Arenicola cristata antibacterial peptide NZ17074 derived peptide N6 and application thereof
A technology for derivatizing peptides and antibacterial peptides, applied in application, antibacterial drugs, peptides, etc., can solve problems such as constraints, and achieve the effects of small molecular weight, good bactericidal effect, and easy artificial synthesis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1 Design and synthesis of sea earthworm antimicrobial peptide NZ17074-derived peptide N6
[0023] 1. Based on the NZ17074 parent peptide sequence, by replacing and adding or subtracting amino acid residues, by appropriately increasing the antimicrobial peptide hydrophobicity and changing the number of disulfide bond pairs, a mutant antimicrobial peptide N6 was finally determined, trying to improve The bacteriostatic activity of the antimicrobial peptide on Gram-negative bacteria, the nucleotide sequence of the antimicrobial peptide N6 gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:2, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:1.
[0024] 2. Antimicrobial peptides are synthesized using a solid-phase synthesis method through a twelve-channel semi-automatic peptide synthesizer. The purity of the synthesized peptides (>90%) was determined by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography C18 column, and the molecular weights of the derived peptides N6 and N6 were confirmed...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Example 2 Bacteriostatic experiment of sea earthworm antimicrobial peptide NZ17074 derived peptide N6
[0026] The pathogenic bacteria in this embodiment come from China Veterinary Microbial Culture Collection Management Center (CVCC), China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee General Microbiology Center (CGMCC) and China Industrial Microbiology Culture Collection Management Center (CICC), and the specific bacterial strains are as shown in the table 1.
