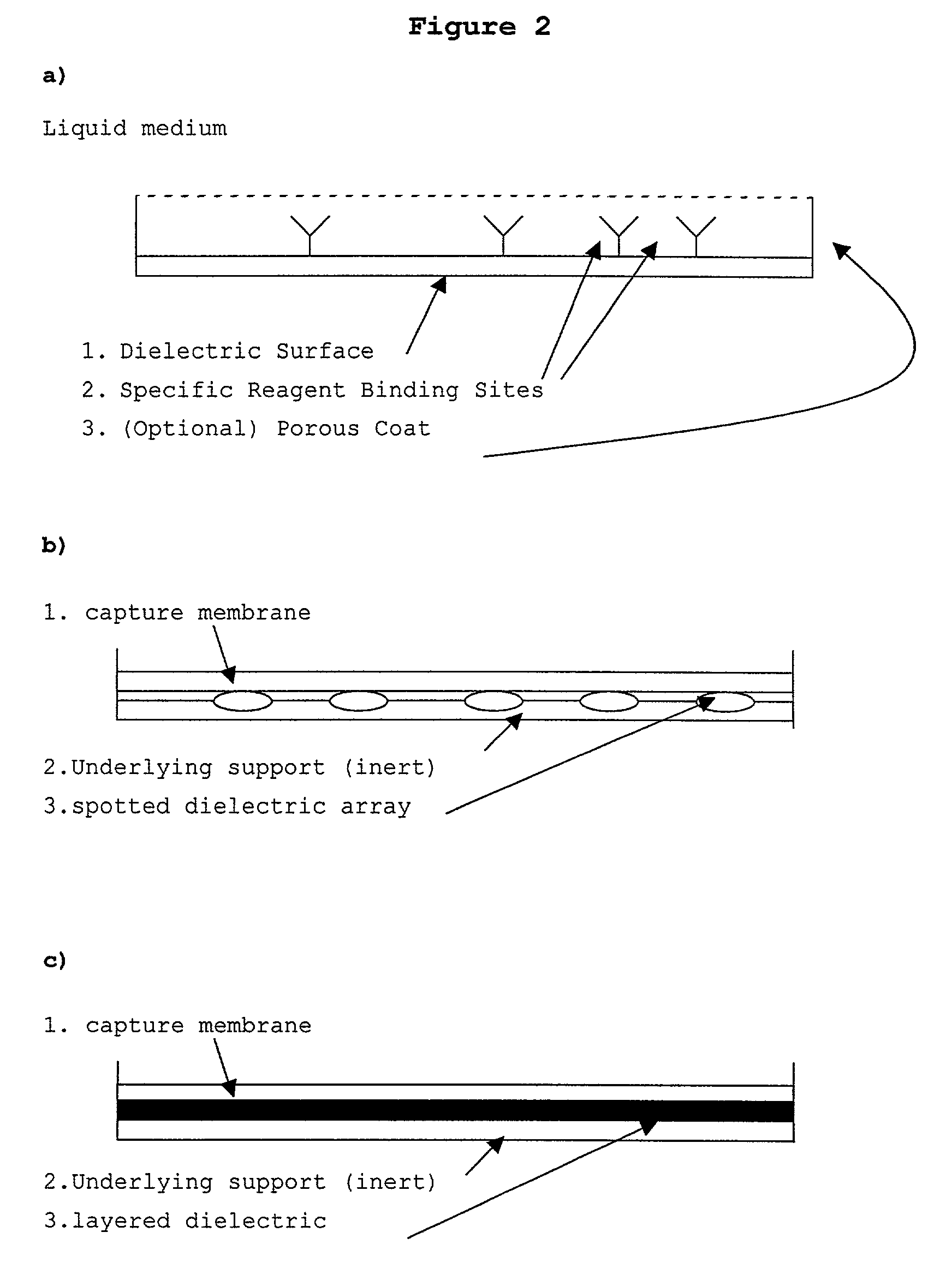
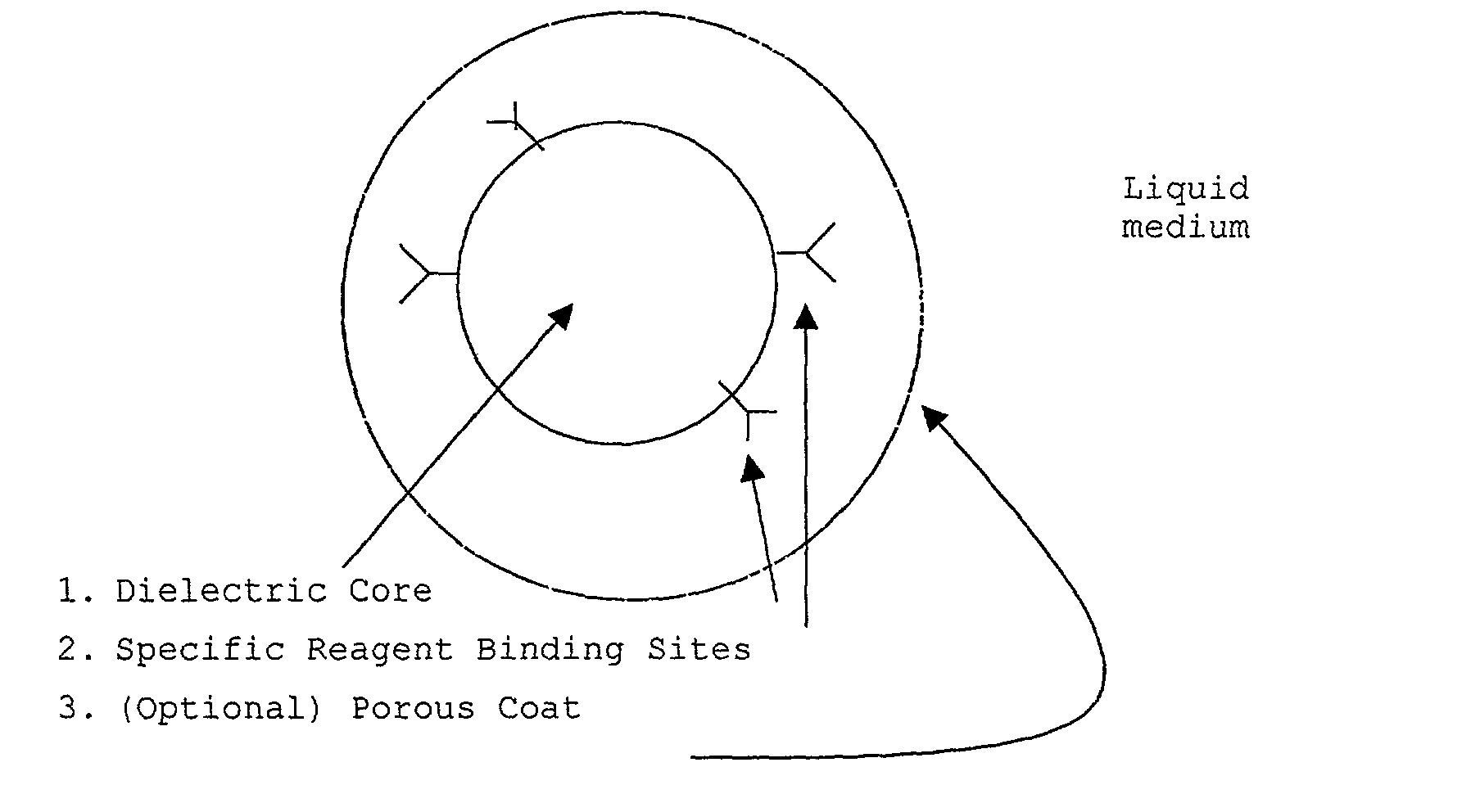
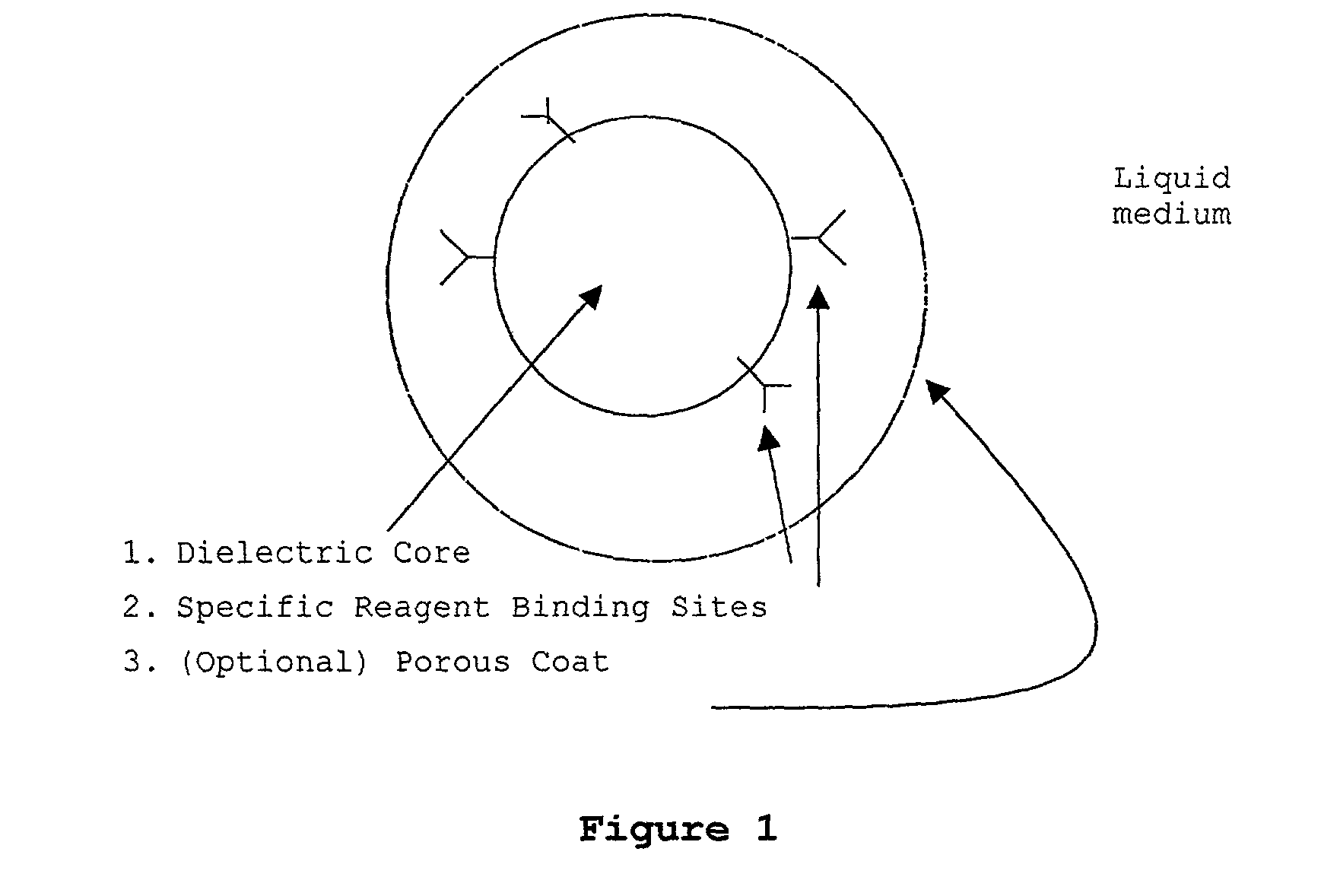
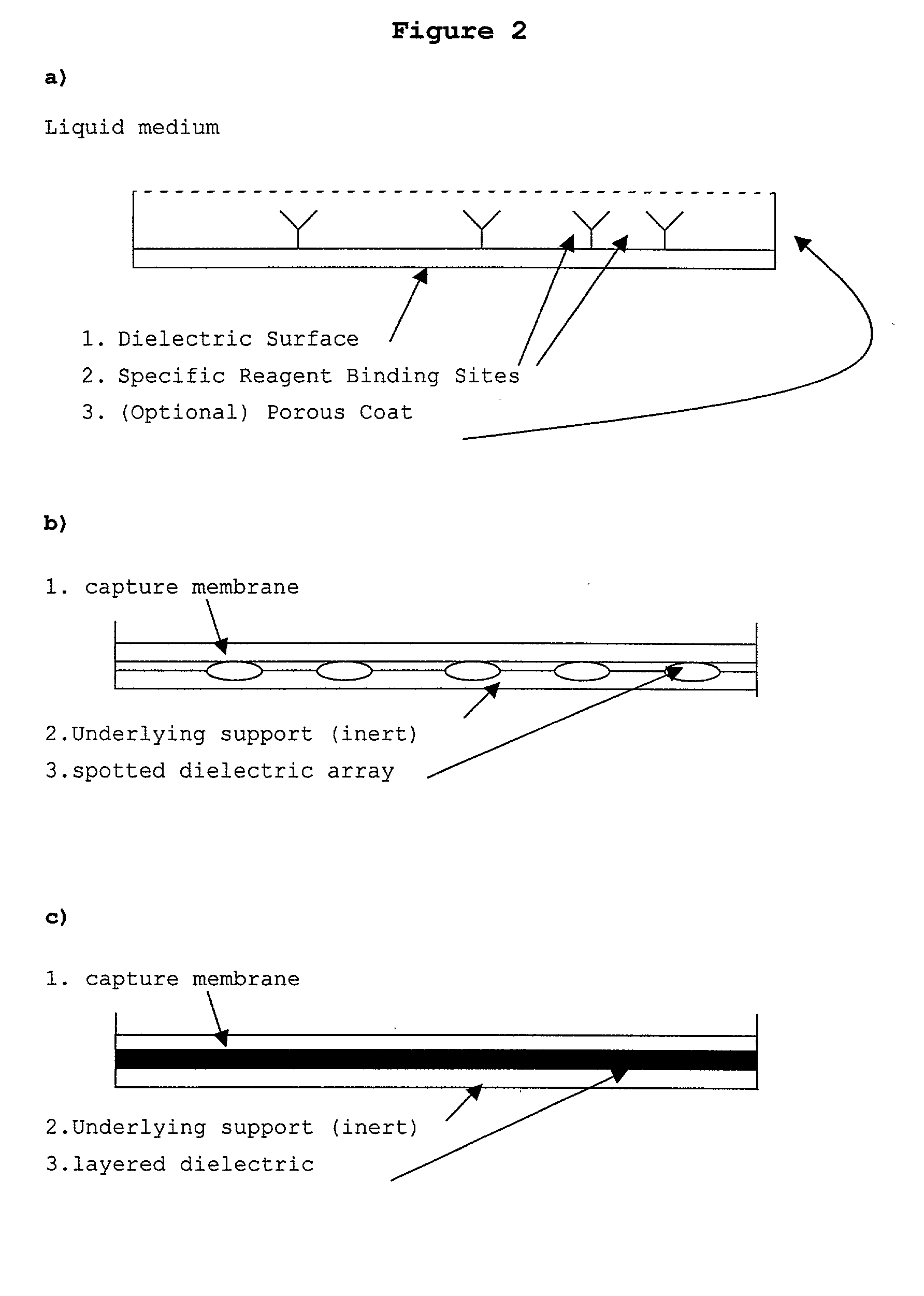
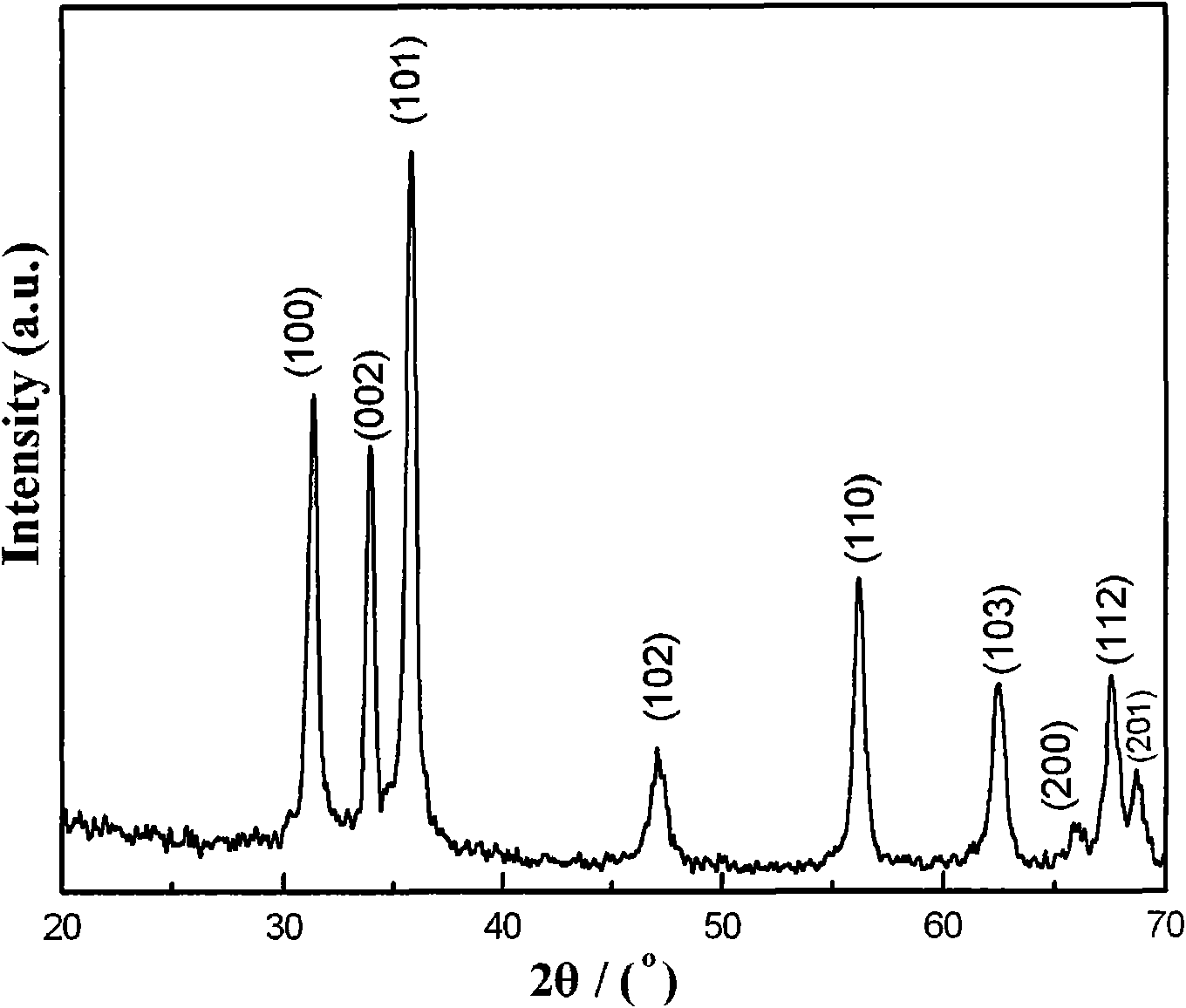
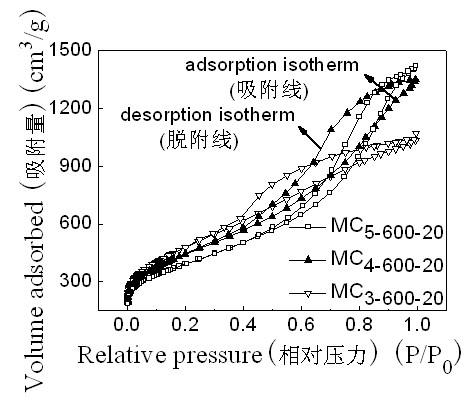
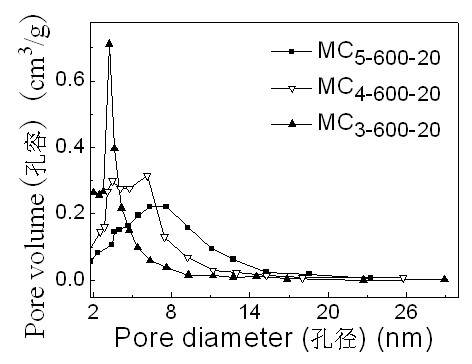
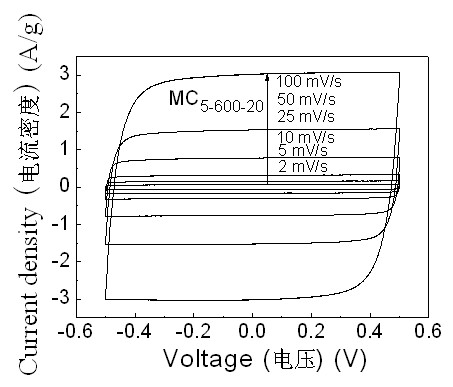
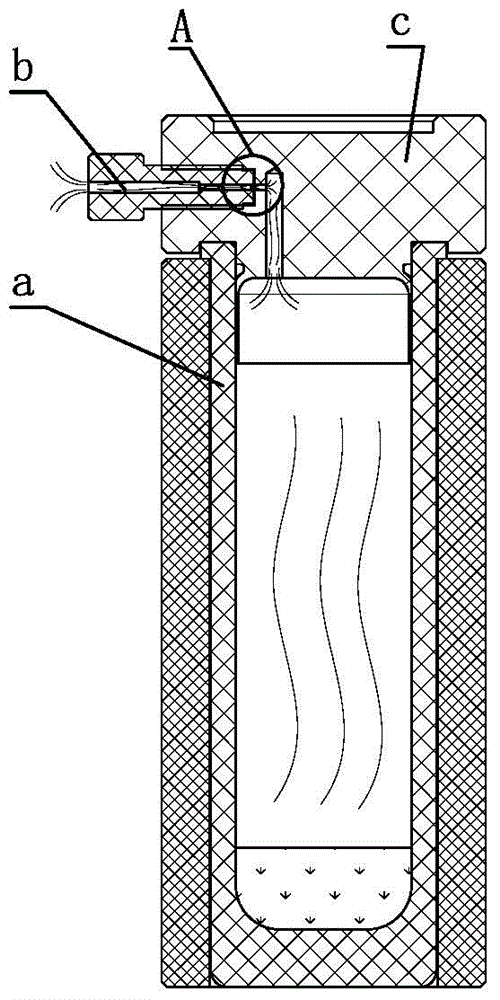
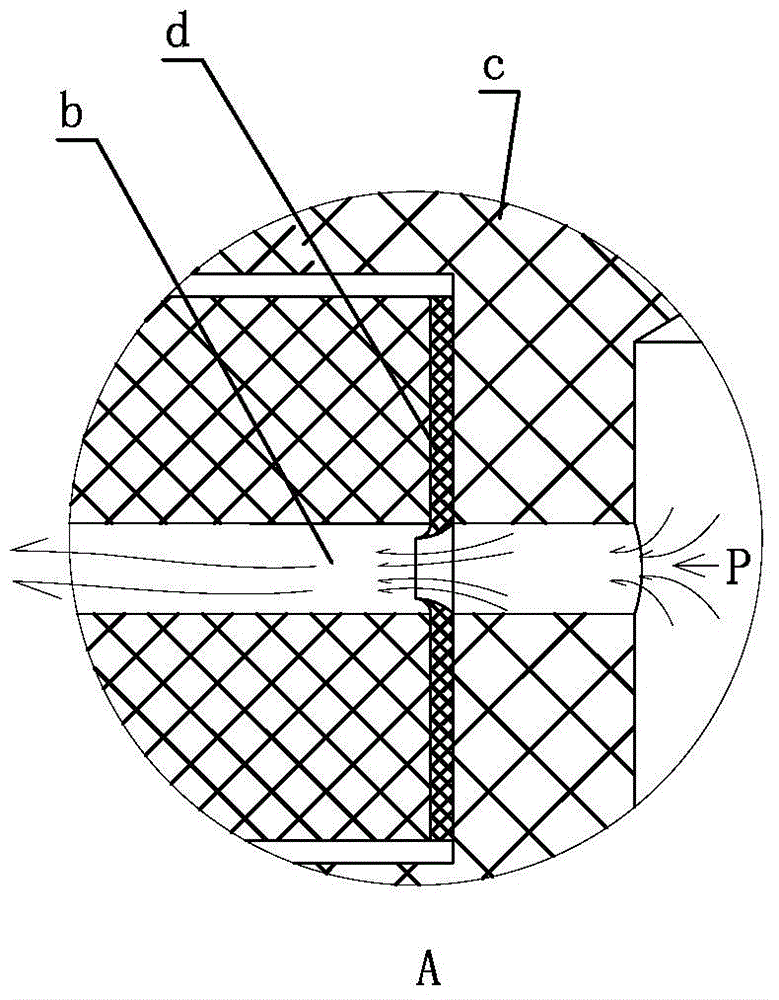
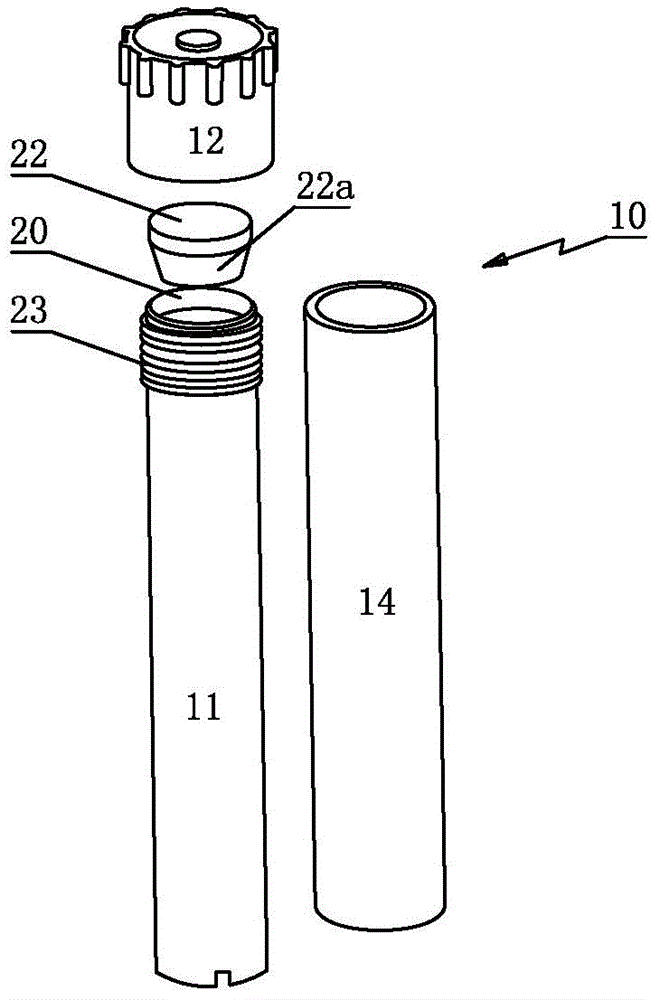
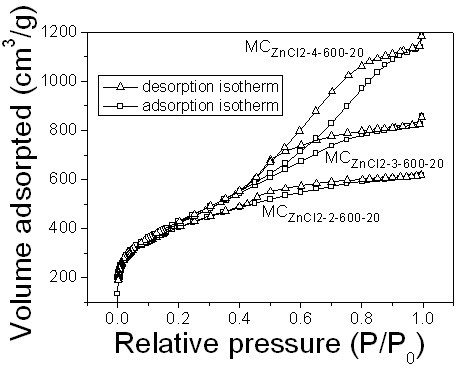
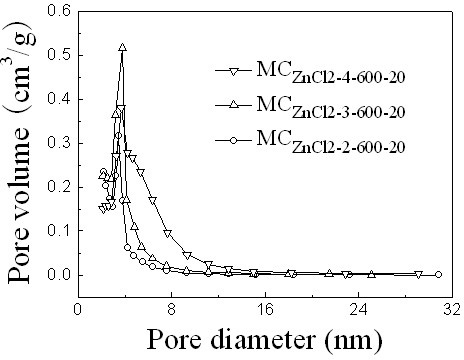
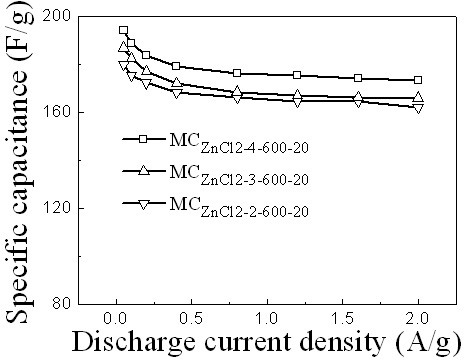
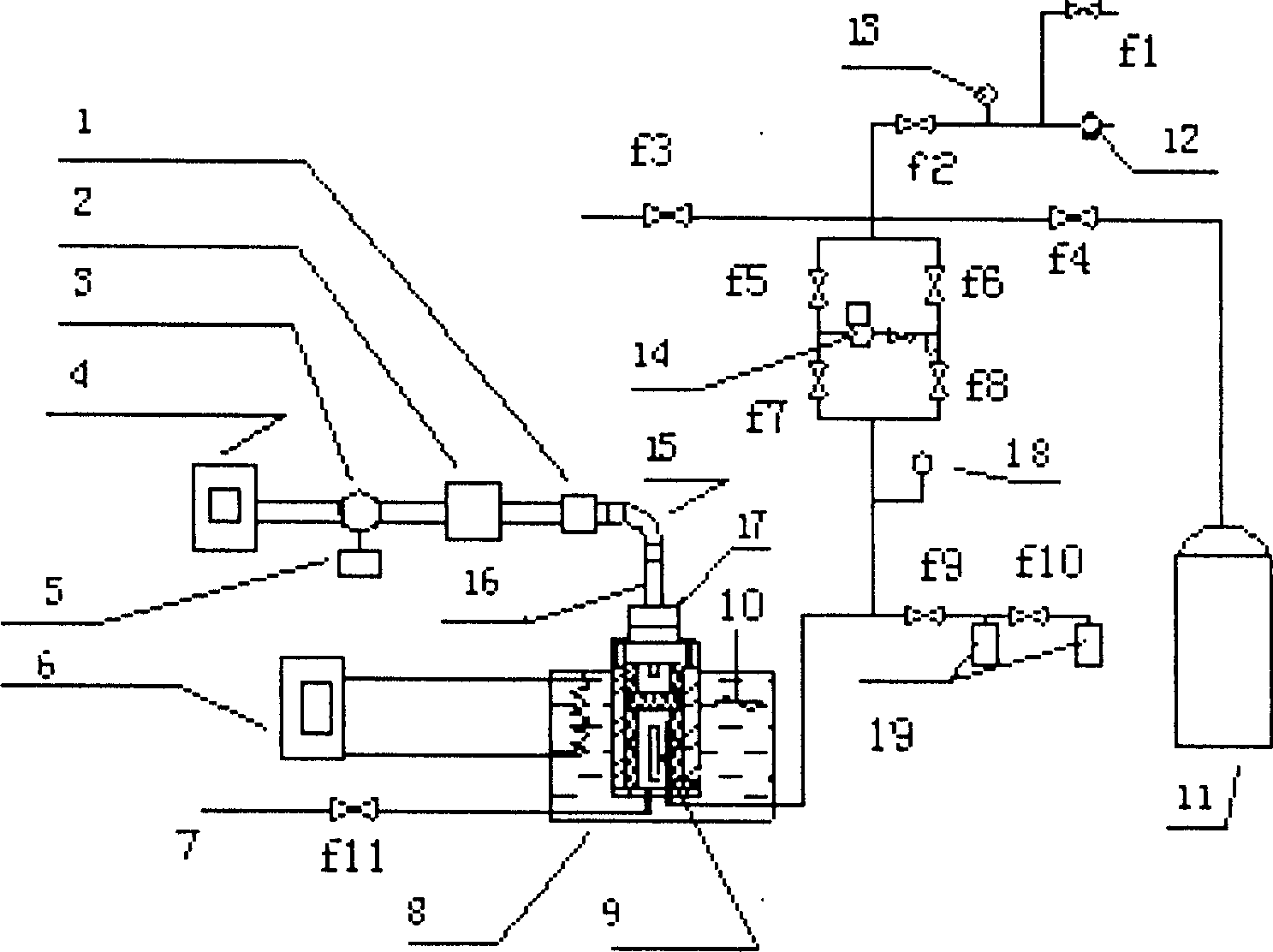
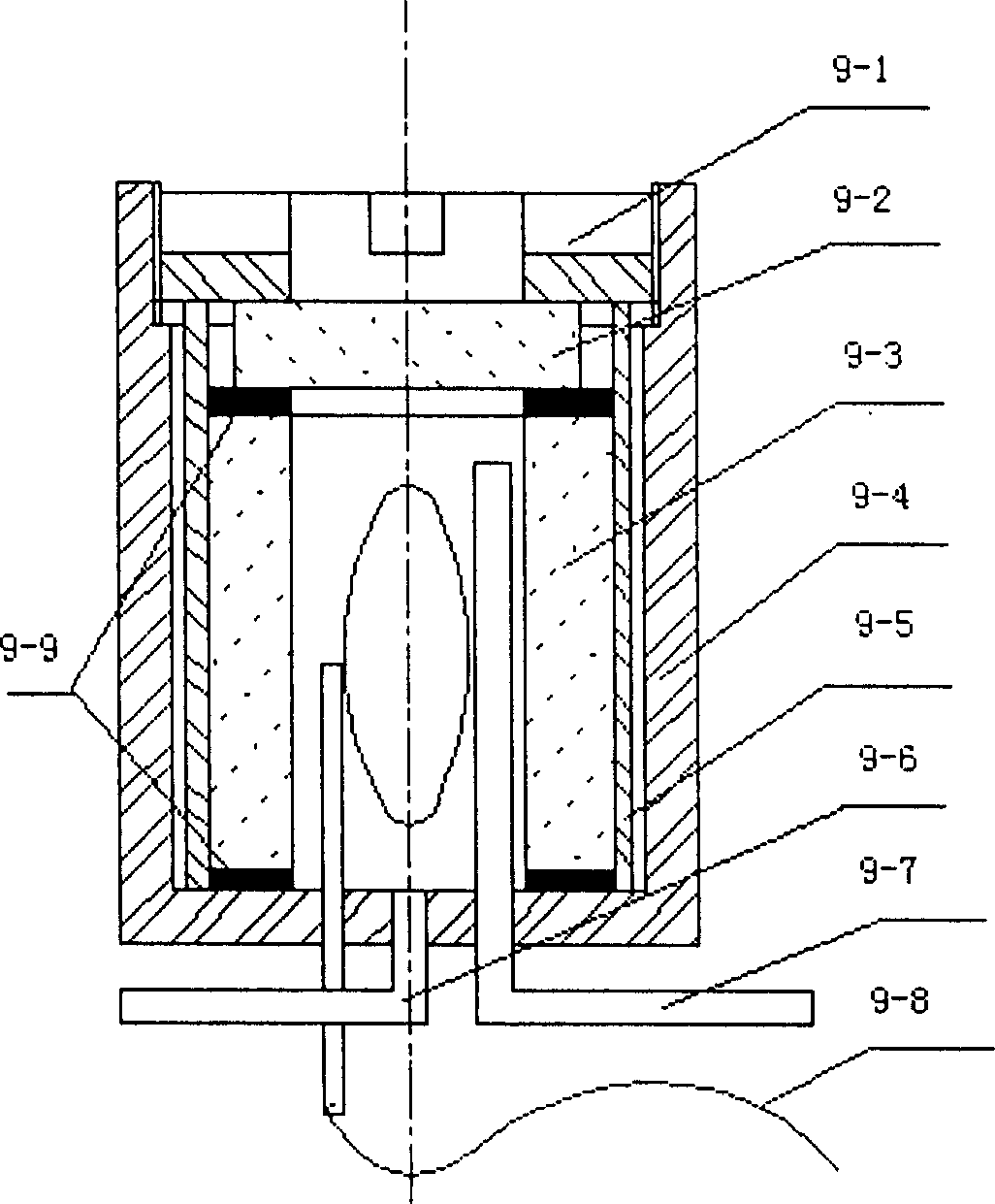
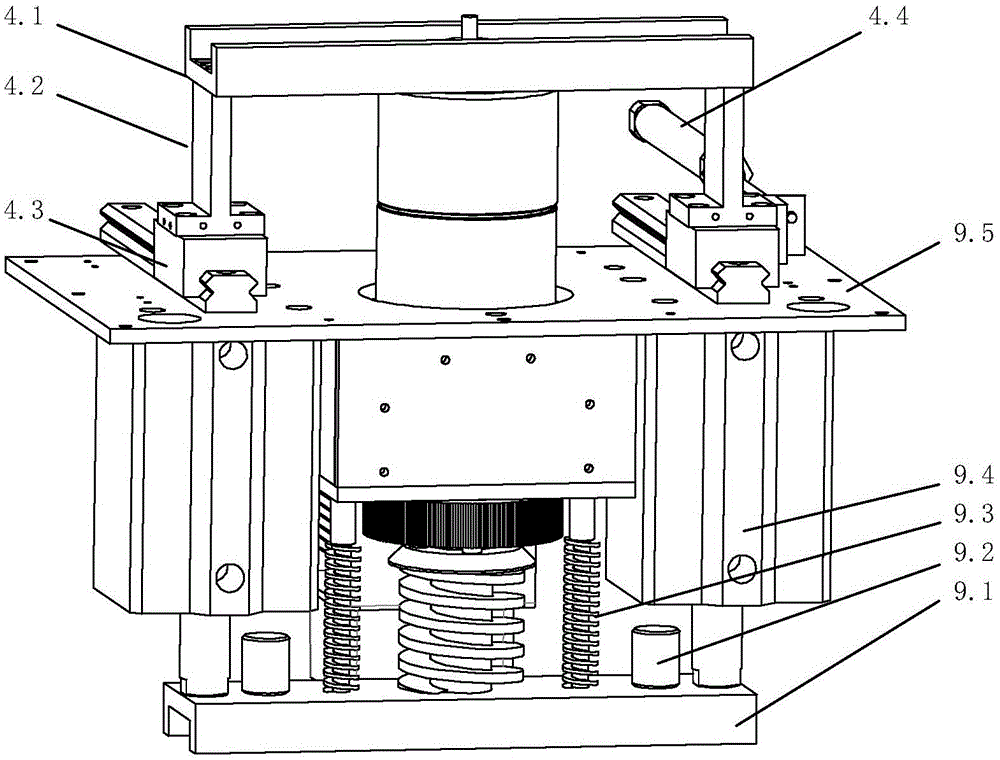
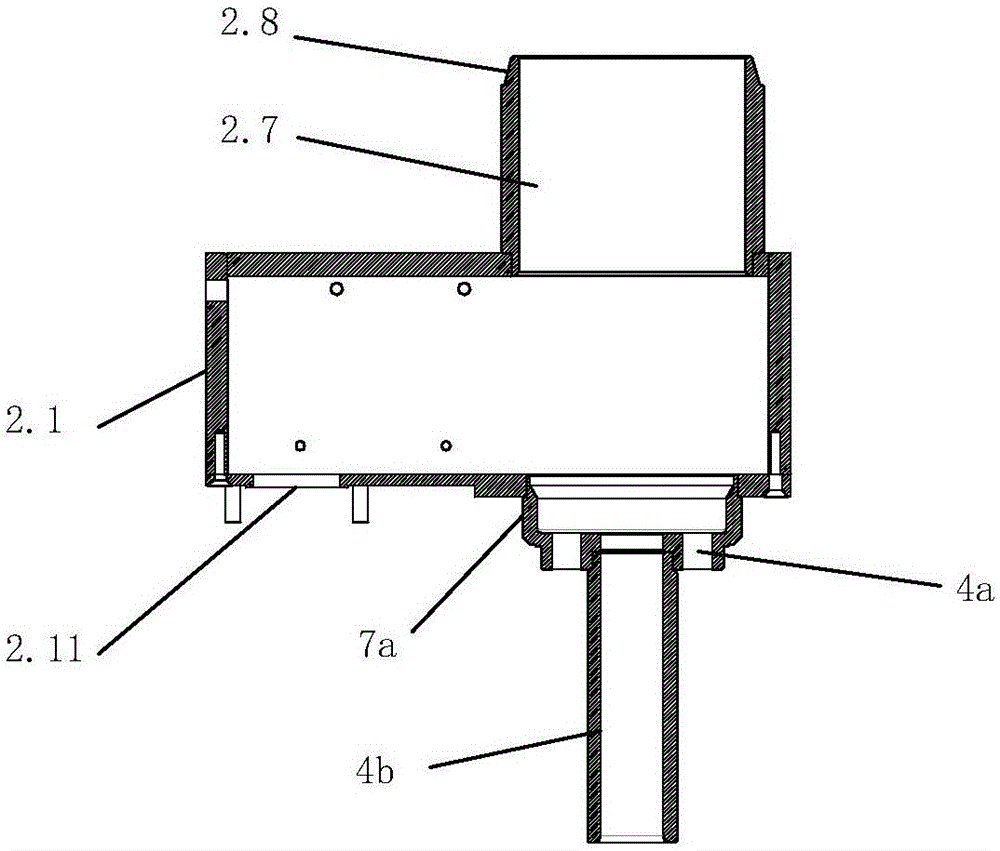
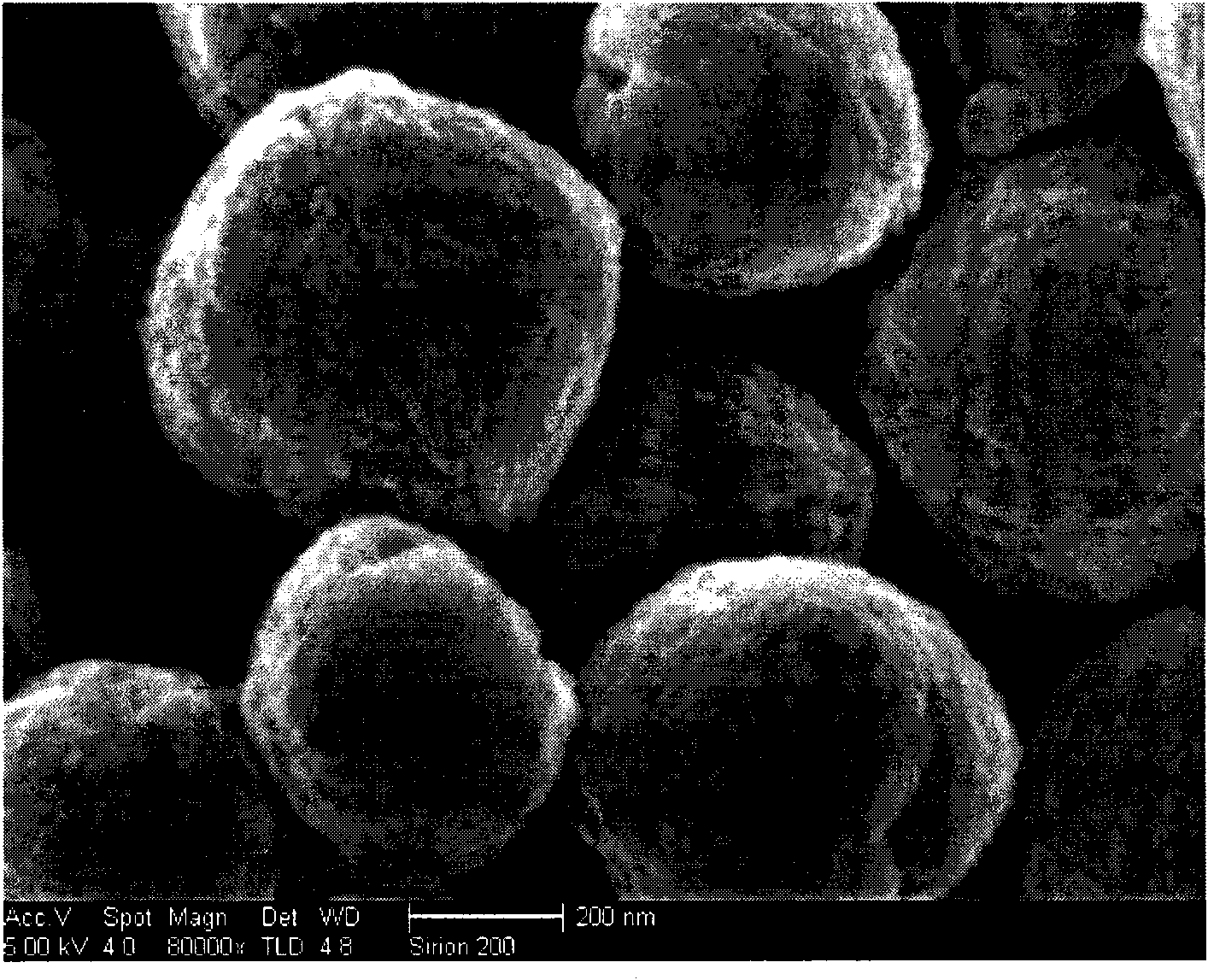Patents
Literature
126 results about "Microwave chemistry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microwave chemistry is the science of applying microwave radiation to chemical reactions. Microwaves act as high frequency electric fields and will generally heat any material containing mobile electric charges, such as polar molecules in a solvent or conducting ions in a solid. Polar solvents are heated as their component molecules are forced to rotate with the field and lose energy in collisions. Semiconducting and conducting samples heat when ions or electrons within them form an electric current and energy is lost due to the electrical resistance of the material. Microwave heating in the laboratory began to gain wide acceptance following papers in 1986, although the use of microwave heating in chemical modification can be traced back to the 1950s. Although occasionally known by such acronyms as MAOS (Microwave-Assisted Organic Synthesis), MEC (Microwave-Enhanced Chemistry) or MORE synthesis (Microwave-organic Reaction Enhancement), these acronyms have had little acceptance outside a small number of groups.
