Preparation method of damp-proof, breathable and super-hydrophobic activated carbon
An activated carbon and super-hydrophobic technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, alkali metal oxides/hydroxides, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as the ability to adsorb non-polar organic substances, achieve excellent moisture-proof properties, and improve durability The performance and pore structure have little influence on the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] (1) Pre-treatment: put the activated carbon sample in an oven at 120°C, dry for 24 hours, fully remove moisture, and set aside;
[0018] (2) Surface modification: add the dried activated carbon and octadecyltriethoxysilane into the vacuum drying oven at the same time according to the mass ratio of 250:1, vacuumize, adjust the temperature to 120°C, and keep the time for 24h.
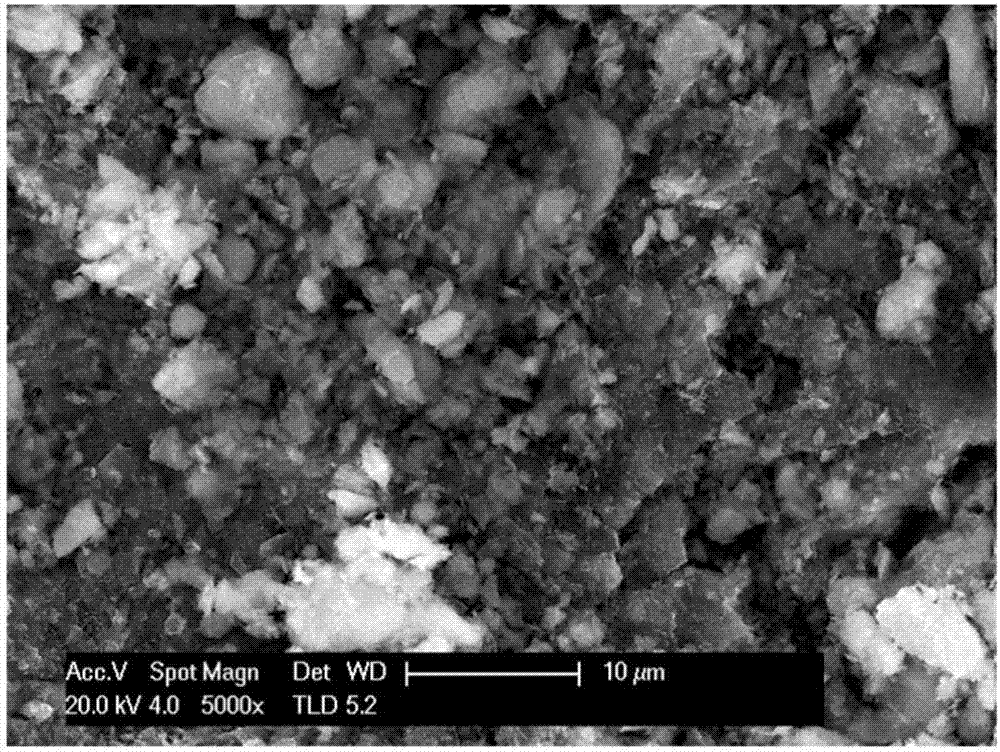
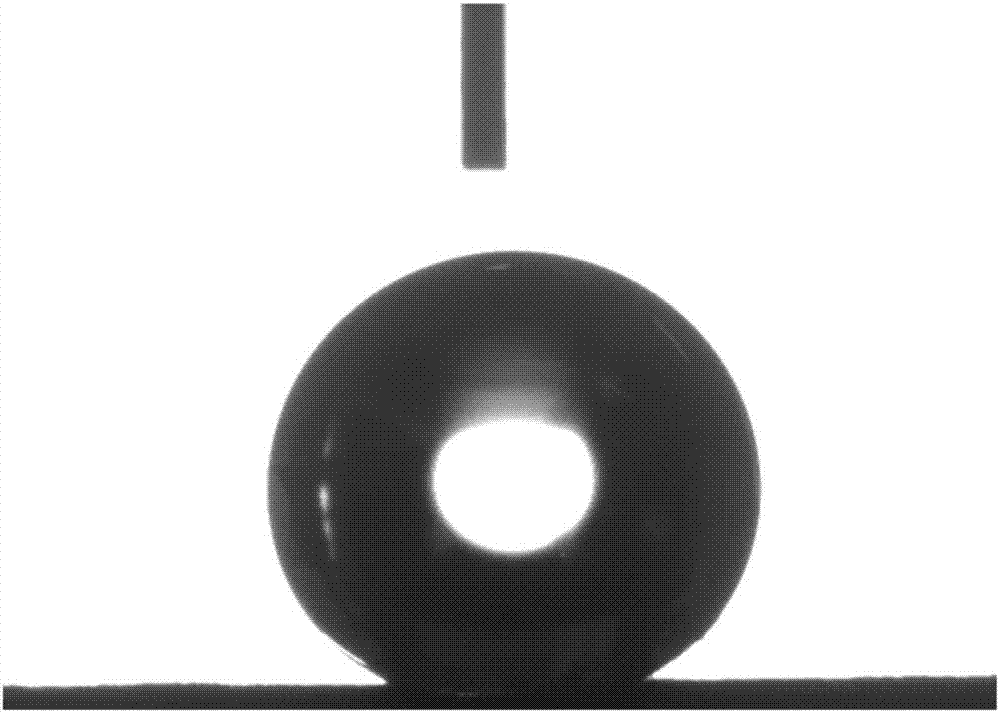
[0019] (3) Drying and curing: the modified activated carbon was placed in an oven at a temperature of 150°C and kept for 0.5h to complete the preparation. After modified by this method, the surface of activated carbon still maintains its porous structure ( figure 1 ), while the static contact angle of water droplets on the surface of the sample can reach 150.4±0.8° ( figure 2 ).
