiment
[0050] For the preliminary research on the combination of TSN and STAT3, we used the structure STAT3 (PDB Id: 1BG1) in the database for computer simulation. Artificially mimicking TSN small molecules into the STAT3 pocket. Find potential binding sites of TSN and STAT3.
[0051] 2. SH2 domain protein purification
[0052] The prokaryotic expression plasmid of STAT3-SH2 domain was constructed, and the vector was pGEX-4T-1. The constructed expression plasmid was transformed into E.coli BL21(DE3) expression strain. When the OD value of the bacterial solution was around 0.6, 1 mM isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) was added to induce the expression of the target protein at 37°C, and the soluble protein was obtained by ultrasound. The target protein was purified by GST bead, and identified by SDS gel electrophoresis and Coomassie stai...
Embodiment 3
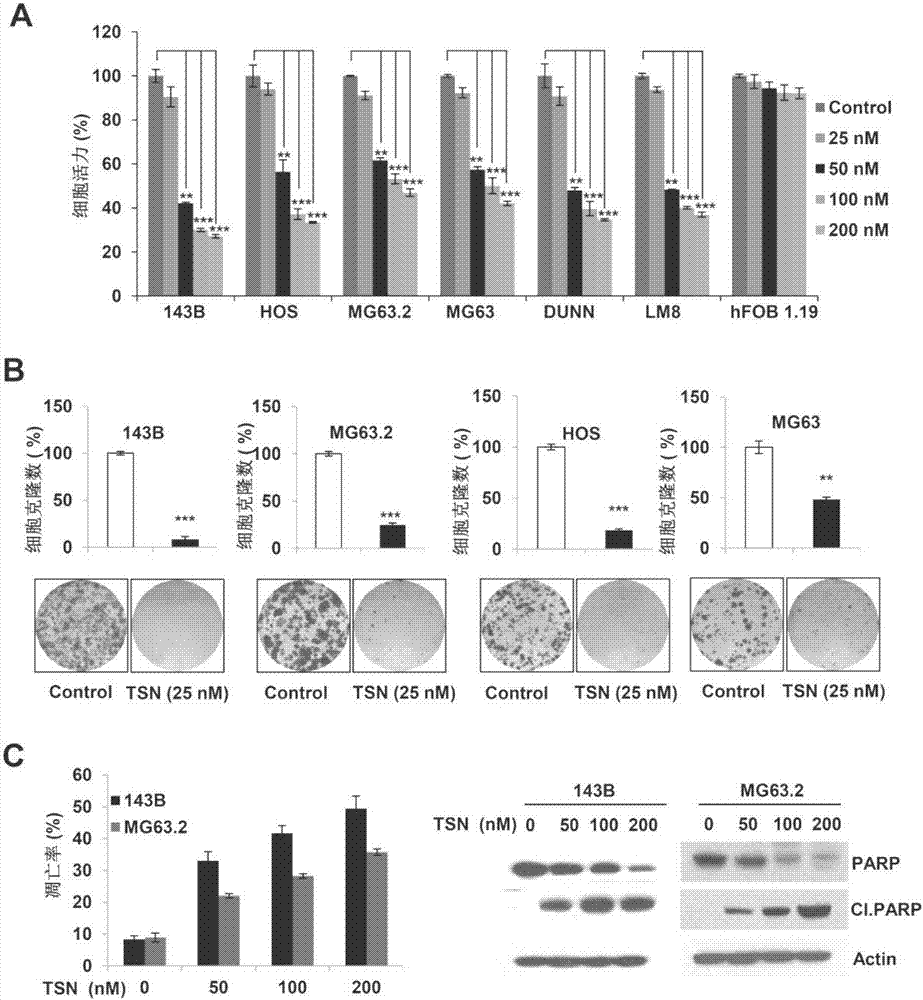
[0060] Embodiment 3: Toosendanin (TSN) inhibits the proliferation, clone formation and induces apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells
[0061] 1. Technical methods
[0062] 1. Cell culture and cell survival experiments
[0063] Osteosarcoma cells 143B, HOS, MG63.2, MG63, DUNN, LM8 and human osteoblasts used in the present invention are cultivated in a 37°C constant temperature incubator (humidity 95%, CO 2 Concentration 5%). Cell viability was determined by MTS method. Cells at 5 x 10 3 Inoculate to a 96-well plate at a density per well, add different concentrations of the monomer compound after 24 hours, add the same amount of DMSO to the control group, and set 6 replicate wells in each group. After continuing to culture for 48 hours, add 20 μl MTS and incubate at 37° C. for 1-4 hours, and detect the absorbance at 490 nm with a microplate reader. Experiments were repeated 3 times independently. Cell viability (%) = OD value of drug added / OD value of control group × 100%.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com