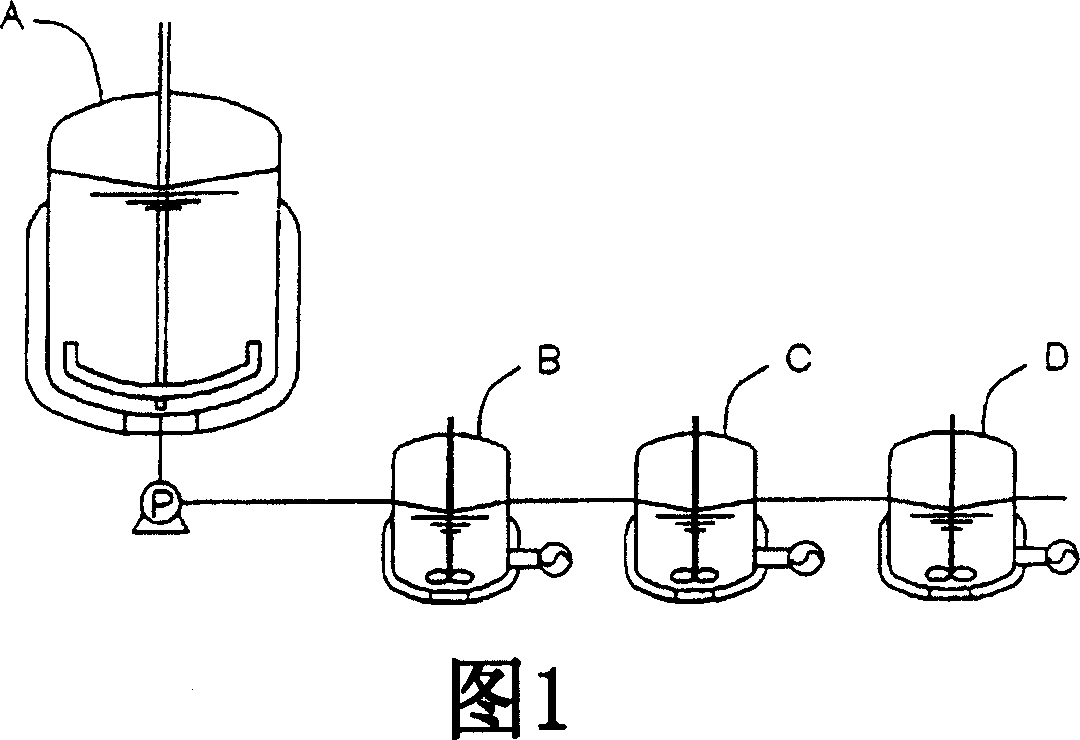
Directed microwave chemistry
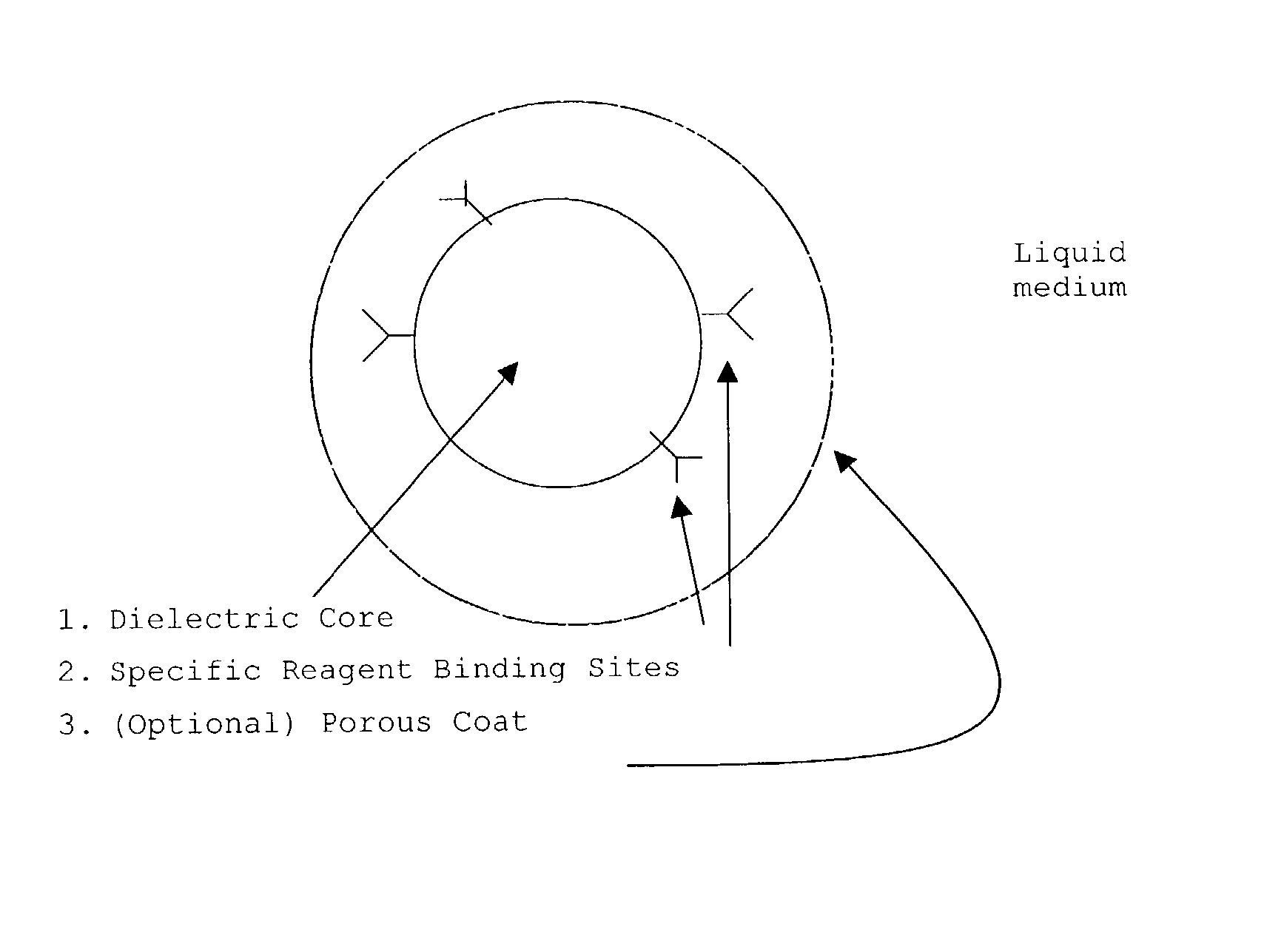
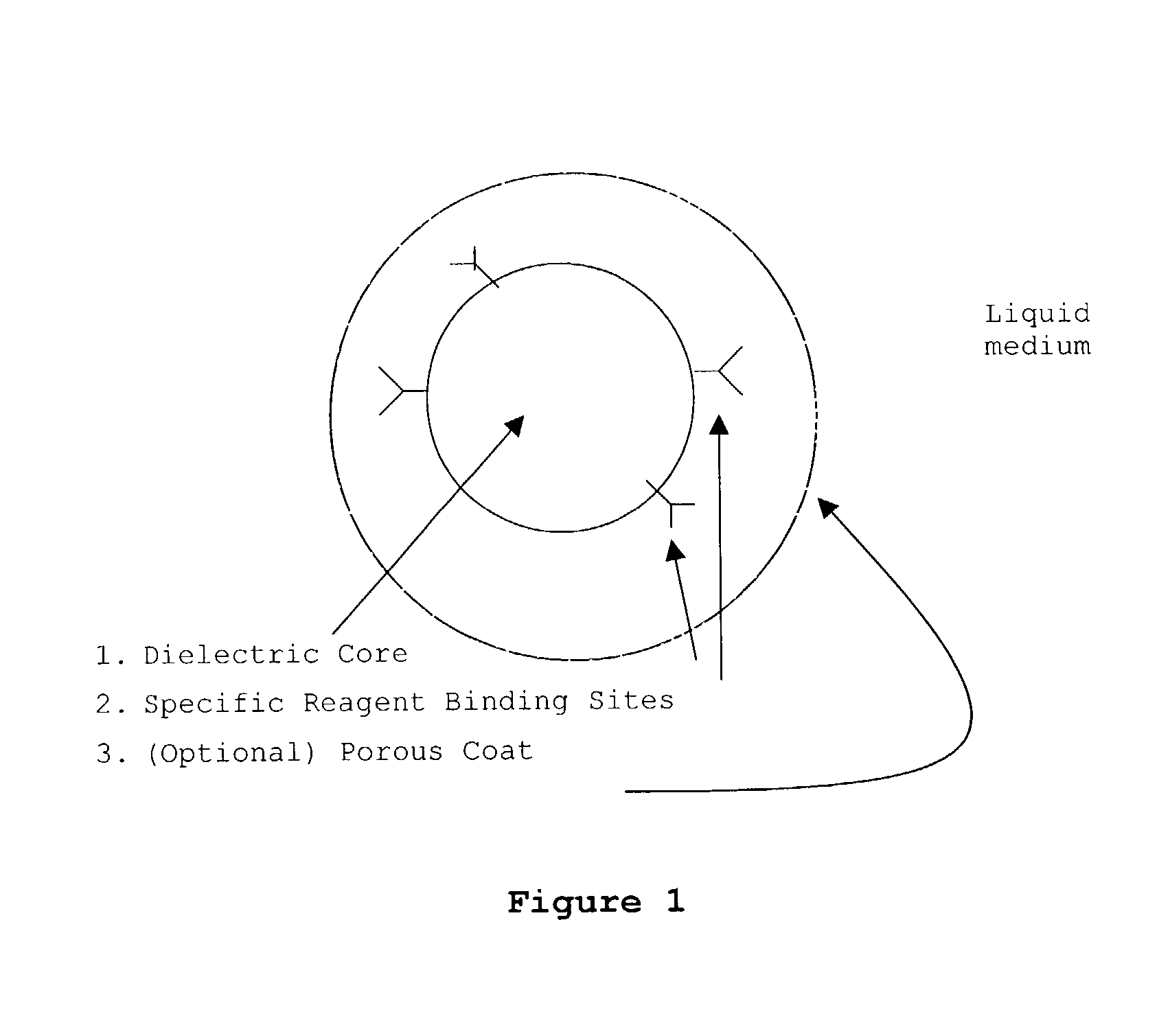
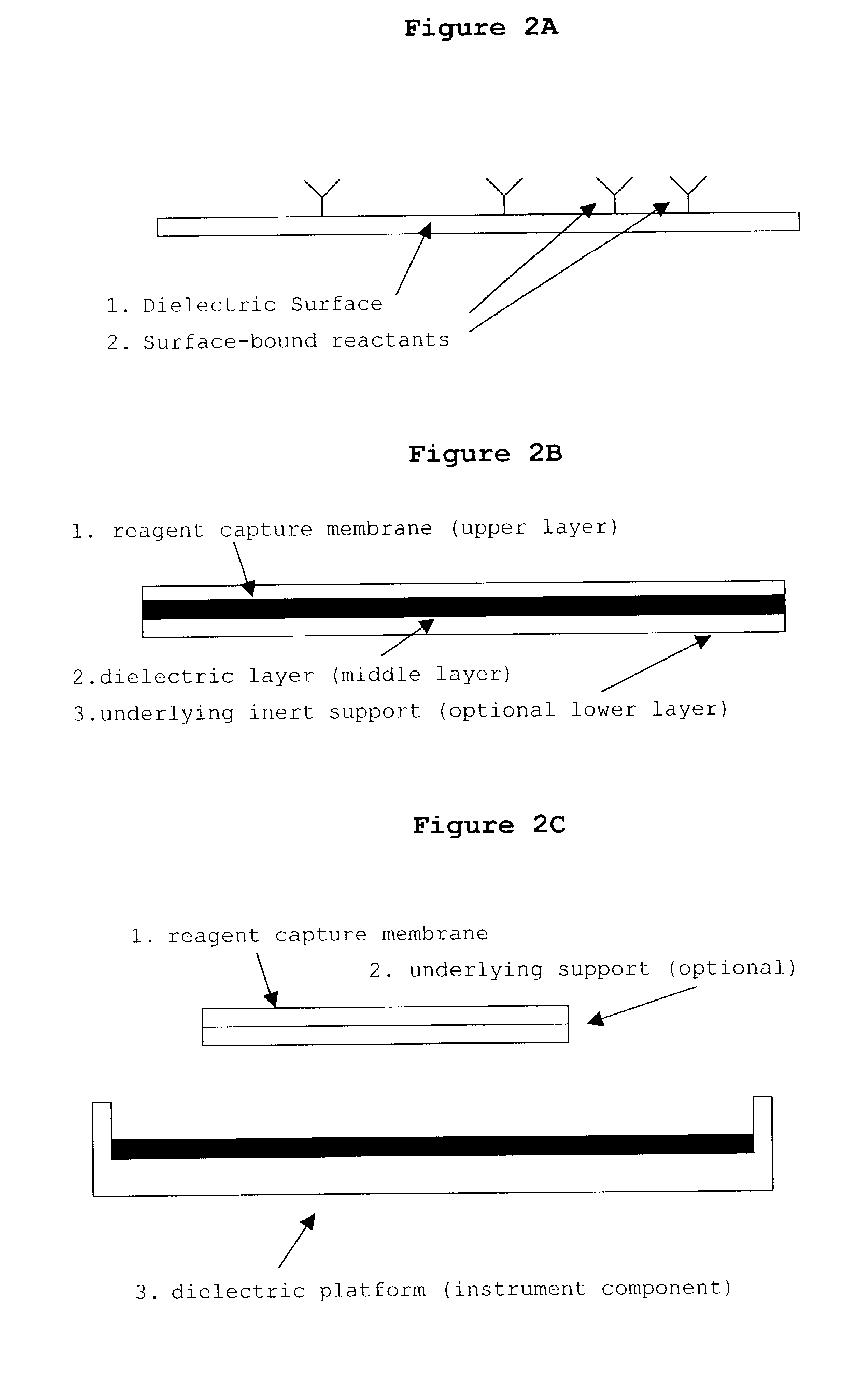
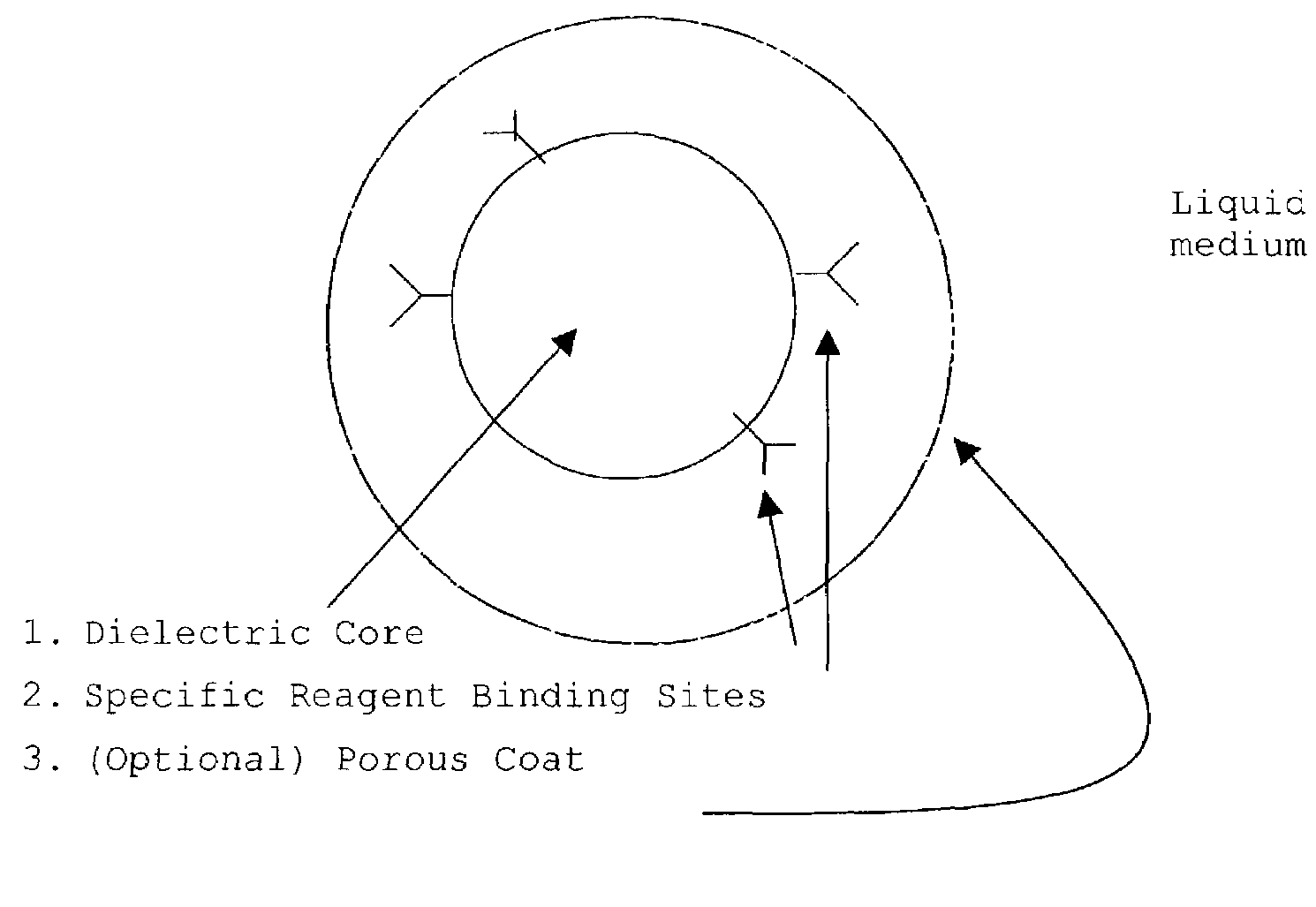
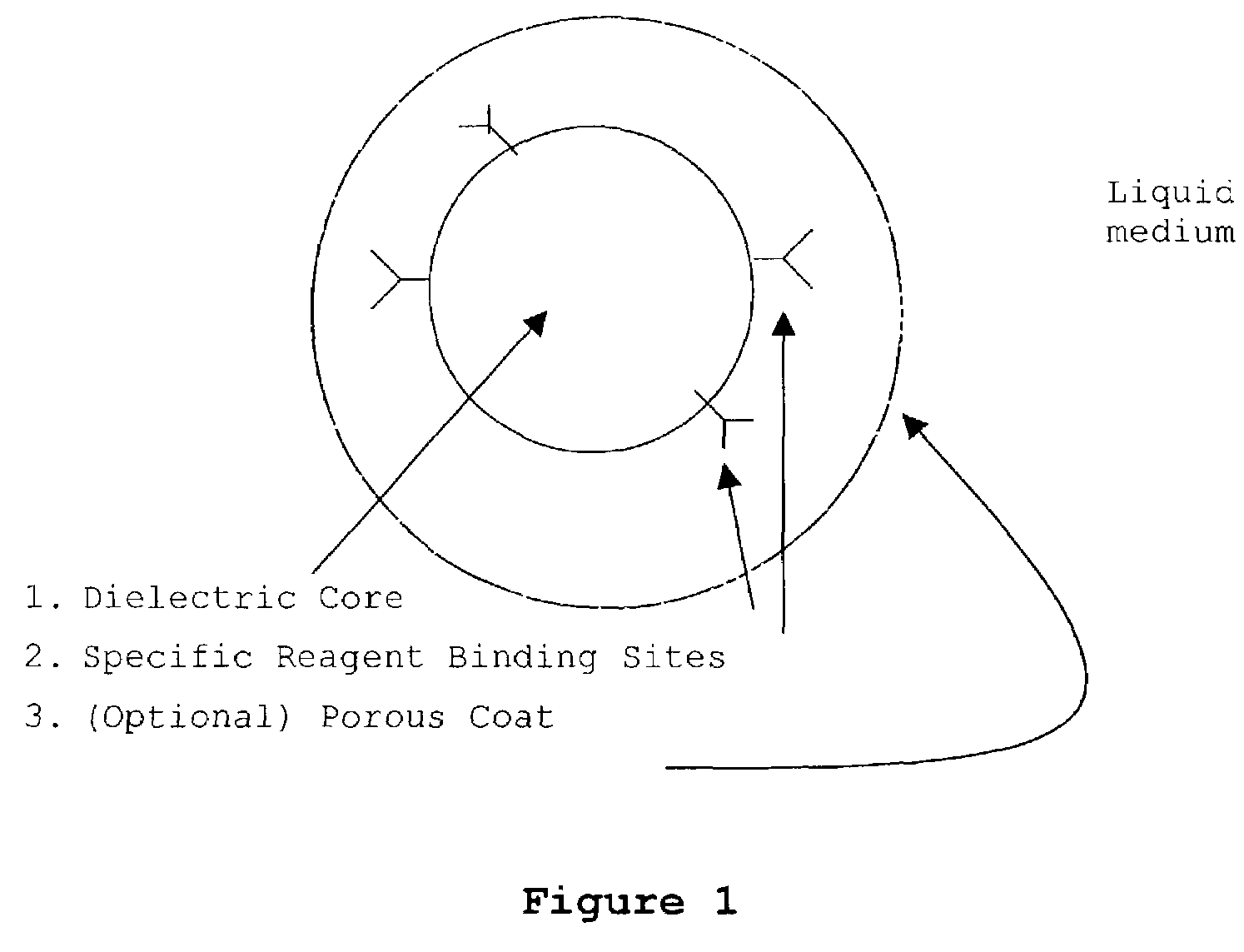
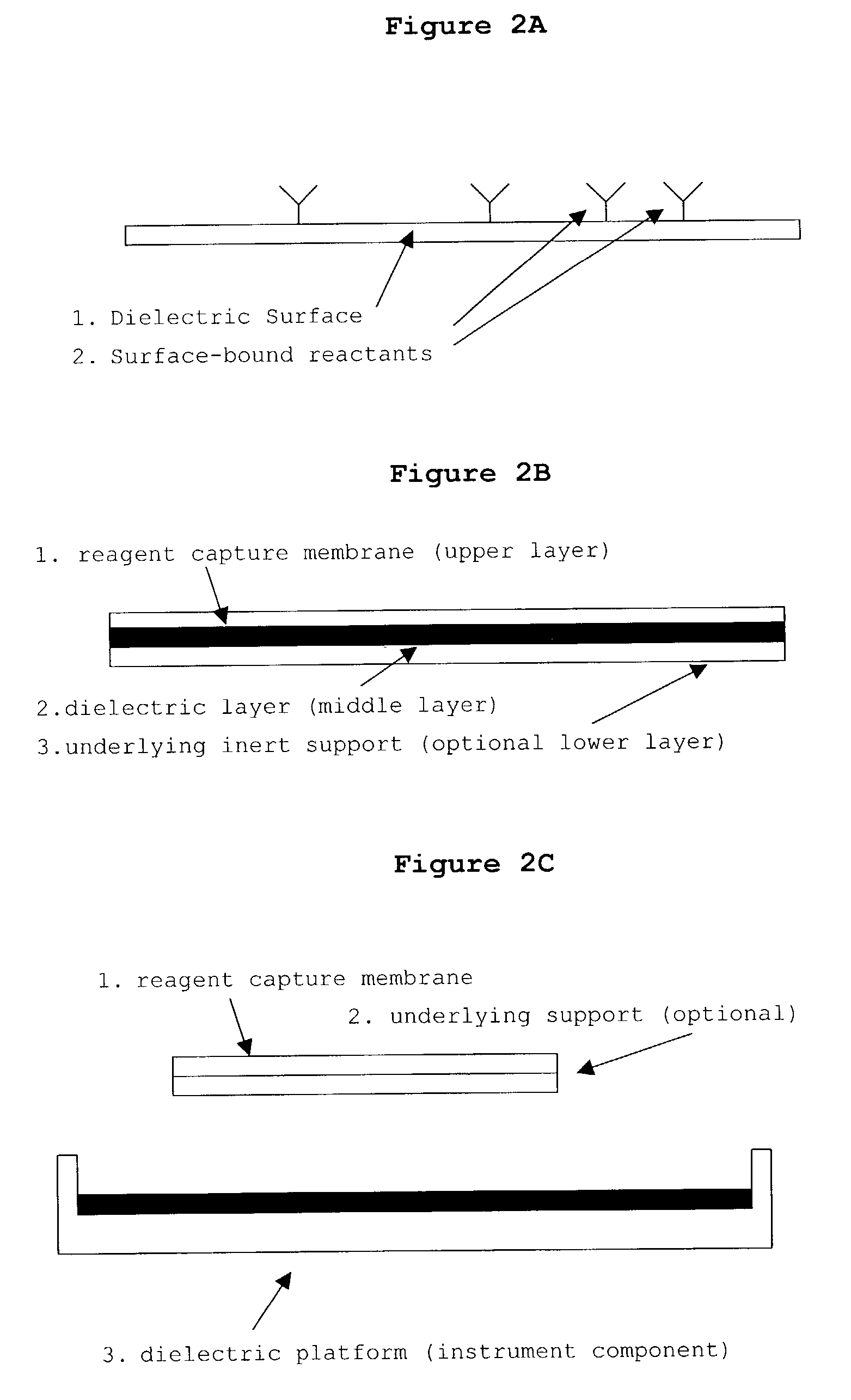
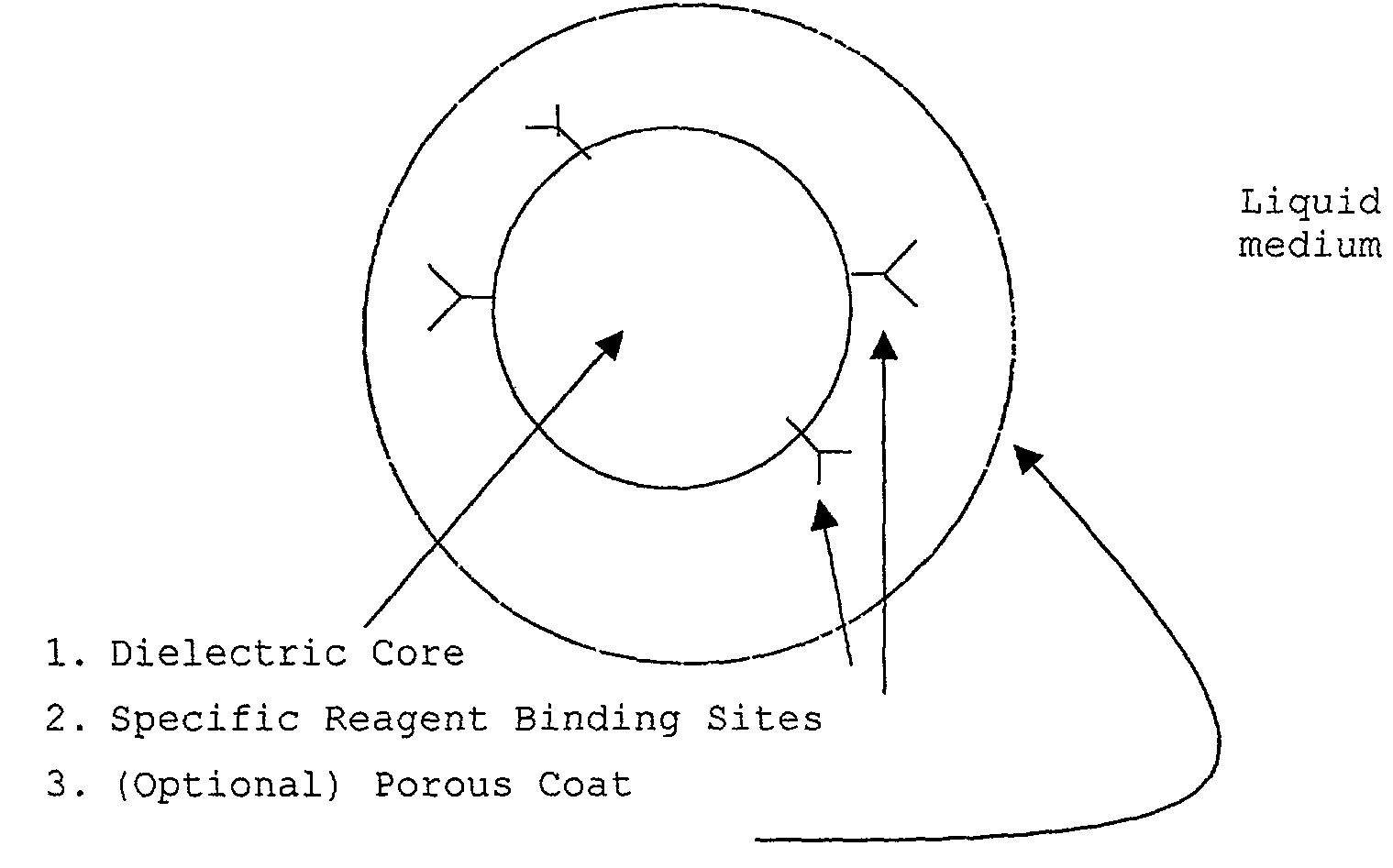
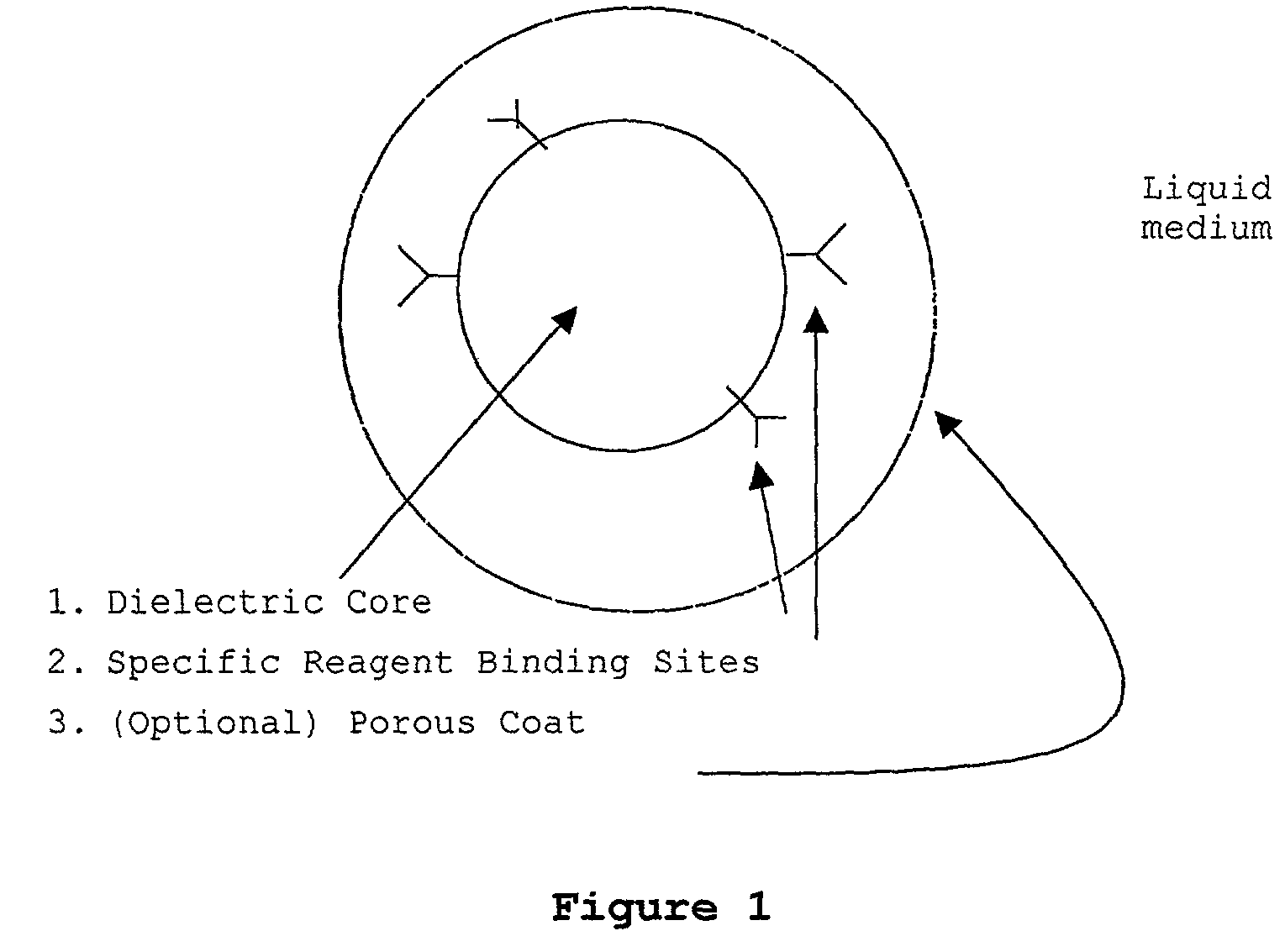
InactiveUS20030082633A1Promote resultsImprove adsorption capacityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsChemical reactionChemical transformation
The present invention concerns a novel means by which chemical preparations can be made. Reactions can be accelerated on special chips using microwave energy. The chips contain materials that efficiently absorb microwave energy causing chemical reaction rate increases. The invention is important in many small scale chemical transformations including those used in protein chemistry and in combinatorial chemistry.
Owner:MIRARI BIOSCI
Directed microwave chemistry
InactiveUS7348182B2Improve adsorption capacityFast bindingImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsChemical reactionChemical physics
The present invention concerns a novel means by which chemical preparations can be made. Reactions can be accelerated on special chips using microwave energy. The chips contain materials that efficiently absorb microwave energy causing chemical reaction rate increases. The invention is important in many small scale chemical transformations including those used in protein chemistry and in combinatorial chemistry.
Owner:MIRARI BIOSCI
Methods and compositions for directed microwave chemistry
InactiveUS7351590B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsArtificial enzymeChemical measurement
The present invention concerns a novel means by which specific chosen reactions can be accelerated through the use of a new type of artificial enzyme. The invention allows specific reactions to occur at an accelerated rate, even in the presence of other non-chosen molecules, which may be very similar in structure to the chosen reactant. The reactions may be stoichiometric or catalytic.
Owner:MILESTONE SRL
Methods and compositions for directed microwave chemistry
InactiveUS20020197645A1Facilitate decision-makingReduce chanceImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsArtificial enzymeChemical measurement
The present invention concerns a novel means by which specific chosen reactions can be accelerated through the use of a new type of artificial enzyme. The invention allows specific reactions to occur at an accelerated rate, even in the presence of other non-chosen molecules, which may be very similar in structure to the chosen reactant. The reactions may be stoichiometric or catalytic.
Owner:MILESTONE SRL
Preparation method of activated carbon material for electrochemical capacitor
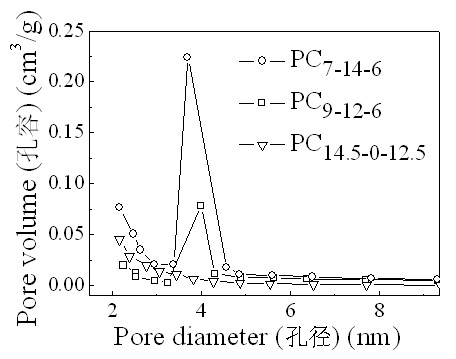
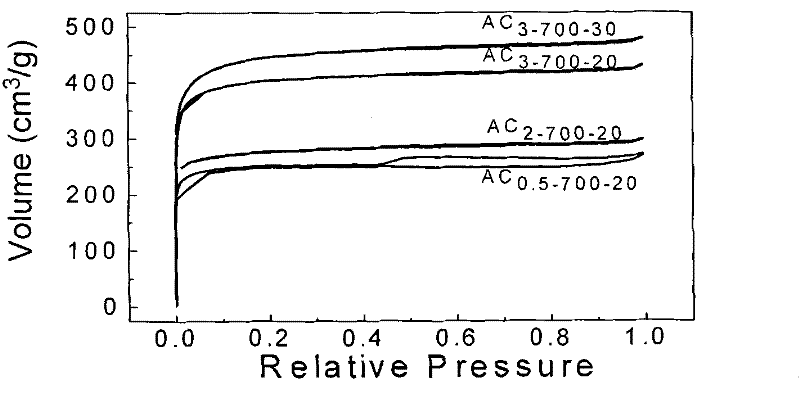
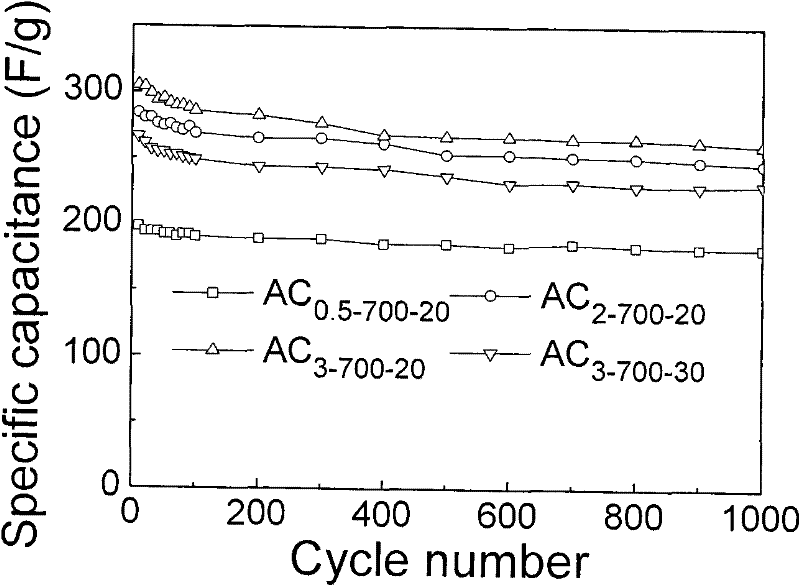
The invention discloses a preparation method of an activated carbon material for an electrochemical capacitor and belongs to the technical field of carbon material and microwave chemistry. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: using peanut shells as a raw material, processing the peanut shells by using a KOH solution and a potassium hydroxide alkali solution, transferring the peanut shells processed by the potassium hydroxide alkali solution into a corundum crucible, placing the corundum crucible into a microwave reactor for microwave heating and activation to obtain the activated carbon material for an electrochemical capacitor. According to the method, with peanut shells as a carbon source and potassium hydroxide as an activator, the activated carbon material is prepared by microwave-assisted heating of the potassium hydroxide activated peanut shells. The activated carbon material prepared by the preparation method is characterized in that its specific surface area is 990-1277m<2> / g, total pore volume is 0.47-0.63cm<3> / g, and the yield is 14.2-24.4%. The activated carbon material, which is prepared as an electrode material for an electrochemical capacitor, hasgood stability and excellent comprehensive performance.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing porous carbon material by using magnesium oxide template in cooperation with activation of potassium hydroxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing a porous carbon material by using a magnesium oxide template in cooperation with the activation of potassium hydroxide, and belongs to the technical field of carbon materials and microwave chemistry. The method comprises the following steps of: grinding coal tar pitch serving as a carbon source, nano magnesium oxide serving as a template and the potassium hydroxide serving as an activating agent; transferring the mixture to a corundum crucible; and putting into a microwave reactor, performing one-step microwave heating activation, and thus obtaining the porous carbon material for an electrochemical capacitor, wherein the specific surface area of the obtained porous carbon material is between 439 and 1,394m<2> / g, the total pore volume is between 0.23 and 0.94cm<3>, the average pore size is between 1.95 and 3.36mm, the ratio of the volume of a non-micro pore to the total pore volume is between 26.1 and 86.2 percent, and the porous carbon yield is between 37.8 and 84.9 percent. The invention has the advantages that: the method is quick and energy-saving; and the prepared porous carbon is used as an electrode material of the electrochemical capacitor and has extremely high stability and high comprehensive performance.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
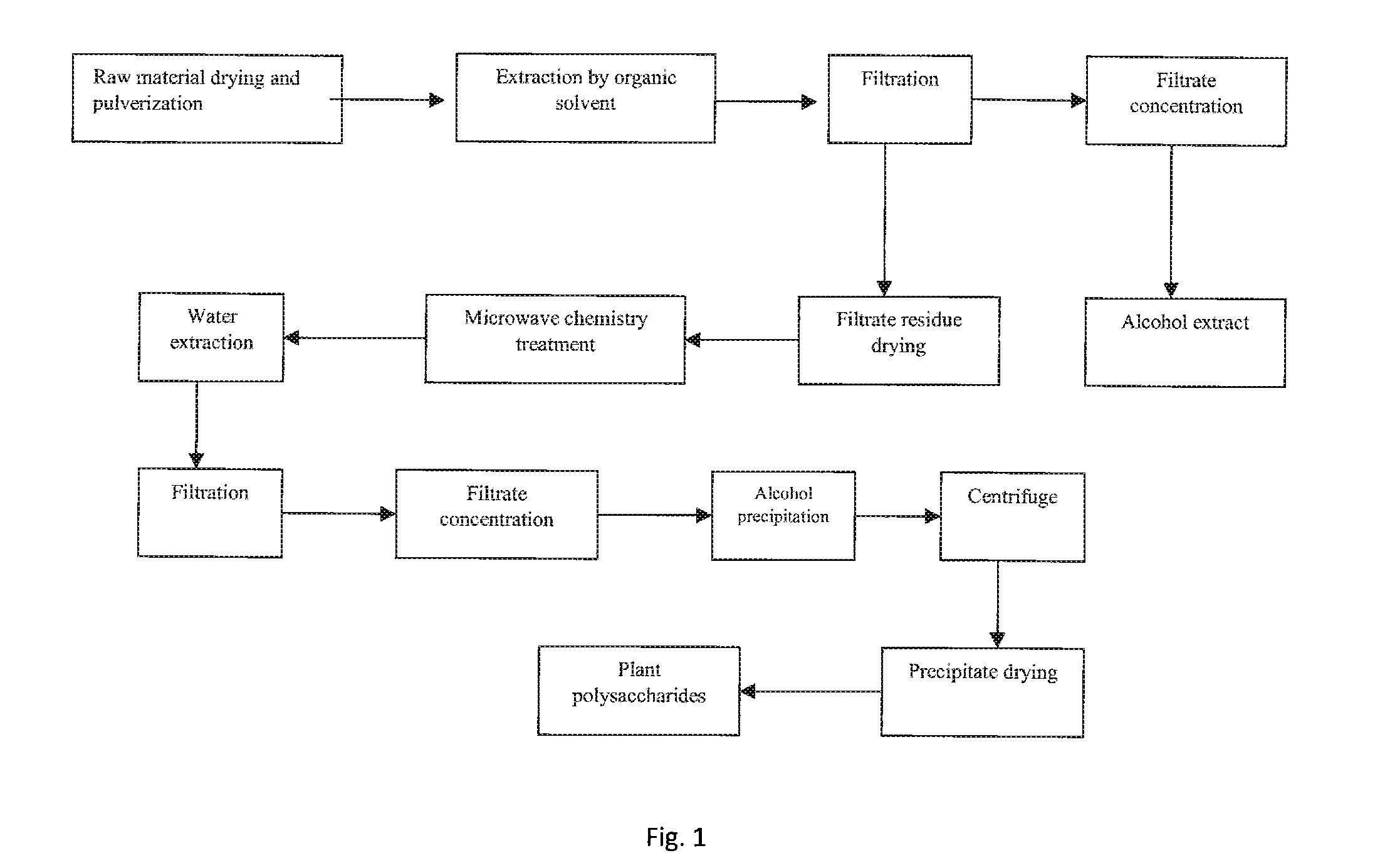
Method for extracting polysaccharides from higher plants and fungi through microwave chemical treatment
ActiveUS20140309414A1Evenly heatedHigh activitySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationChemical treatmentSolubility
This invention relates to a field of pharmaceutical chemistry, relates to a process of extracting high water soluble polysaccharides from higher plants or fungi. The present invention discloses a process of extracting higher plants and fungi polysaccharides based on a microwave chemistry method, comprising: putting the residue or pulverized higher plants and fungi after being degreased by an organic solvent into a microwave reaction chamber to react with an acid solution; and then distilling to remove excess acid or washing with organic solvent to remove the acid; adding water solution for extraction, subjecting the extracting solution after concentration to alcohol precipitation, separating precipitates aka polysaccharides therefrom.The present invention has significant advantages like fast processing rate, high polysaccharides yield, low organic acid consumption and efficient and easy to recycle, low water consumption, low power consumption, etc., and obtained polysaccharides have high yield and purity, good water solubility, and good biological activity.
