Method for efficiently reducing hexavalent chromium in water by magnetic electric conduction macromolecule synergistic microwave
A conductive polymer, synergistic microwave technology, applied in the reduction water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, circuits, etc. The advantages are obvious, the site area is reduced, and the effect of preventing ferrite corrosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] A method for efficiently reducing hexavalent chromium in water with magnetically conductive polymers in cooperation with microwaves, the steps of which are as follows:
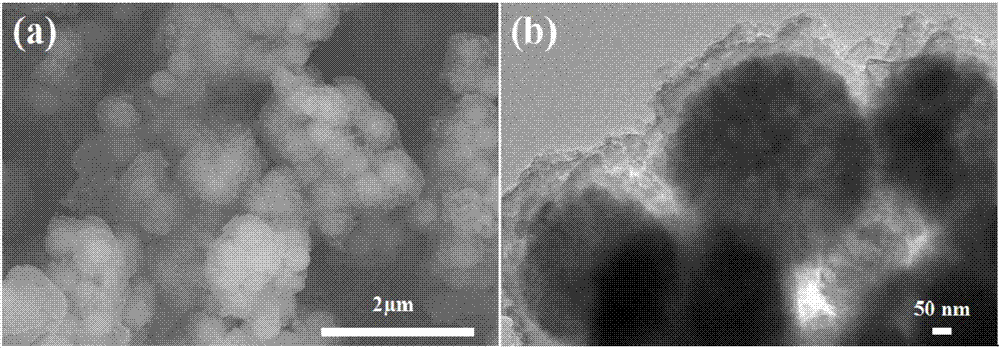
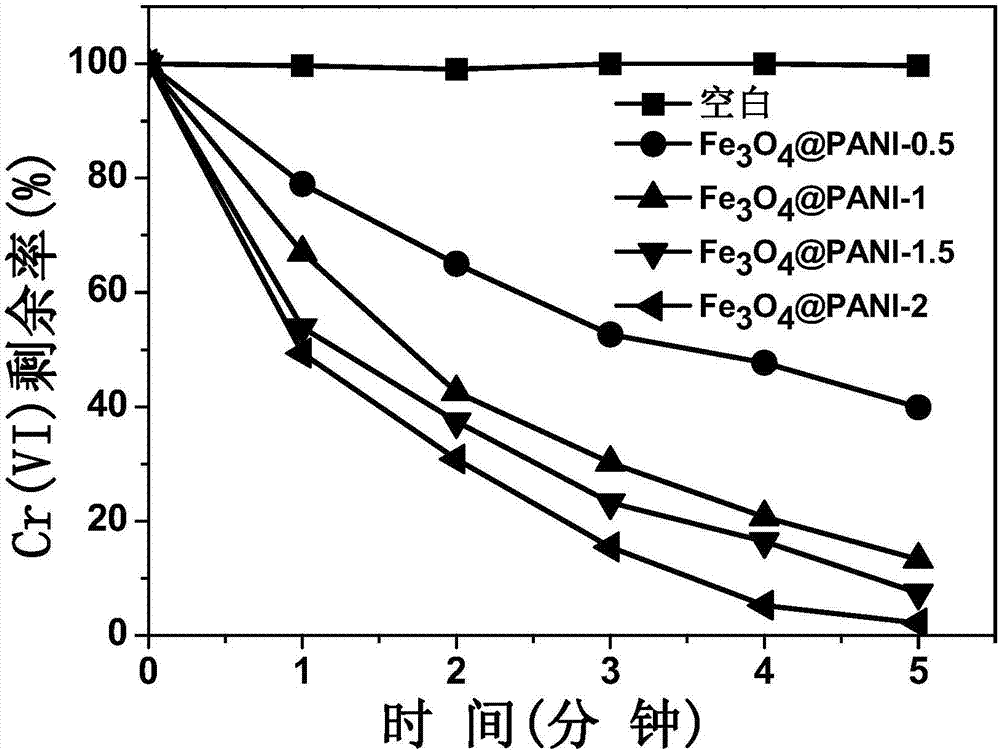
[0033] a. Microwave-assisted efficient reduction of hexavalent chromium: put 50mL aqueous solution containing 1mmol / L hexavalent chromium into a conical flask, adjust its pH to 2 with sulfuric acid, add 0.2g / L magnetic conductive polymer composite Fe 3 o 4 @PANI, after mixing, transfer the mixture to the microwave chemical reactor, start the microwave, the microwave power is 900W, the irradiation time is 5min, Fe 3 o 4 @PANI absorbs microwaves to quickly reduce hexavalent chromium;