[0027] The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration) of the derivative peptide was determined with reference to the method established by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute) (WIEGAND et al., Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimalinhibitory concentration (MIC )of antimicrobial substances.Nature protocols,2008,3(2):163-175), slightly modified according to the specific situation, the operatio...
Embodiment 3
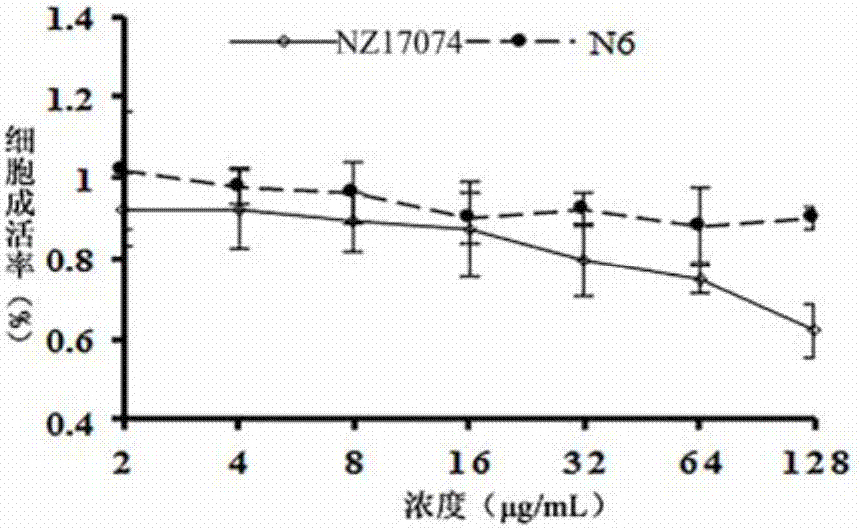
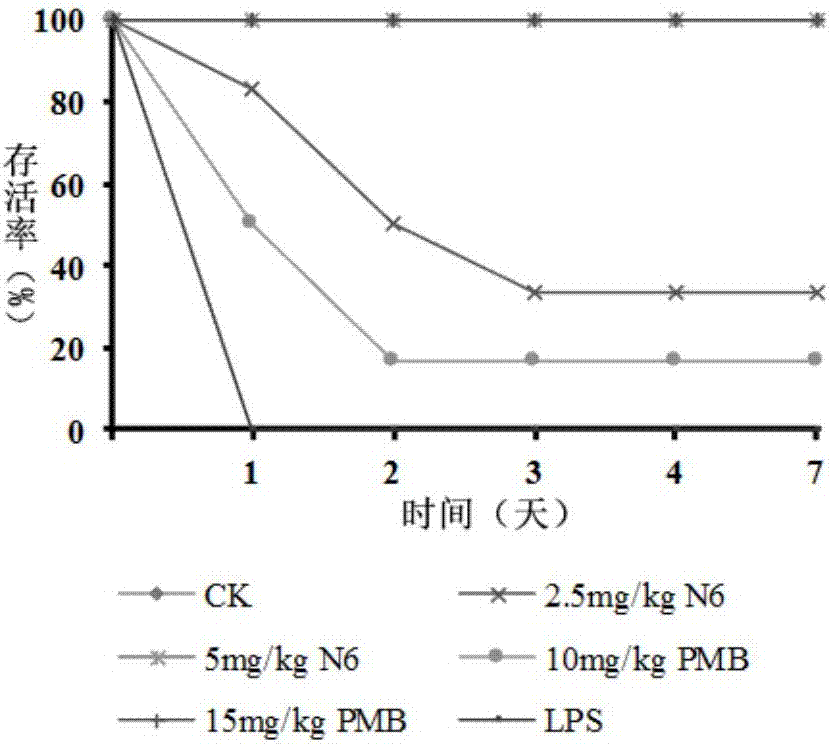
[0035] Example 3 Cytotoxicity study of sea earthworm antimicrobial peptide NZ17074-derived peptide N6
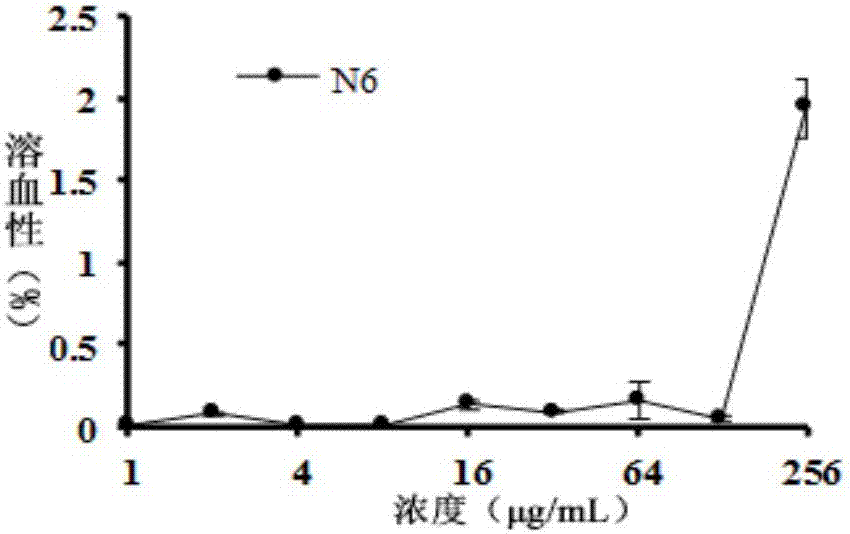
[0036] 1. Determination of hemolysis
[0037] Hemolyticity is an important indicator to measure whether antimicrobial peptides are suitable for intravenous injection therapy. The specific operations are as follows:
[0038] 6-week-old ICR female mice with SPF grade were taken, blood was collected from eyeballs, and collected using heparin sodium anticoagulant tubes. The collected blood was centrifuged at 1500 rpm for 10 min at 4° C., and the erythrocytes were repeatedly washed three times with 10 mM PBS (pH 7.3) until the supernatant was colorless and transparent, and an 8% erythrocyte suspension was prepared.
[0039] The sample peptide was dissolved in sterile 0.9% physiological saline, prepared into a stock solution with a concentration of 512 μg / mL, and diluted 2-fold to a final concentration of 1 μg / mL. 100 μL of erythrocyte suspension and antimicrobial peptide soluti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com