Owner:SHENYANG KESI HIGH TECH
Microwave assisted molecular blotting magnetic microsphere preparation method and uses
InactiveCN101101282AUniform particle sizeParticle size controllableComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationCross-linkFunctional monomer
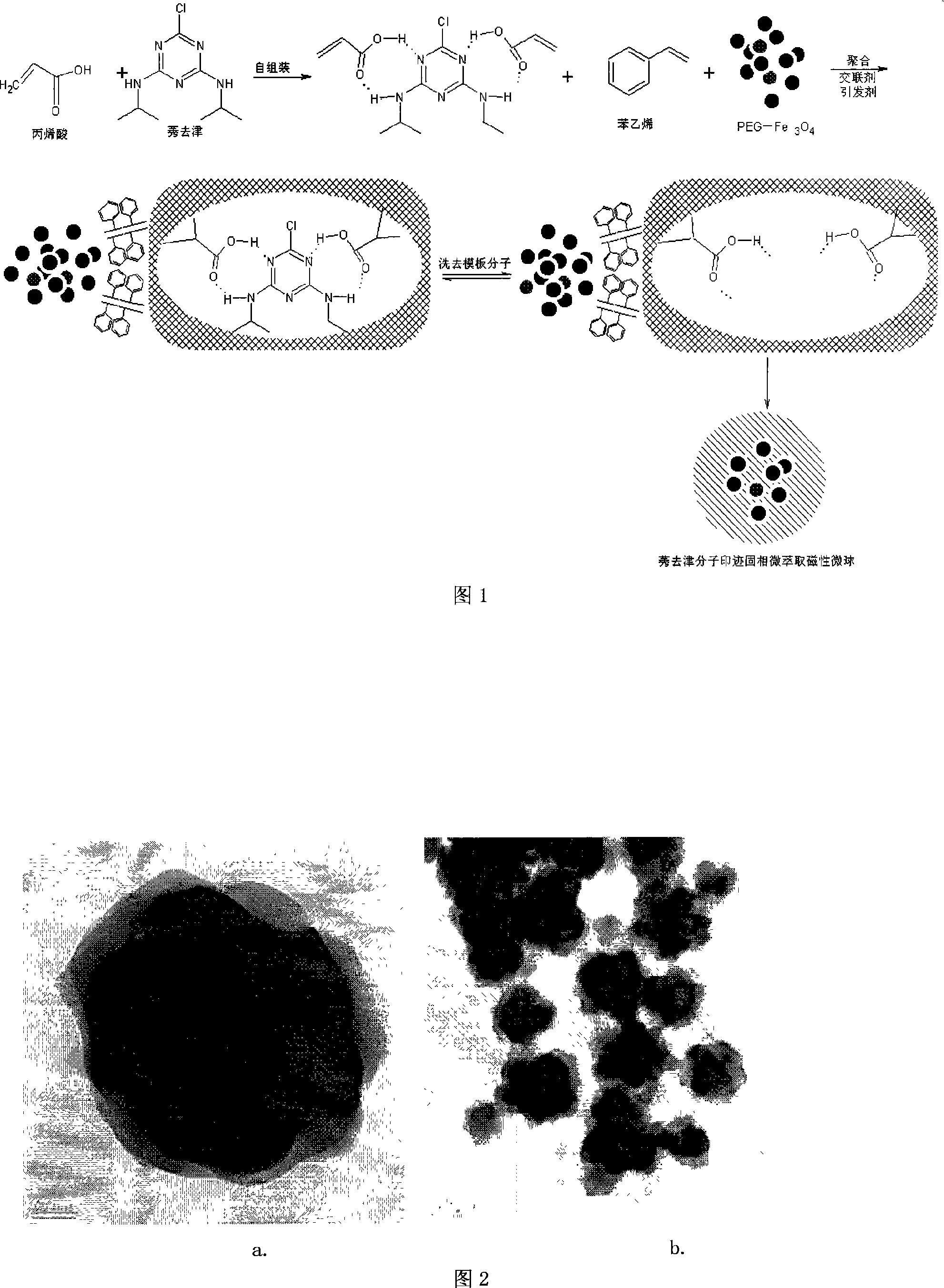
The invention belongs to the field of modern isolation analysis materials science and engineering, it relates to preparation method and application of microwave assistant molecular print magnetic microsphere, the procedure as follows: adopting microwave chemical reactor, taking nanometer magnetic fluid as magnetic nuclei, by cleaning and external modification, ultrasound detracting to water; mounted pattern molecule and functional monomer self-assembly; adding polymeric liquor by step, cross link agent and initiator, making it mixes and separates with magnetic fluid fully by stirring of machine, microwave procedure controlled temperature and heats up, until raising polymerization; Magnetic separates the foregoing magnetic microsphere, removing mounted pattern molecule, vacuum drying, aging. The molecular print magnetic microsphere has not only recognize ability of mounted pattern molecule and its analogue, but also has the approved characteristic of 'gathering hyphen recycle', the process of preparation heats up with microwave, decreasing the time of print aggregation, improving homogeneity and print efficiency of polymer form. The molecular print magnetic sphere applies to gather, isolate and analysis of structure analogue in the environmental sample, eatable etc complex samples.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
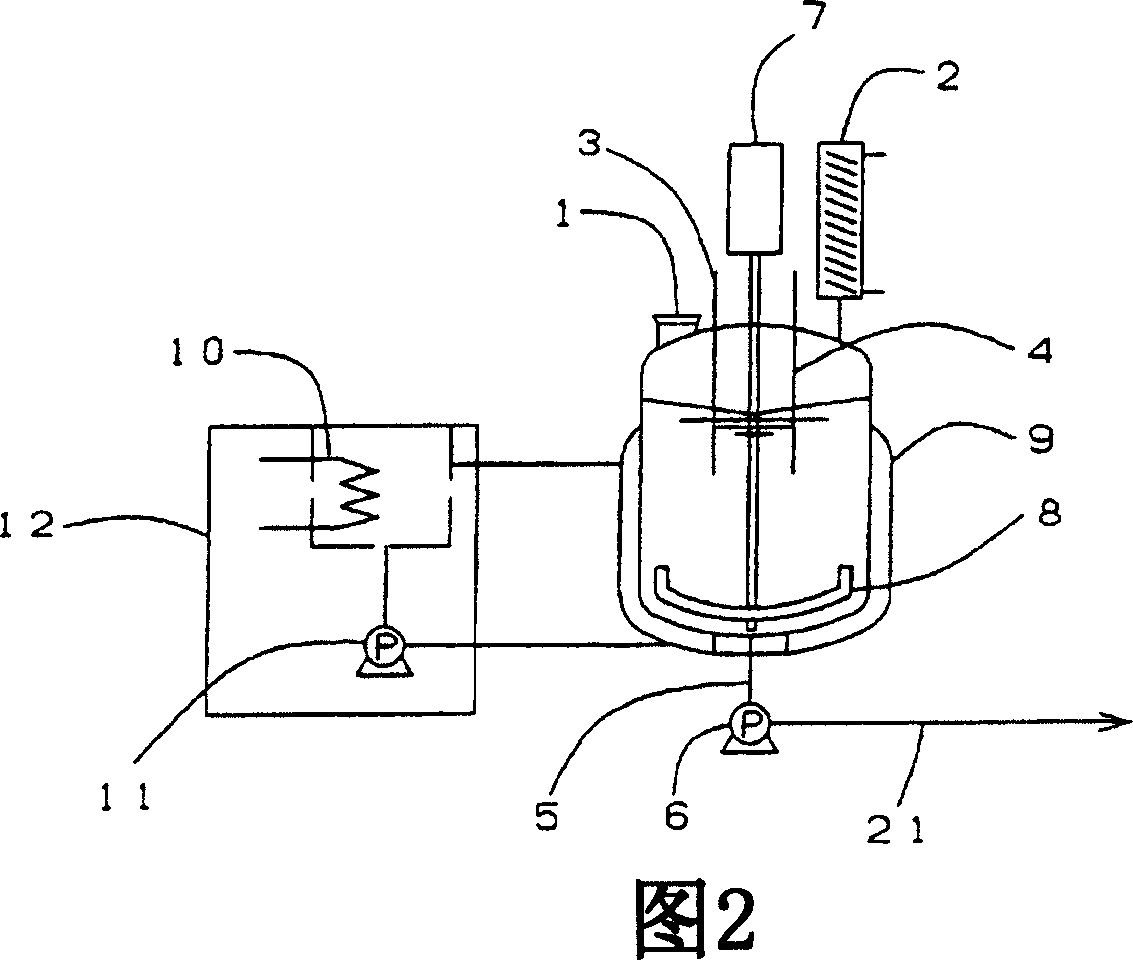
Chemical Reaction Apparatus Utilizing Microwave
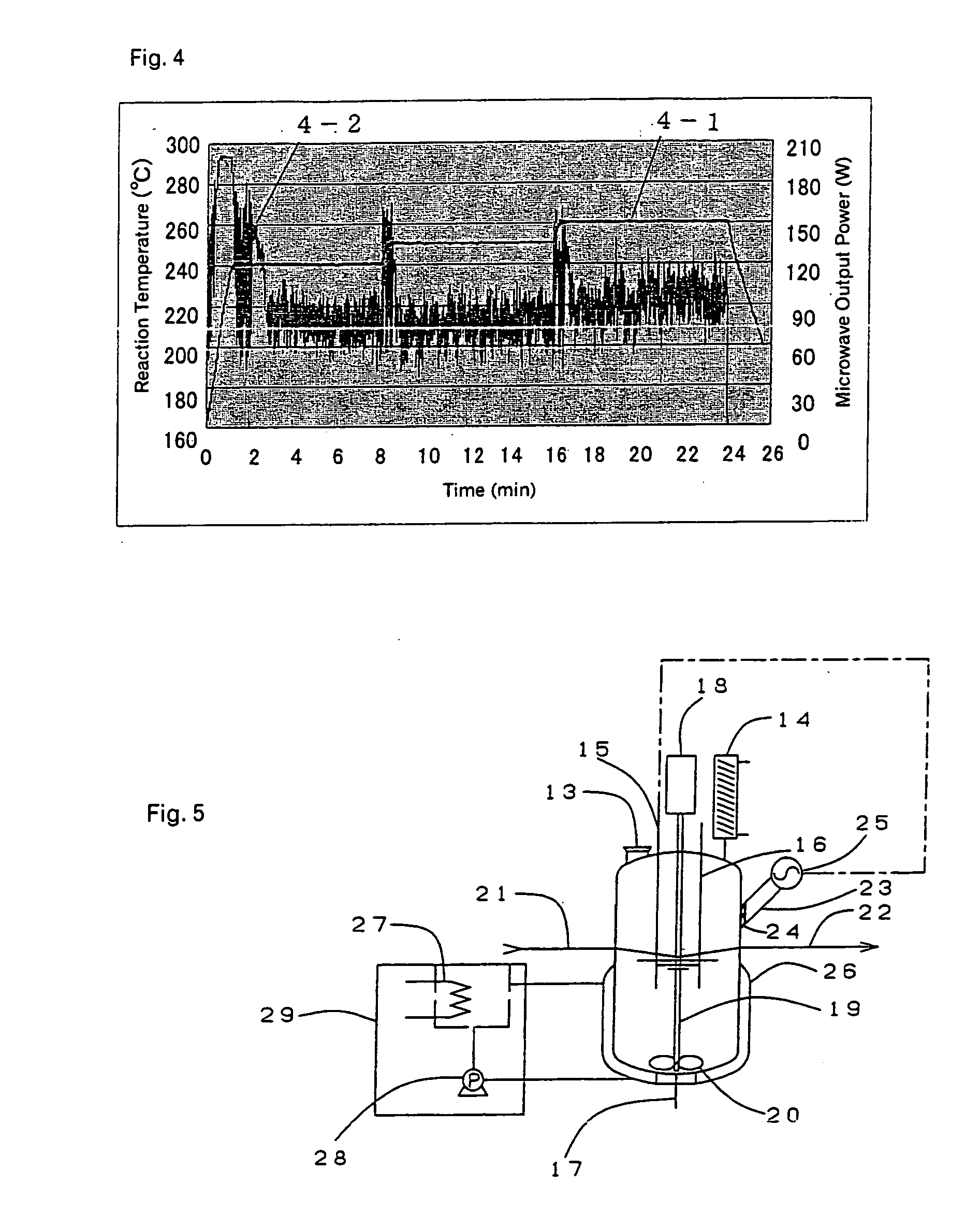
InactiveUS20070295717A1Efficient executionOrganic chemistry methodsDielectric heating circuitsTemperature controlChemical reaction
The present invention relates to a microwave chemical reaction apparatus characterized by comprising a means for heating a reaction liquid, which is capable of irradiating microwaves while controlling the output power according to the temperature of the reaction liquid, together with a means for forcibly cooling the reaction liquid from the outside, and being capable of precisely controlling the reaction temperature. The microwave chemical reaction apparatus can control the reaction temperature precisely, for example, within ±1° C. of a predetermined temperature, and can be applied to fine chemical reactions. Further, since reactions proceed rapidly in such an apparatus, mass production can be achieved by a relatively small-sized reaction apparatus.
Owner:SANKO CHEM CO LTD +2
Device and method for preparing activated carbon material for electrochemical capacitor
InactiveCN102205962AFacilitate the activation of pore formationAvoid temperature gradientsElectrolytic capacitorsPotassium hydroxideBiological activation
The invention provides a device and method for preparing an activated carbon material for an electrochemical capacitor, belonging to the technical fields of coal chemical industry and microwave chemistry. The method comprises the following preparation processes of: deashing coal particles serving as raw materials by using hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric acid, modifying the deashed coal by using nitric acid in an auxiliary way, mixing the modified coal serving as a carbon source with potassium hydroxide and deionized water, stirring to obtain a mixture, stirring and evaporating the mixture to obtain a solid mixture, and then performing microwave-assisted activating, washing, drying and grinding on the solid mixture to obtain the activated carbon. The invention has the advantages that the activation time is only 20-30 minutes, the mass ratio of potassium hydroxide to coal is (0.5-3):1, the preparation process is simple, the microwave-assisted heating is uniform, efficient and energy-saving, the consumption of the potassium hydroxide is reduced, and the activation process has the advantages of uniformity and high efficiency. The prepared activated carbon is used as an electrode material of the electrochemical capacitor and has better stability and excellent comprehensive property.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Chemical reaction apparatus utilizing microwave
InactiveCN1946477AEfficient responseOrganic chemistry methodsMicrowave heatingTemperature controlChemical reaction
Disclosed is a microwave chemical reaction apparatus comprising a means for heating a reaction solution, which is capable of irradiating the reaction solution with microwaves while controlling the output power according to the temperature of the reaction solution, and a means for forcibly cooling the reaction solution on the outside. The microwave chemical reaction apparatus is characterized by being capable of precisely controlling the reaction temperature. In this microwave chemical reaction apparatus, the reaction temperature can be controlled precisely, for example, within +-1 1 DEG C of a predetermined temperature, and thus this apparatus can be applied to precise chemical reactions. Since reactions proceed rapidly in such an apparatus, mass production can be achieved by a relatively small-sized reaction apparatus.