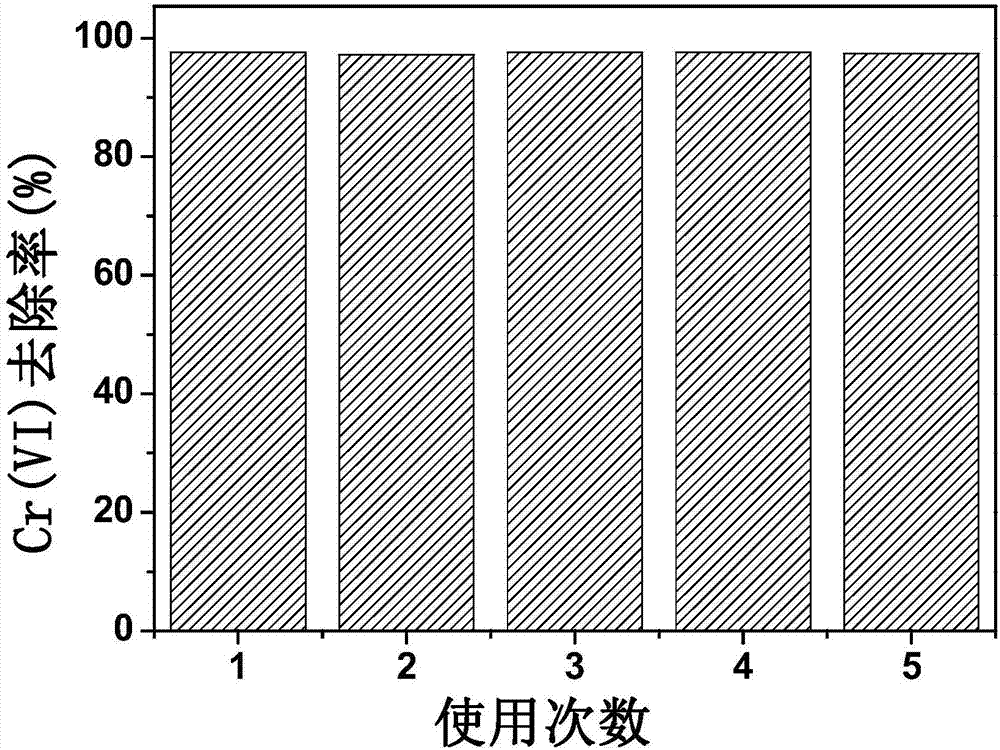
[0034] b. Magnetic separation and recycling of magnetic conductive polymers: After the reaction is complete, use a magnet to separate the Fe in step a 3 o 4 @PANI, after washing with pure water, it can be directly put into the next reaction batch;
[0035] c. The trivalent chromium generated by the reduction reaction i...
Embodiment 2
[0042] With embodiment 1, difference is: adopt oxalic acid to adjust pH to 3 in step a, Fe 3 o 4 The dosage of @PANI was reduced to 0.1g / L, and the duration of microwave irradiation was reduced to 3min. Under other conditions being the same, the reduction rate of Cr(VI) reaches 99%.
Embodiment 3
[0044] With embodiment 1, difference is: in step a, adjust pH to 4 with hydrochloric acid, Fe 3 o 4 The dosage of @PANI was increased to 1.0g / L, the microwave power was 540W, and the irradiation time was 2min. Under other conditions being the same, the reduction rate of Cr(VI) reaches 96%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com