An Achromobacter strain resistant to the toxicity of sulfonamide antibiotics and its application
An achromobacter, sulfonamides technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, bacteria, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of reducing denitrification enzyme activity, affecting the normal operation of sewage treatment system, reducing the abundance of denitrifying microbial community, etc. Convenient operation, high-efficiency aerobic denitrification capacity, and the effect of huge economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
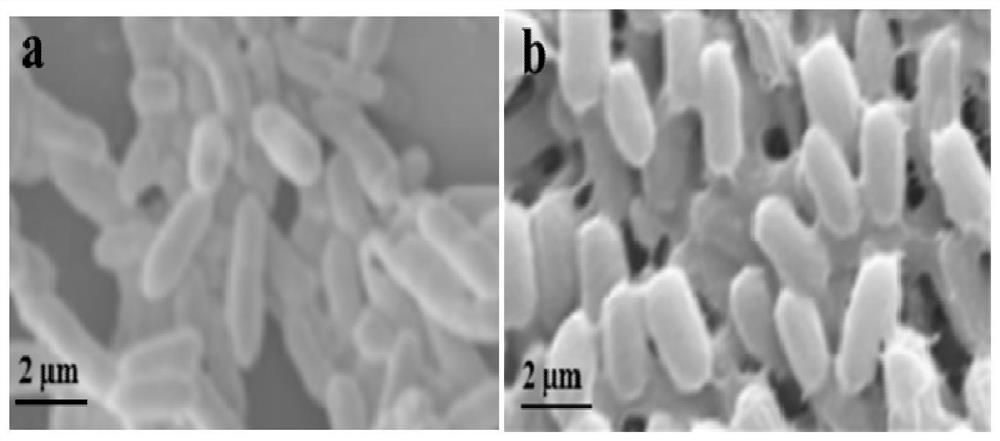
[0027] Embodiment 1. Utilize scanning electron microscope to observe the apparent form of achromobacter when sulfonamide antibiotic exists
[0028] The high-efficiency aerobic denitrification bacterial strain used in the method is Achromobacter sp., which is isolated from a landfill leachate treatment system.
[0029] Inoculate Achromobacter sp. into 1L of LB medium (containing 5g of NaCl, 10g of tryptone, and 5g of yeast extract per liter) to prevent the invasion of miscellaneous bacteria and maintain the growth vigor of the bacteria for enrichment to cultivate. Centrifuge the cultured bacterial liquid, wash three times with 0.5% NaCl, and make the optical density OD 600 For 1-2 bacteria suspension. Then the bacterial suspension was inoculated respectively in the LB medium containing 0 and 8 μg / L SMX by 10% inoculum size, and after 8 hours, the sample was removed by centrifugation for 5 min at 8000 rpm and 4° C., and washed with PBS (phosphate buffer) and washed twice. Fi...
Embodiment 2
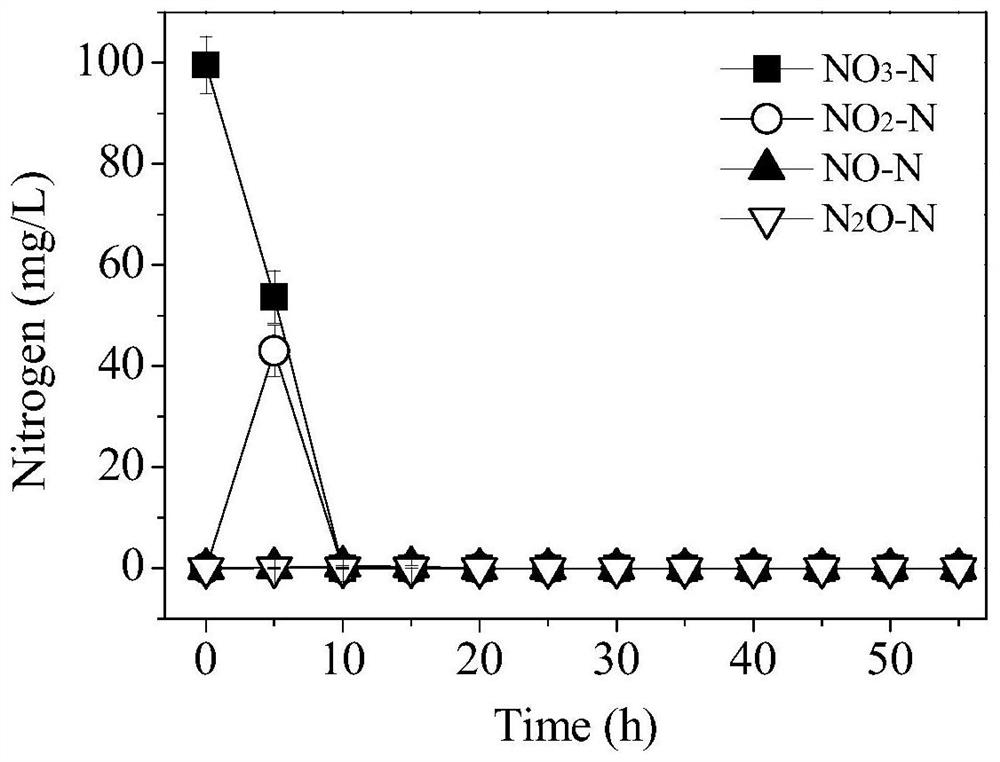
[0031] Example 2. The aerobic denitrification characteristics of Achromobacter in blank control group (0 μg / L SMX)
[0032] The denitrification performance test medium (BM) formula is per liter of water: 8.45g CH 3 COONa, 0.63g NH 4 Cl, 0.61g NaNO 3 ,1.76g K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O, 0.20g MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.02g CaCl 2 ,0.005g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.1mL trace element solution. Adjust the pH value of the medium to 7.5, and sterilize at 121°C for 30min.