Owner:SANKO CHEM CO LTD +2
Preparation method of zinc oxide nanosphere
InactiveCN101920986AReduce the temperatureFriendly cleanNanostructure manufactureZinc oxides/hydroxidesMicrosphereReaction temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method of a zinc oxide nanosphere which fills a gap of the prior art on a zinc oxide microsphere / nanosphere. In the invention, the zinc oxide nanosphere is prepared by adopting a microwave chemical hydrothermal synthesis method, that is to say, the zinc oxide nanosphere is prepared by using an aqueous solution of simple zinc sources, such as zinc acetate, and the like and trolamine as a precursor solution through a microwave irradiation process. The preparation method of the zinc oxide nanosphere does not use any templates, additives and organic solvents, has a clean process, friendly environment, lower reaction temperature, and shorter reaction time, and microwave irradiation for 10 minutes at the temperature of 60 DEG C is enough, thereby saving energy sources with simplicity and high efficiency. The zinc oxide nanosphere product has even size distribution with the nanosphere diameter of 250-400nm, monodispersity, high production rate and low cost and is suitable for industrial production, and raw materials are easy to obtain.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV
Method for preparing mesoporous carbon material for electrochemical capacitor by using rice hulls as raw materials
The invention discloses a method for preparing a mesoporous carbon material for an electrochemical capacitor by using rice hulls as raw materials, and belongs to the technical field of carbon materials and microwave chemistry. The method comprises the following steps of: activating the hulls serving as a carbon source by using zinc chloride serving as an activating agent through microwave auxiliary heating to obtain the mesoporous carbon material in one step, wherein the specific surface area of the obtained mesoporous carbon material is between 1,409 and 1,738m<2> / g, the total pore volume is between 0.71 and 2.14cm<3> / g, the average pore size is between 1.99 and 6.08nm, the ratio of the volume of a non-micro pore to the total pore volume is between 66.2 and 99.5 percent, and the mesoporous carbon yield is between 30.4 and 37.0 percent. The method for preparing the mesoporous carbon material is simple, efficient and energy-saving; and the prepared mesoporous carbon material has a higher ratio of the volume of the non-micro pore to the total pore volume, and has extremely high quick charging and discharging performance when used as an electrode material of the electrochemical capacitor.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
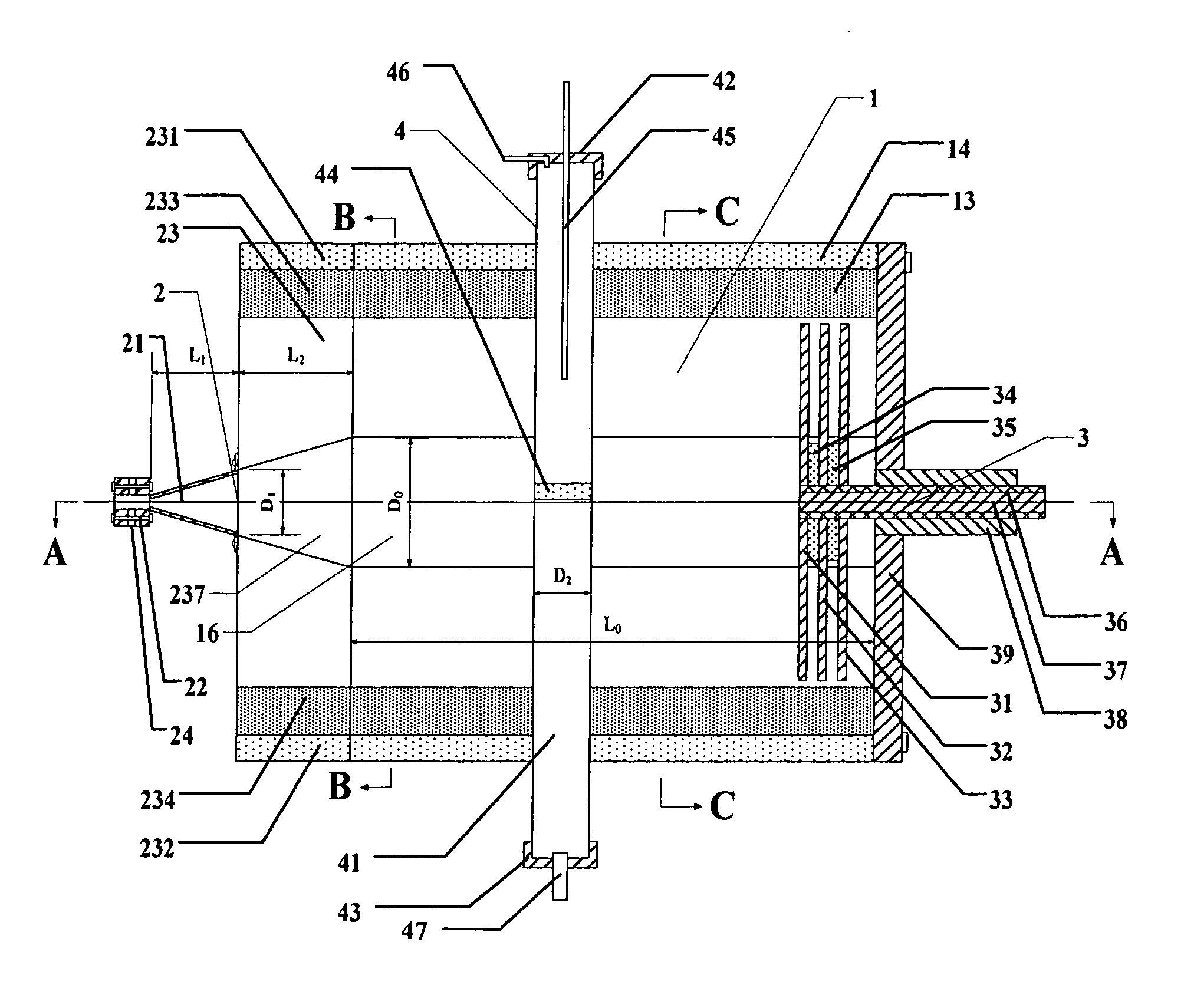
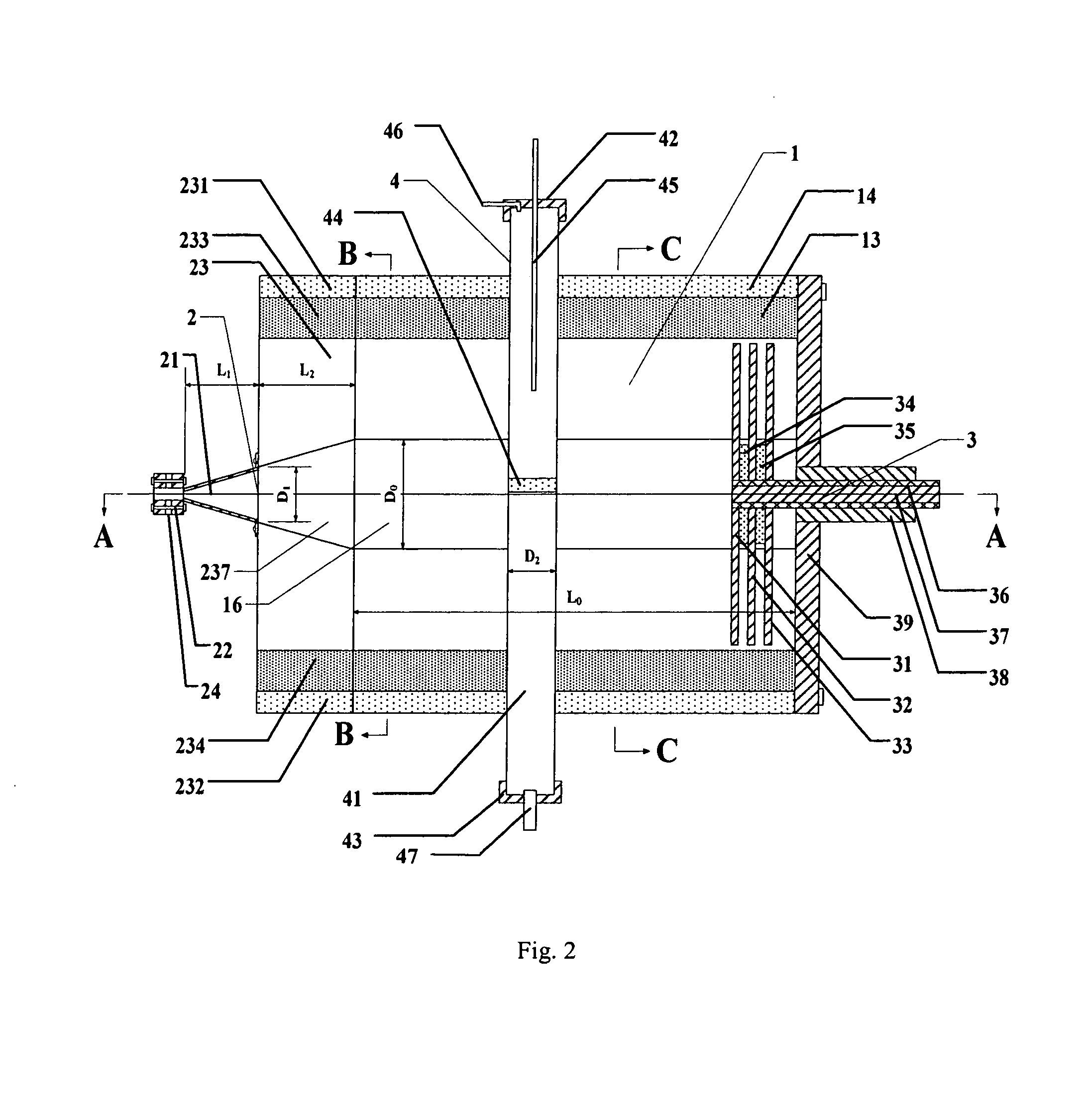
Recess waveguide microwave chemical plant for production of ethene from natural gas and the process using said plant
ActiveUS8337764B2Reduce pressureGlobal natural gas resources are relatively abundant.HydrocarbonsHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon condensationVena contracta diameterChemical reactor
Owner:YANG HONGSHENG +1
Microwave non-polar ultraviolet light catalyzing integrated reaction device
InactiveCN101239299AHigh removal rateEasy to control temperatureWater/sewage treatment by irradiationEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesHigh energyCooling chamber
The present invention provides a microwave electrodeless ultraviolet light catalytic integrated reacting device, relates to a reaction device of microwave-ultraviolet coupled system. The aim of the invention is to resolve the high energy consumption, low utilization rate of the microwave and ultraviolet light problems in the reaction device of microwave-ultraviolet coupled system. A cycle cooling collar (4) and a reactor (3) are baked into a integrity, a cycle cooling chamber (8) is formed between the cycle cooling collar (4) and the reactor (3), a lamp base (6) is fixed on the base board (3-1) of the reactor (3), an electrodeless ultraviolet light (5) is mounted on the lamp base (6), a double-layer reactor (1) is placed on the base board (2-1) of a microwave chemical experiment instrument (2), the side wall of the microwave chemical experiment instrument (2) has two openings (2-2). The invention can obtain higher difficult degradable organic removal rate under the short radiation time, the invention also has advantages of a controlled reaction system, adjustable light intensity of the ultraviolet lamp, a simple structure and easily promote, it also promotes the light catalyzing oxidizing water treating technology applied in the pratical project.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
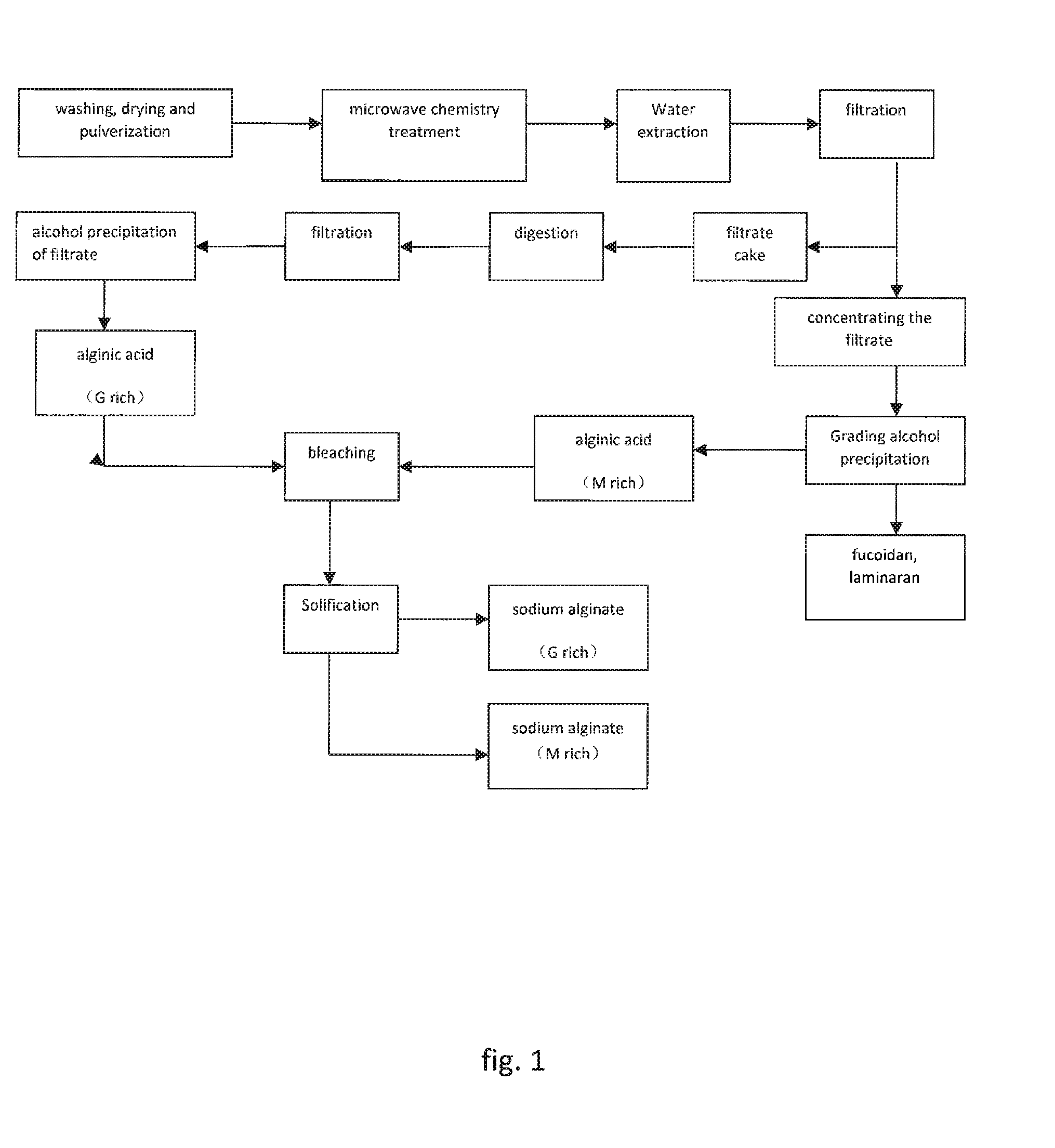
Method for extracting brown algae polysaccharide via microwave chemical process
ActiveUS20140296496A1Narrow molecular weight distributionHigh puritySugar derivativesImmunological disordersDigestionDrug biological activity
This invention relates to an extraction process of brown algae polysaccharides in a field of pharmaceutical chemistry. This invention particularly discloses a process of extracting brown algae polysaccharides based on a microwave chemistry method and brown algae polysaccharides obtained by said process. The process of the invention comprises: 1) putting pulverized brown algae powder into a microwave reaction chamber, adding acid solution to conduct reaction; optionally concentrating the mixer, and then washing with organic solvent to remove excess acid; conducting grading alcohol precipitation after water extract to obtain mannuronic acid rich fragment (M rich) algin, fucoidan and / or laminaran respectively; and adding an alkali solution to the brown algae residue to conduct alkaline digestion, filtering the residue off, adjusting pH of the filtrate to neutral, conducting alcohol precipitation to obtain guluronic acid rich fragment (G rich) algin precipitates. The present invention has significant advantages like fast processing rate, high yield of polysaccharides, strong controllable polysaccharide degradation, using less organic acid and efficient recovery, small water consumption, low power consumption, etc., the active polysaccharides has high yield and content, better water-soluble, and good biological activities.
Owner:SHENYANG KESI HIGH TECH
Method for microwave chemical modification treatment of wool
InactiveCN101671949ASimple processReduce pollutionPhysical treatmentAnimal fibresAcid dyeThermal water
The invention relates to a method for microwave chemical modification treatment of wool, which comprises: the wool is immersed in finishing liquid containing a chemical finishing agent for 20 to 40 minutes, is immersed twice and rolled twice, wherein the take-up ratio is from 70 to 120 percents, microwave irradiates 1 to 6 minutes, the power is from 300 to 700 W, and the wool is sufficiently washed by hot water of 50 to 60 DEG C, and dried. The invention has simple technology, energy source saving and environmental pollution reduction or prevention, and is suitable for industrial production. The wool after the modification processing of the invention can greatly improve the dyeing performance of wool-use active dyes and acid dyes on wool.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Self-relieving chemical reaction kettle capable of being suitable for microwave working environment
ActiveCN104056584AGuaranteed tightnessGuaranteed accuracyPreparing sample for investigationEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesChemical reactionWorking environment
The invention discloses a self-relieving chemical reaction kettle capable of being suitable for microwave working environment, belonging to the field of analytical instruments. The self-relieving chemical reaction kettle comprises a sleeve and a sample dissolving cup, and is characterized in that a sealing cover is arranged at the top of the sleeve, an exhaust cavity is arranged inside the sealing cover, a plurality of exhaust holes are formed in the top surface of the sealing cover, a first detachable connecting structure is arranged between the lower end of the sealing cover and the top of the sleeve, a sealing plug with a center pressure guiding hole is arranged at the upper end of the sample dissolving cup, the sealing plug is arranged between the top of the sample dissolving cup and the lower end of the sealing cover, a relieving module is arranged at the upper end of the sealing cover; the relieving module comprises a choke plug, a spring casing, a movable block, a spring and a cap which are sequentially arranged; the choke plug is of an inverted U-shaped structure with an upward opening and an inner cavity, and the spring casing, the movable block, the spring and the cap are sequentially sleeved in the inner cavity of the choke plug. Through arranging the sealing plug and the relieving module, the self-relieving function of a digestion tank is realized; the self-relieving chemical reaction kettle can be widely applied to the fields of design and manufacture of microwave chemical digestion equipment.
Owner:PREEKEM SCI INSTR
Method for preparing mesoporous carbon material for electrochemical capacitor
ActiveCN102424383ACarbon savingCarbon source is easy to getWaste processingSolid waste disposalPhosphoric acidEnergy conservation
The invention provides a method for preparing a mesoporous carbon material for an electrochemical capacitor, and belongs to the technical fields of carbon materials and microwave chemistry. In the method, peanut shells are taken as a carbon source, zinc chloride or phosphoric acid is taken as an activating agent, and the mesoporous carbon material is prepared by one step of activating the peanut shells through microwave-assisted heating; and the obtained mesoporous carbon material has the specific surface area of between 1,307 and 1,552m<2> / g, the total pore volume of between 0.67 and 1.83cm<3> / g, and the average pore size of between 2.06 and 5.02nm; non-micropore volume is 62.7 to 99.2 percent of the total pore volume; and the yield is 32.3 to 44.9 percent. The carbon source is a renewable agricultural waste, and has the characteristics of low price and high availability; the microwave heating has the advantages of uniformity, quickness and energy conservation; and the obtained mesoporous carbon serves as a material for the electrochemical capacitor, and has high stability and excellent comprehensive properties.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
High pressure visible micro wave chemical reaction device
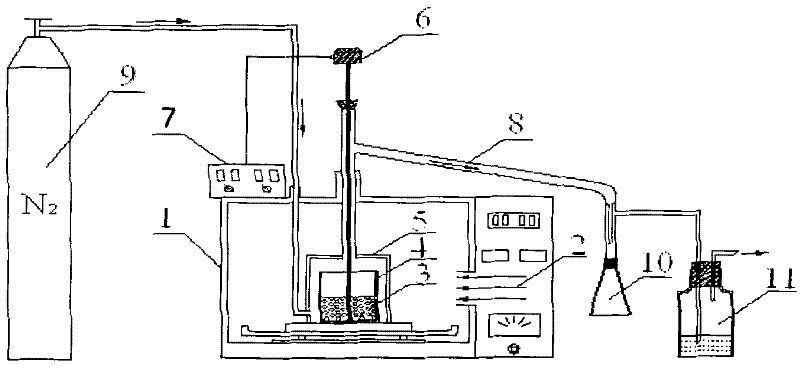
InactiveCN1555912AUnique heating performanceUniform temperature fieldEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesChemical reactionSteel jacket
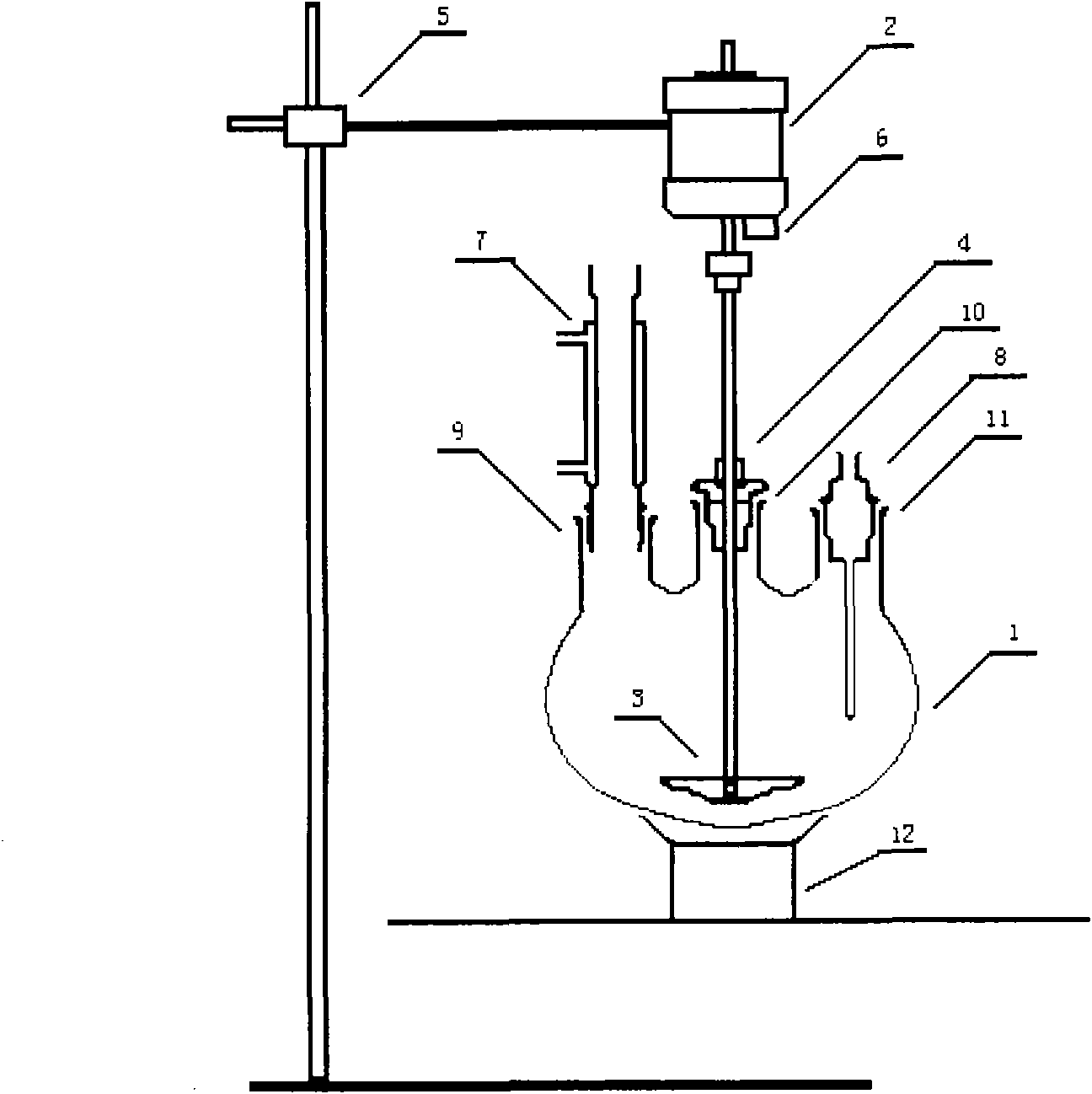
A visual high-pressure microwave heating chemical reactor is composed of microwave generating / controlling / transmitting system, chemical reactor, constant-temp system and reactive gas I / O and metering system. Said chemical reactor consists of stainless steel jacket, protecting stainless steel rings, high pressure resistant glass cylinder, high pressure resistant microwave guide and enclosing head.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microwave chemical reaction device using dielectric radiator
InactiveCN101518722AImprove uniformityReduce interferenceEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesDielectricChemical reaction
The invention provides a microwave chemical reaction device using a dielectric radiator, which comprises a reaction vessel and a microwave energy transmission system. The microwave energy transmission system comprises the dielectric radiator and a wave guide, wherein the dielectric radiator passes through the wall of the reaction vessel and extends into the reaction vessel; and the dielectric radiator is connected with a microwave source through the wave guide. The number of the microwave energy transmission systems is determined by the power and volume of the microwave chemical reaction device; for the microwave chemical reaction device with small power and volume, the microwave energy transmission systems can be one set or two sets, and for the microwave chemical reaction device with large power and volume, a plurality of independent microwave energy transmission systems can be arranged. When the microwave energy transmission systems are more than two sets, the position of the dielectric radiator in each set of the microwave energy transmission system in the reaction vessel can make energy coupling of the dielectric radiator and the other dielectric radiators in all microwave energy transmission systems be less than or equal to -10 dB.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Microwave chemical reactor
ActiveCN101579617AEasy to addEasy to condenseEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesMicrowave ovenConstant power
The invention relates to a microwave chemical reactor suitable for various laboratories. By modifying a household microwave oven, the reactor mainly comprises two parts, namely a measurement and control part for various parameters, and a power supply instrument part of a chemical reactor and the microwave chemical reactor. The microwave chemical reactor has the following performance: power is continuously adjustable; different levels of constant power is output; constant temperature is controlled; a mechanical agitator can adjust the speed and display the stirring speed; the microwave power is displayed, energy in the furnace chamber of the microwave oven is evenly distributed, and all the parameters in the reaction process are sampled and recorded by a computer.
