Fluorescence quantitative detection primers and probe for BRAF gene V600E mutation
A technology of DNA probes and probes, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of unnecessary use, high sequencing cost, and long experiment cycle, and achieve the effects of reducing false positives, short experiment cycle, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1, the design and selection of primers and probes for detecting BRAF gene V600E mutation
[0034] The design principles of the primers and probes used to detect the BRAF gene V600E mutation in the present invention are as follows: a specific fluorescent probe is added while adding a pair of primers during PCR amplification, and a reporter fluorescent group is marked at both ends of the probe. group and a quencher fluorophore. When the probe is intact, the fluorescent signal emitted by the reporter group is absorbed by the quencher group; during PCR amplification, the 5'-3' exonuclease activity of Taq enzyme degrades the probe, so that the reporter fluorescent group and the quencher group The fluorescent group is separated, so that the fluorescence monitoring system can receive the fluorescent signal, that is, every time a DNA strand is amplified, a fluorescent molecule is formed, and the accumulation of the fluorescent signal is completely synchronized with t...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Embodiment 2, the test of experimental reaction system and reaction condition
[0048] The DNA extracted from tissue samples and FFPE paraffin section samples (NGS was positive for BRAF V600E), as well as the fluorescence quantitative kit KAPA PROBE FAST qPCR Kits (KAPA BIOSYSTEMS, #KK4703) were used for the experiment. The size of the experimental system was determined according to the kit recommendation as 20 μl.
[0049] In the case of the same experimental environment and other conditions, the concentration of forward and reverse primers in the experimental system was optimized and tested, and finally it was determined that the final concentration of 500nM can achieve the best detection effect.
[0050] Under the same experimental environment and other conditions, the concentration of fluorescent probes in the experimental system was optimized and tested, and it was finally determined that the final concentration of 500nM can achieve the best detection effect.
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Embodiment 3, determination of standard sample detection lower limit
[0057] For different types of standard samples (Horizin BRAF V600E cfDNA Reference StandardSet and Horizon BRAF V600E FFPE Reference Standard), use standard positive samples and negative samples to configure positive samples with different mutation frequencies, and then perform detection limit experiments. The specific experimental method steps are the same as in Example 2.
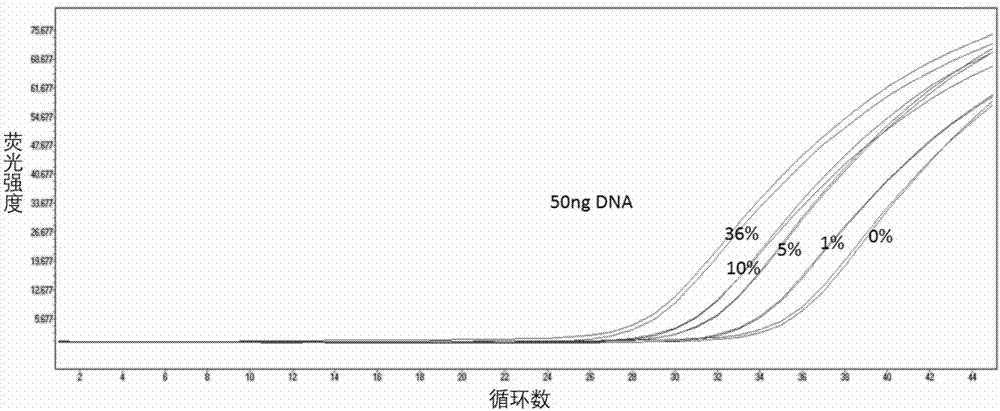
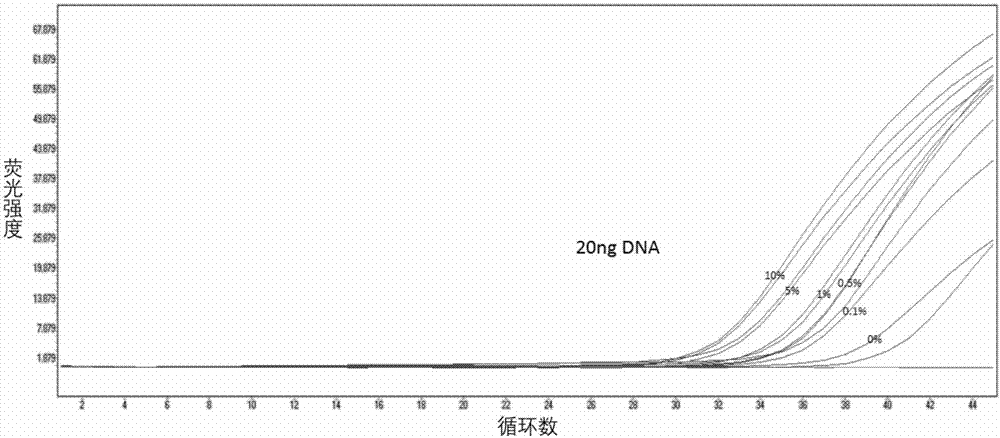
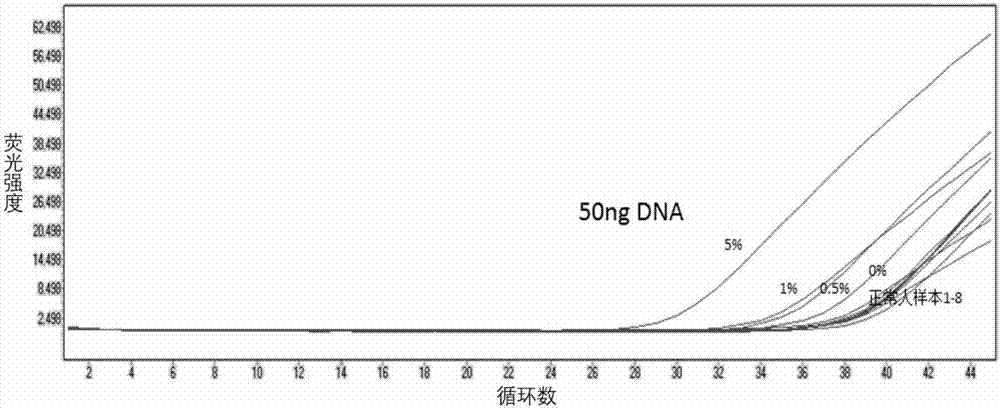
[0058] See the experimental results figure 1 , figure 2 with image 3 . It can be seen that the present invention can detect the lowest 50ng of DNA and the lowest mutation rate of 0.5%, and the final fluorescence curve Ct value is less than or equal to 36. It shows that the primers and probes provided by the present invention have good sensitivity.
[0059] Mykino (Chongqing) Gene Technology Co., Ltd.
[0060] Primers and probes for fluorescent quantitative detection of BRAF gene V600E mutation
[0061] GNCLN171097
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com