Embodiment 2
[0021] (1) Pre-treatment: Put the activated carbon sample in an oven at 80°C, dry for 24 hours, fully remove moisture, and set aside;
[0022] (2) Surface modification: add the dried activated carbon and heptadecylfluorodecyltrimethoxysilane into a vacuum drying oven at the same time at a mass ratio of 500:1, vacuumize, adjust the temperature to 180°C, and hold for 12 hours.
[0023] (3) Drying and curing: the modified activated carbon was placed in an oven at a temperature of 80°C and kept for 0.5h to complete the preparation. After the modified method, the static contact angle of water droplets on the surface of the sample can reach 149.1±1° ( Figure 4 ).
Embodiment 3
[0025] (1) Pre-treatment: put the activated carbon sample in an oven at 120°C, dry for 6 hours, fully remove moisture, and set aside;
[0026] (2) Surface modification: soak the dried activated carbon into 1wt.% ethanol solution of nonafluorohexylchlorosilane, and place the solution in an oven at 60°C for 2 hours;
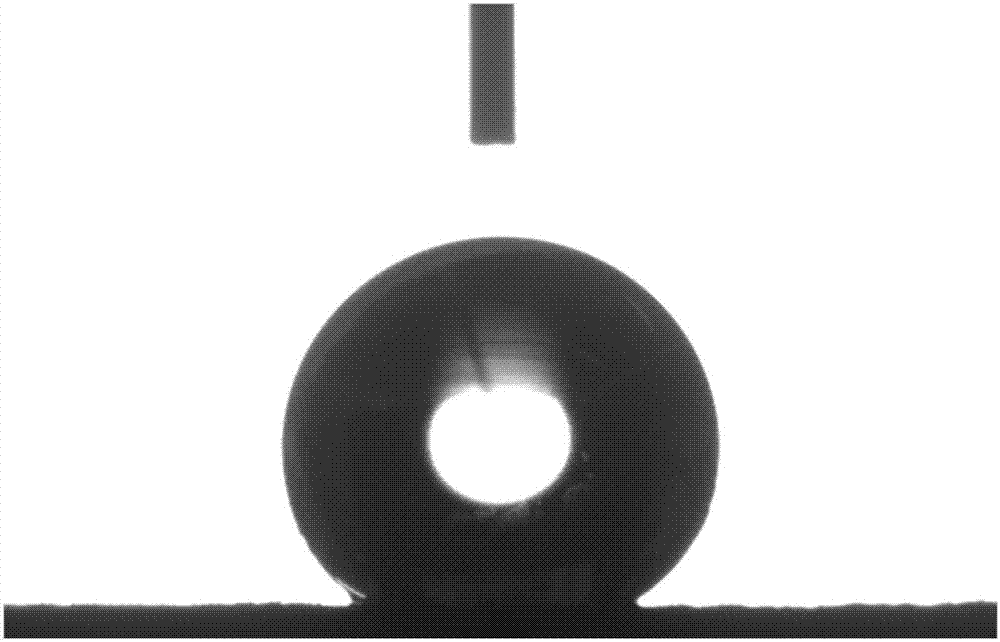
[0027] (3) Drying and curing: the modified activated carbon was placed in an oven at a temperature of 120°C and kept for 1 hour to complete the preparation. After modified by this method, the surface of activated carbon still maintains its porous structure, and the static contact angle of water droplets on the surface of the sample can reach 144.1±0.4° ( image 3 ).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com