Owner:溧阳常大技术转移中心有限公司
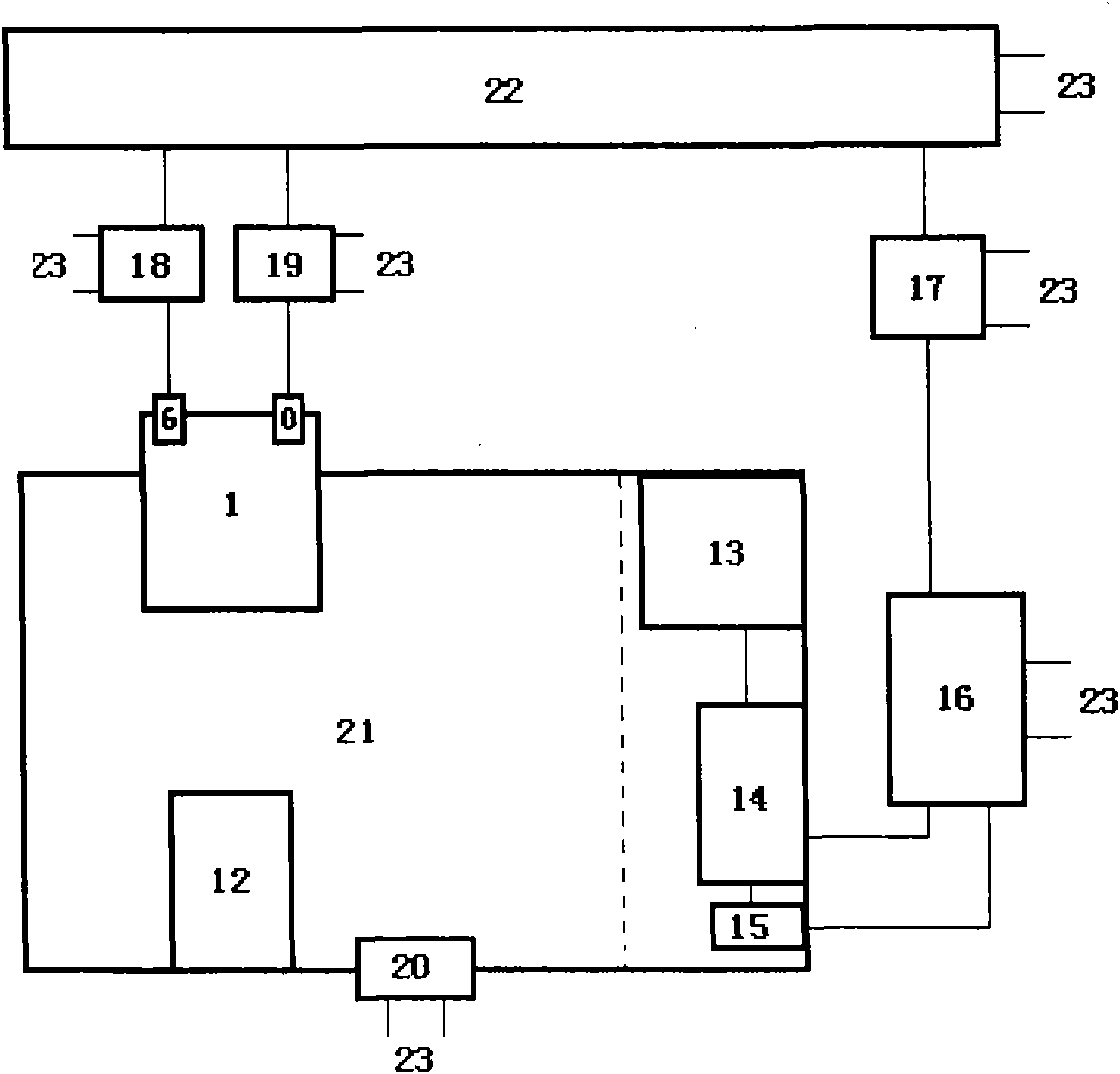
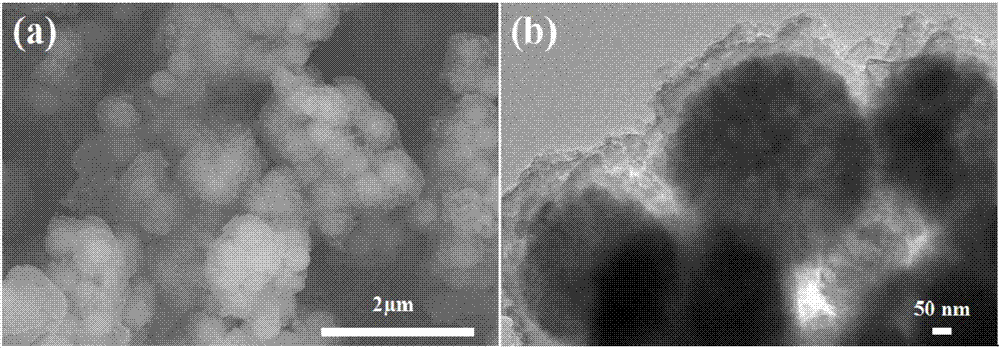
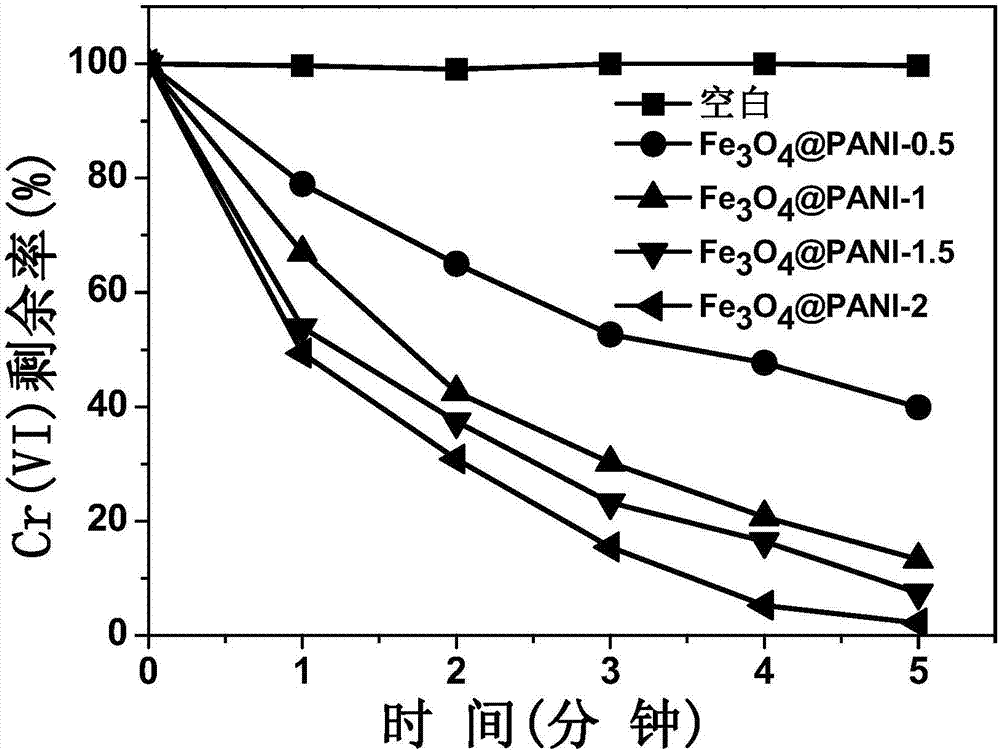
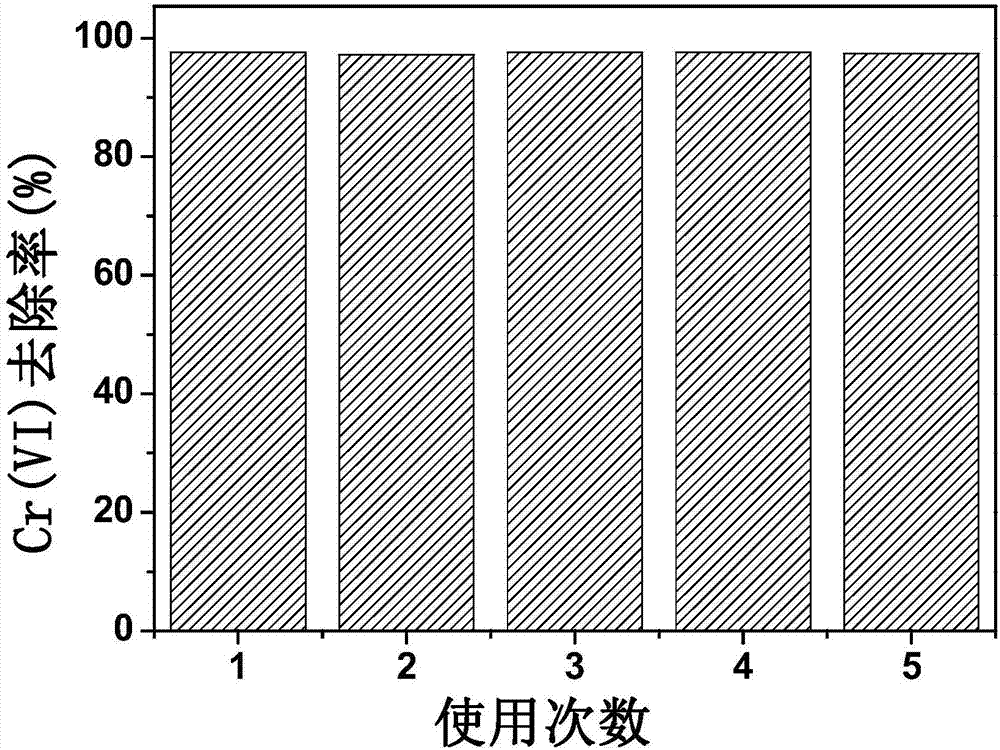
Method for efficiently reducing hexavalent chromium in water by magnetic electric conduction macromolecule synergistic microwave
ActiveCN107352730AImprove recovery rateHigh degree of automationWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentMagnetic separationMagnet
The invention belongs to the field of heave metal waste water, and particularly relates to a method for efficiently reducing hexavalent chromium in water by magnetic electric conduction macromolecule synergistic microwave. The method comprises the following steps that: regulating waste water which contains the hexavalent chromium by inorganic acid or small molecular organic acid to obtain solution of which the pH (Potential of Hydrogen) is acidic; adding a magnetic electric conduction macromolecule material of a nuclear shell structure; after even mixing, transferring to a microwave chemical reactor to react, reducing the hexavalent chromium in the waste water into trivalent chromium, and then, carrying out separation and recovery on the magnetic electric conduction macromolecule material by a permanent magnet; utilizing the magnetic electric conduction macromolecule to effectively adsorb the surface enrichment of the hexavalent chromium and microwave energy, and realizing the efficient reduction of the high-toxicity hexavalent chromium in a microwave field. Compared with other technologies, the method has an obvious kinetic advantage; the regeneration of the magnetic electric conduction macromolecule can be realized by the microwave, and a magnetic separation and recovery material can be recycled. The method is simple, efficient and easy in industrialization and has an obvious economic and environment benefit.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
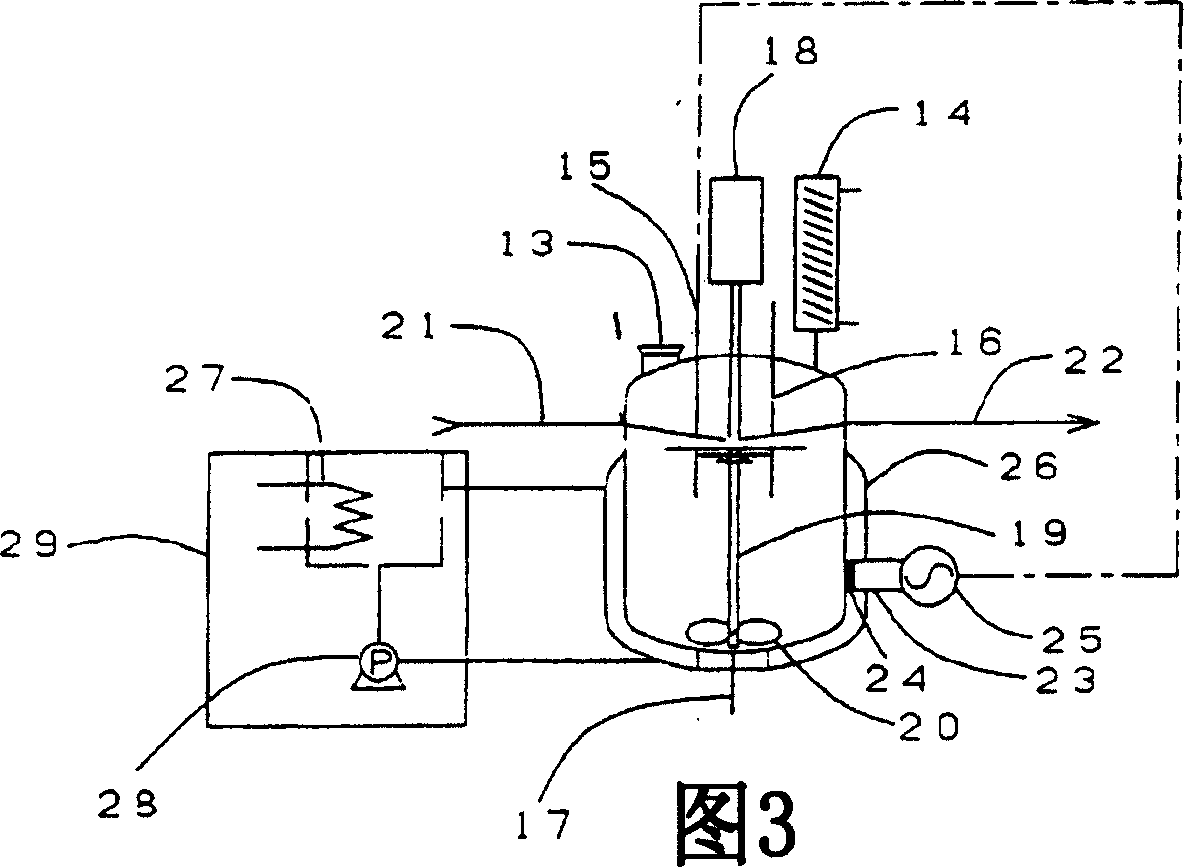
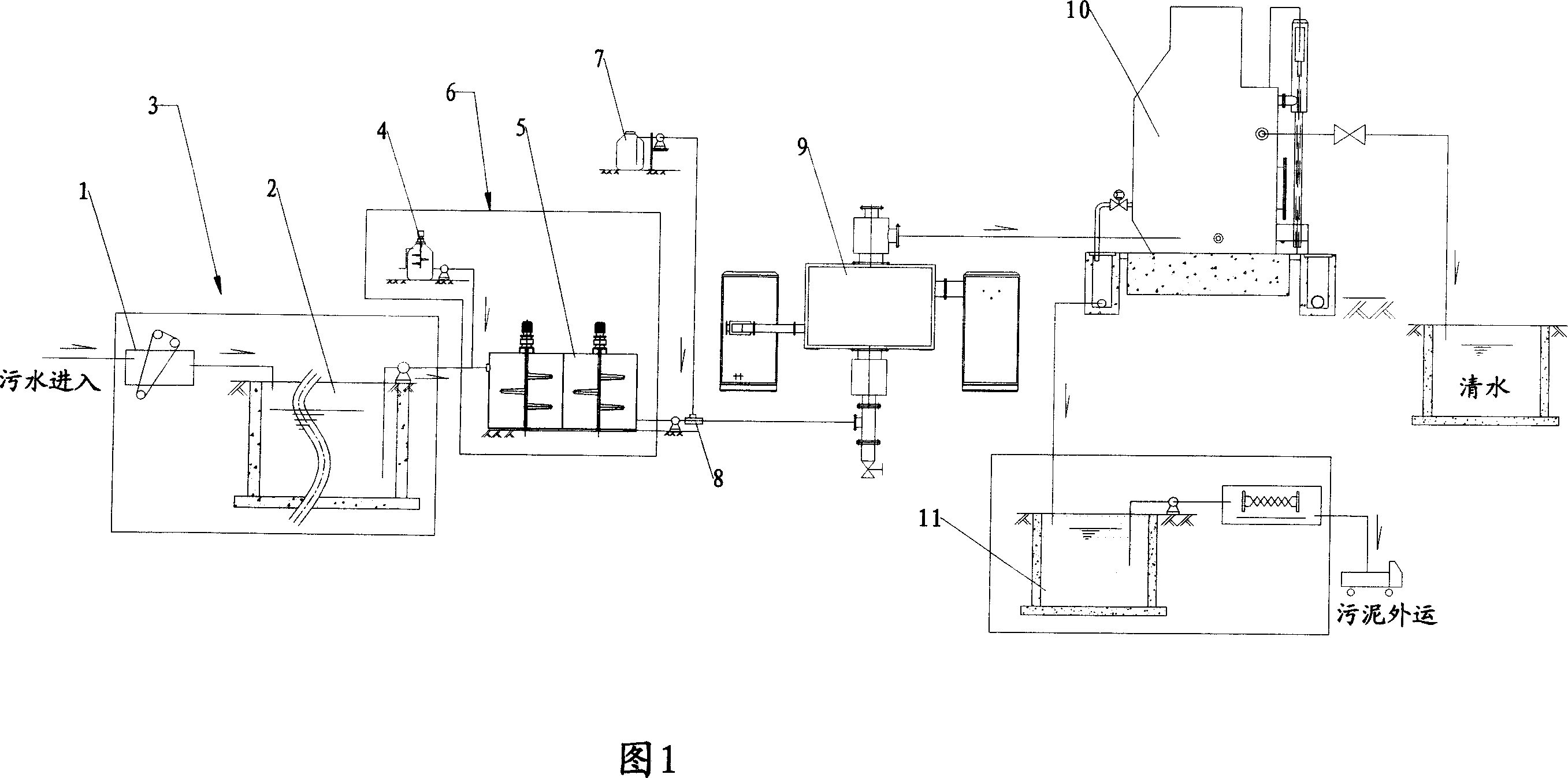
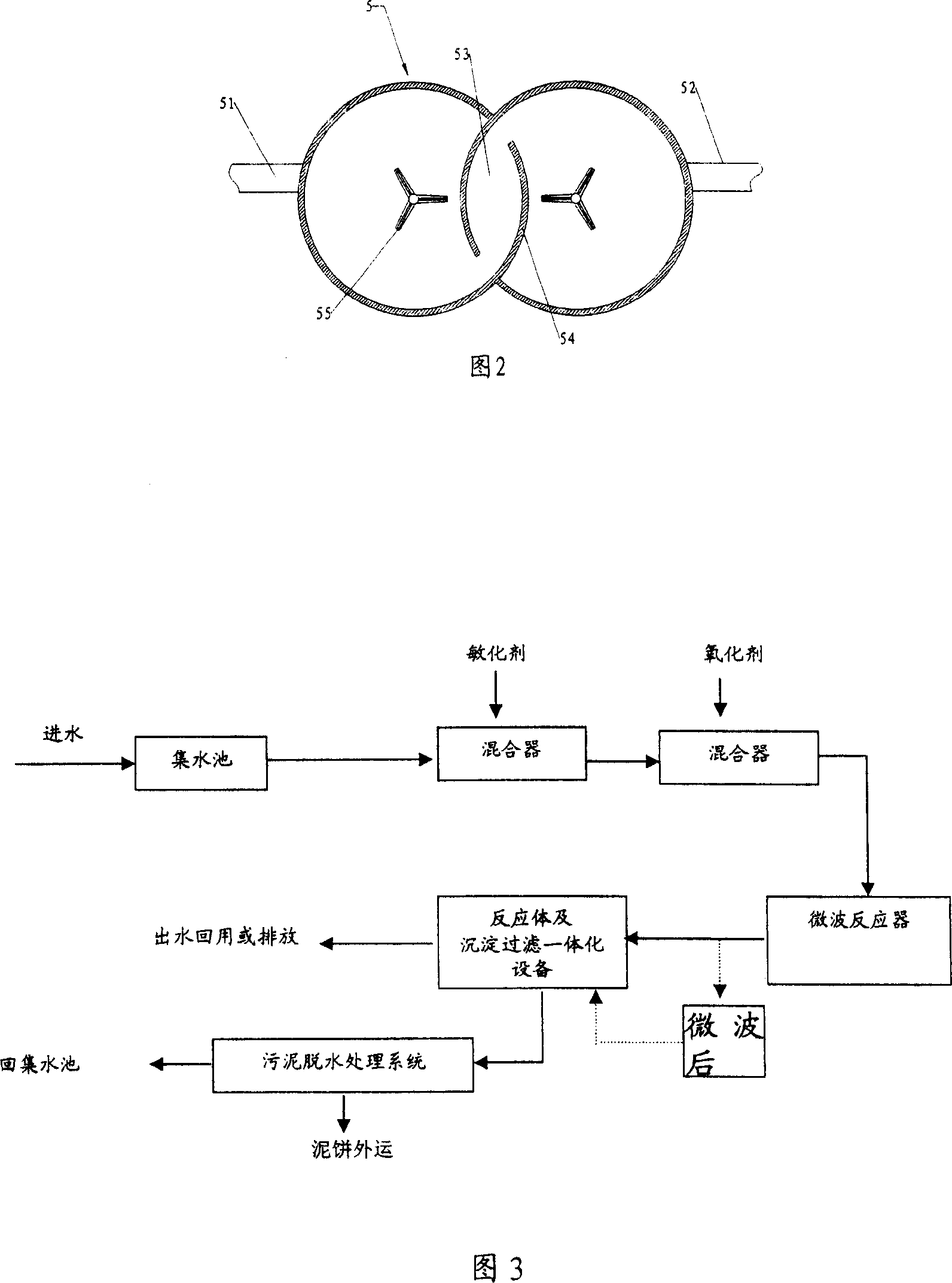
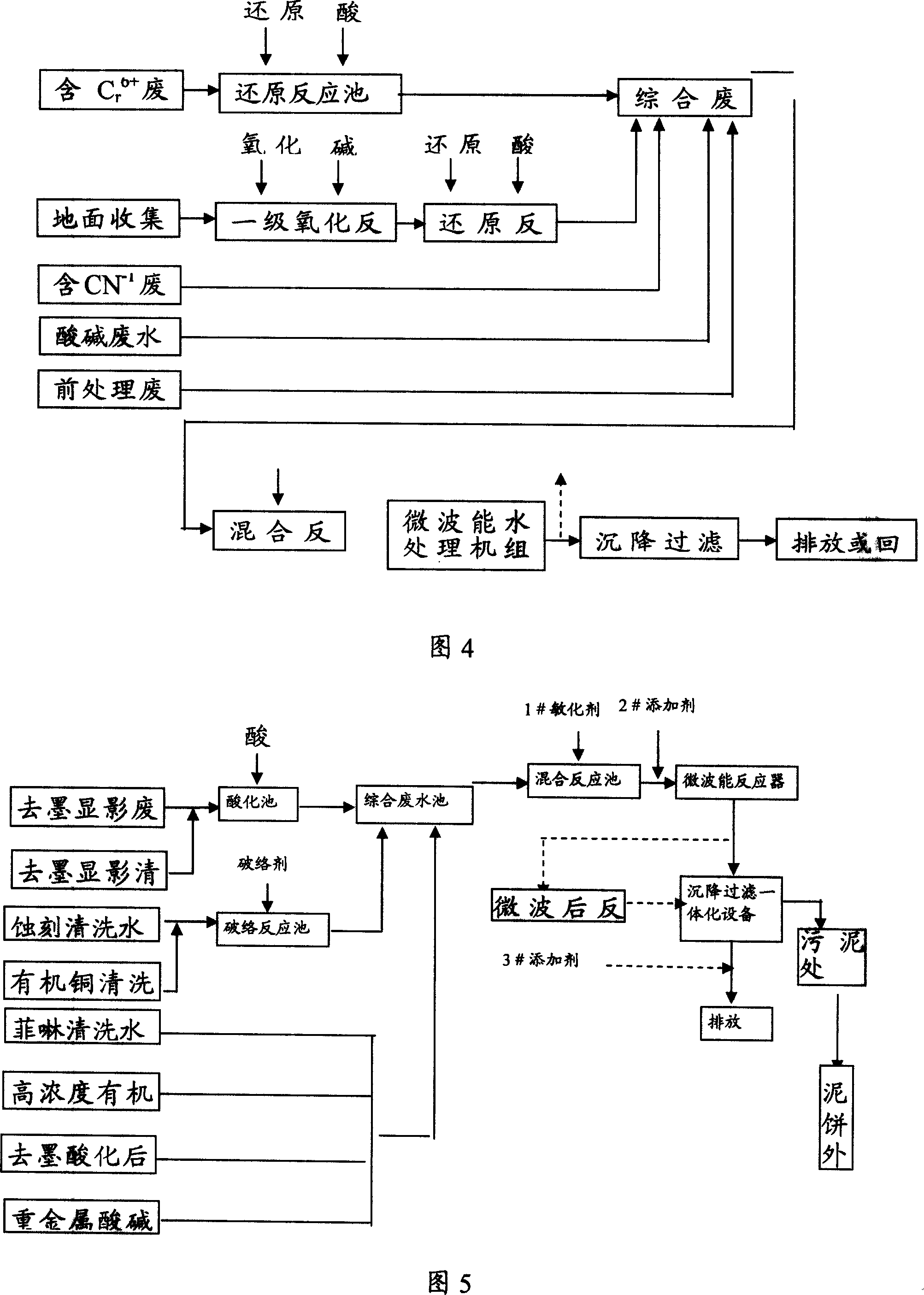
Method for processing sewage by microwave chemistry and corresponding system
ActiveCN101143736AImprove passabilityImprove processing efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSewageSewage treatment
The invention relates to a sewage processing method and system by the microwave chemistry. Before the sewage is transmitted to a microwave reactor (9), a microwave senstizer, which has a higher sensitivity degree to the microwave, is added into the sewage. The senstizer improves the penetration capability and catalysis action of the microwave during the sewage treatment process, reduces the size of the sewage treatment equipment and promotes the sewage treatment efficiency.
Owner:孙宪彬
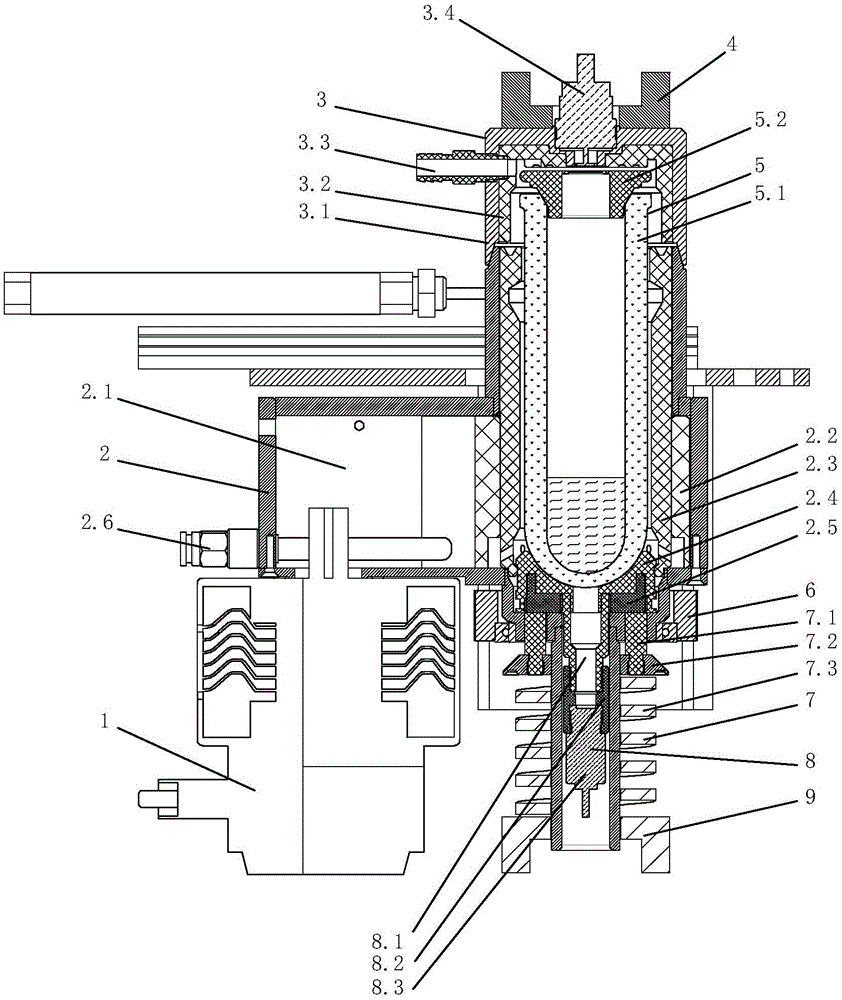
Self pressure release single mode microwave reaction system
ActiveCN105056861AImprove stabilityHigh speedPreparing sample for investigationEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesMagnetic tension forceChemical reaction
A self pressure release single mode microwave reaction system belongs to the field of analysis instruments and consists of a magnetron, a single mode cavity assembly, a single mode sealing cover assembly, a sealing cover sliding assembly, a test tube assembly, a magnetic stirring assembly, an automatic pressure release assembly, an infrared temperature measuring assembly and a single mode cavity lifting assembly; since an automatic pressure release function is integrated in the system, the risk that a test tube is exploded in a reaction process is greatly reduced, and reliability of a microwave chemical reaction system is improved; in a decomposition process, if pressure in the test tube is higher than a predetermined safety pressure value, the system can release pressure automatically, and ensures safety of the decomposition process, after the pressure in the test tube is reduced to be below the safety pressure value, the system can continuously recover a sealing work state, after the decomposition work is done, the system can be subject to automatic cooling and pressure release, and can be uncapped, the whole decomposition process is fast, safe and reliable, and the system can be widely used for the design and manufacture fields of a microwave reaction device.