[0033] The strain Achromobacter sp. was inoculated in BM medium, and cultured with shaking at 30°C and 150 rpm, and 100 μL of headspace gas was extracted every 5 hours for the determination of N 2 O, 2 mL of gas was extracted with a sterile syringe and injected into a 2 L pure helium bag for the determination of NO. At the same time, 2 mL of bacterial suspension was extracted with a sterile syringe, and the bacterial liquid was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 5 min at 4°C, and the supernatant was taken for analysis of the concentratio...
Embodiment 3
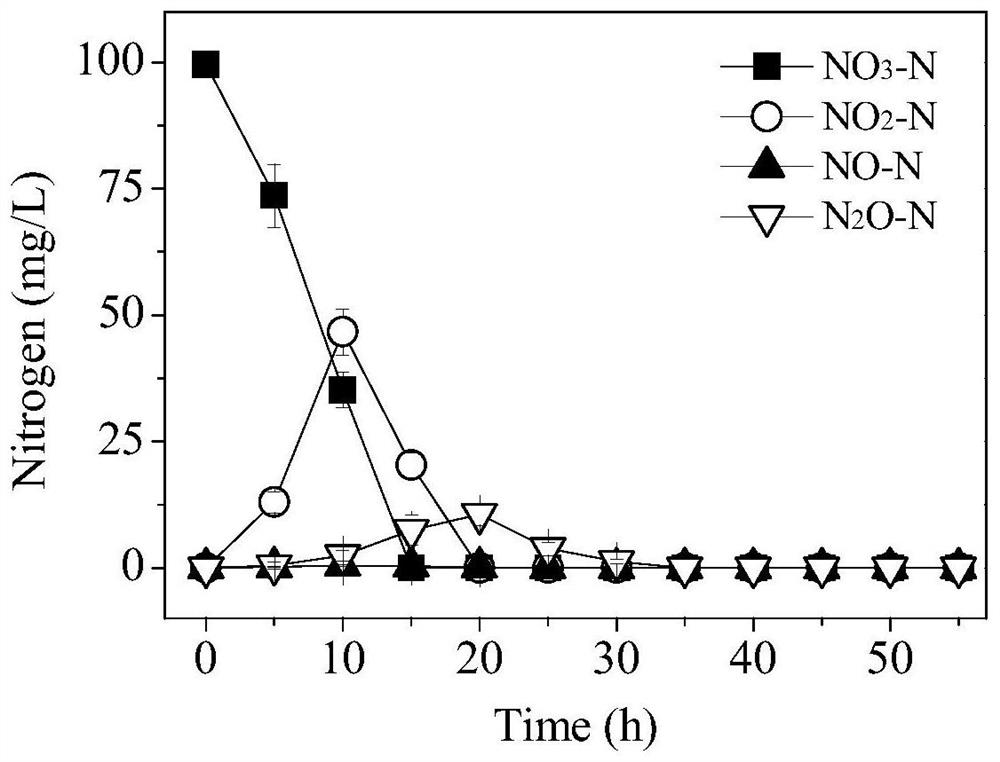
[0035] Example 3. Aerobic denitrification characteristics of Achromobacter in the presence of 2 μg / L SMX
[0036] The strain Achromobacter sp. was inoculated in BM medium containing 2 μg / L SMX to test its aerobic denitrification performance. The result is as image 3 As shown, 100 mg / L nitrate nitrogen was utilized by the strain immediately after inoculation and was completely consumed within 20 h, with an average removal rate of 5.0 mg / L / h nitrate nitrogen. With the reduction of nitrate nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen gradually accumulated and reached the highest value of 46.7mg / L at 10h, and then was reduced at 20h. At the same time, N 2O also accumulated gradually, reaching the highest value of 10.6mg / L at 20h, and then completely reduced at 35h. It must be pointed out that the highest NO accumulation in the intermediate product of the denitrification process is 9.6 μg / L, accounting for only 0.0096% of the nitrate nitrogen removal. It can be seen that the achromobacter can s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com