Spectroscopy-mass spectrometry combined quantitative analysis device for elements in unknown sample
A technology for quantitative analysis of unknown samples, applied in the field of detection, can solve problems such as increasing LIBS quantitative analysis errors and failing to detect nanoparticles, and achieve the effect of high detection sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] In order to make the technical problems solved by the present invention, the technical solutions adopted and the technical effects achieved clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, but not to limit the present invention. In addition, it should be noted that, for the convenience of description, only parts related to the present invention are shown in the drawings but not all content.
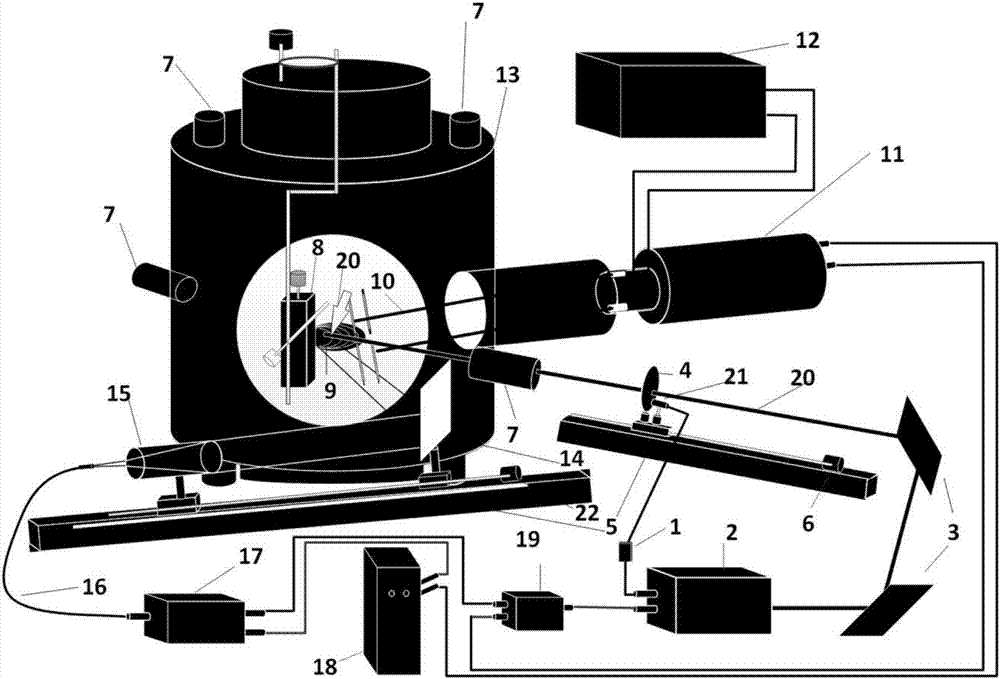
[0019] Please refer to figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the overall structure of the present invention (direct front and upper perspective).
[0020] The automatic focusing module 1 is connected to the stepper motor 6 through the serial port, and the laser 2 is connected through the BNC interface; the laser 2 is connected to the timing control module 19 through th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com