Owner:PREEKEM SCI INSTR
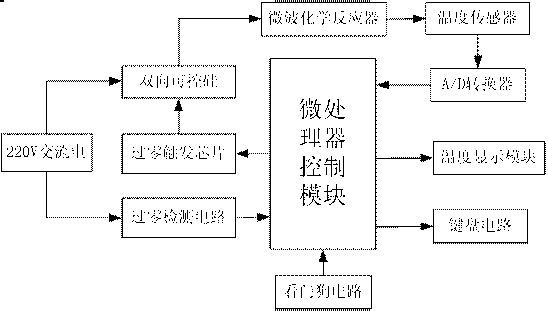
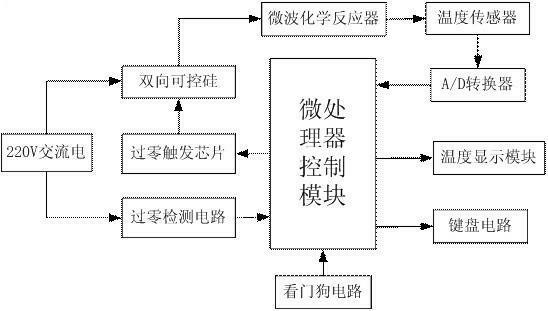
Constant temperature control system for microwave chemical reactor
InactiveCN102698682AReliable temperature protectionEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesTemperature controlSilicon-controlled rectifier
The invention discloses a constant temperature control system for a microwave chemical reactor. The constant temperature control system comprises a microprocessor control module, wherein the microprocessor control module is connected with a bidirectional silicon-controlled rectifier and a temperature sensor; the bidirectional silicon-controlled rectifier is connected with a 220V alternating current power supply and the microwave chemical reactor; the temperature sensor is connected with the microwave chemical reactor; and the microprocessor control module is also connected with a keyboard circuit. By the system, the problem of incapability of accurately controlling the temperature of the reactor in the prior art is solved; and temperatures are acquired, and the on-off of a microwave generator is controlled by the bidirectional silicon-controlled rectifier, so that the temperature of the microwave chemical reactor can be accurately controlled in a set temperature range, and a reliable temperature guarantee is provided for effective completion of a reaction.
Owner:SUZHOU JINXIANG TITANIUM EQUIP
Microwave-assisted low-temperature acid pickling method of rare-earth ore concentrate
InactiveCN102978392AImprove solubilityAvoid radioactive contaminationProcess efficiency improvementEnvironmental resistanceRare earth
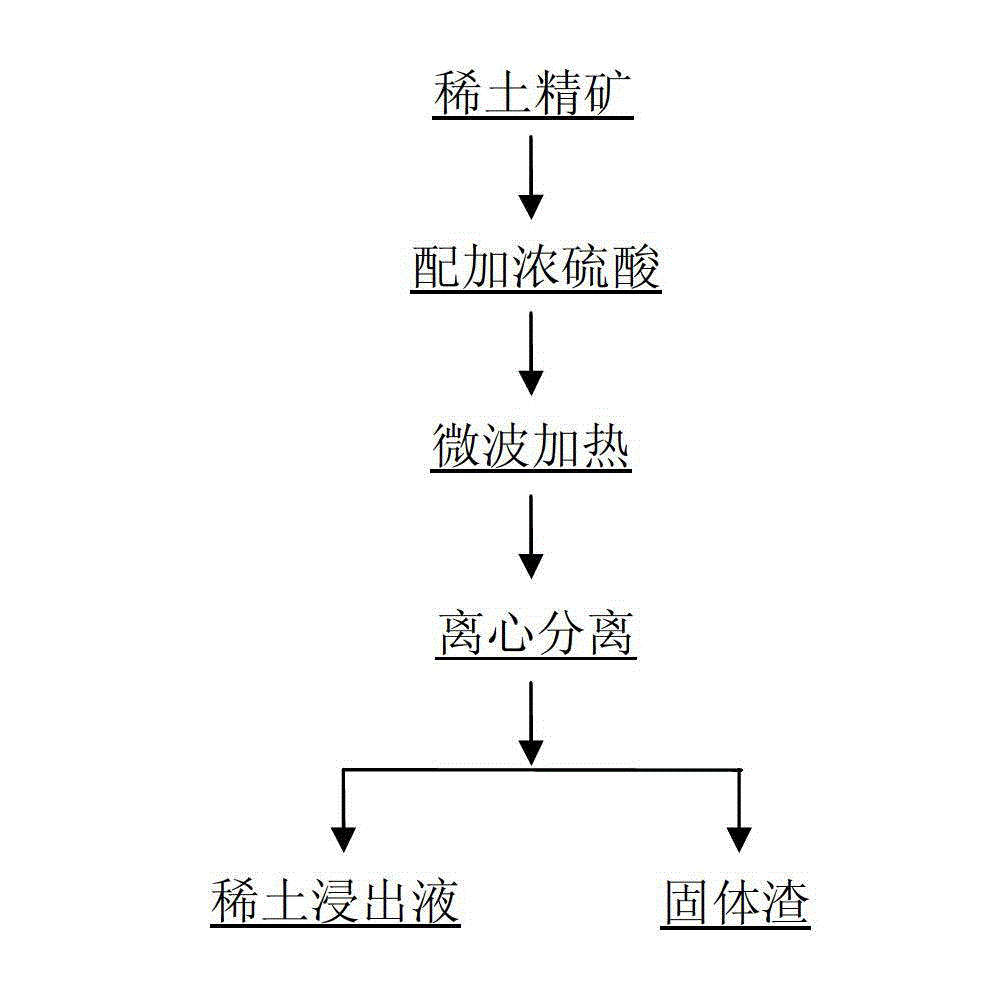
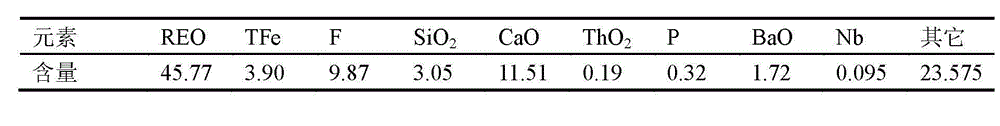
The invention relates to a microwave-assisted low-temperature acid pickling method of rare-earth ore concentrate, and belongs to the technical field of mineral extraction and metallurgy. The microwave-assisted low-temperature acid pickling method comprises the following steps: (1) uniformly mixing the rare-earth ore concentrate with concentrated sulfuric acid based on a certain ratio; (2) heating for 3 to 15 minutes through a microwave chemical reacting furnace at 90 to 200 DEG C, and fully dissolving the rare-earth ore concentrate; and (3) separating rare-earth leaching liquid from leaching residue in a centrifugal water washing way, so as to complete the leaching of the rare earth. According to the microwave-assisted low-temperature acid pickling method of rare-earth ore concentrate, the microwave-assisted and low-temperature acid pickling way is carried out on the rare earth, so that the leaching time is short, the rare-earth leaching rate is high, little consumption is brought to acid agent, the energy consumption is low, the emission of thorium and harmful gas is reduced, the recycle of the thorium is realized, the production efficiency is improved, and the pollution to environment is reduced as well; and the microwave-assisted low-temperature acid pickling method of rare-earth ore concentrate is an economic and environment-friendly method, and brings actual guiding significance to the rare-earth smelting process.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Passivator for alkaline soil and application of passivator
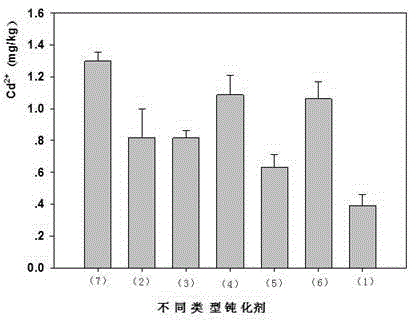
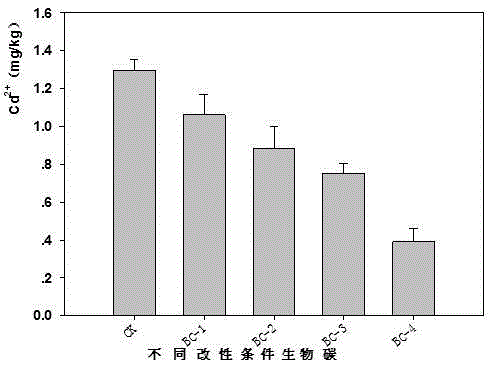
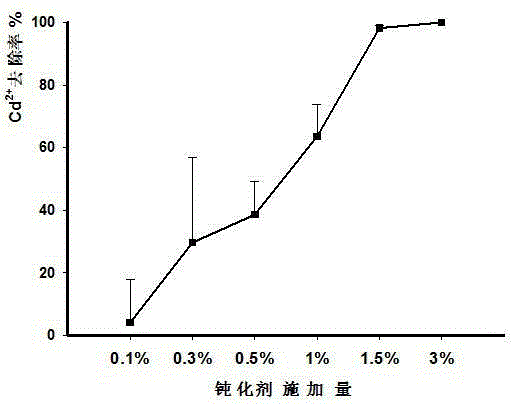
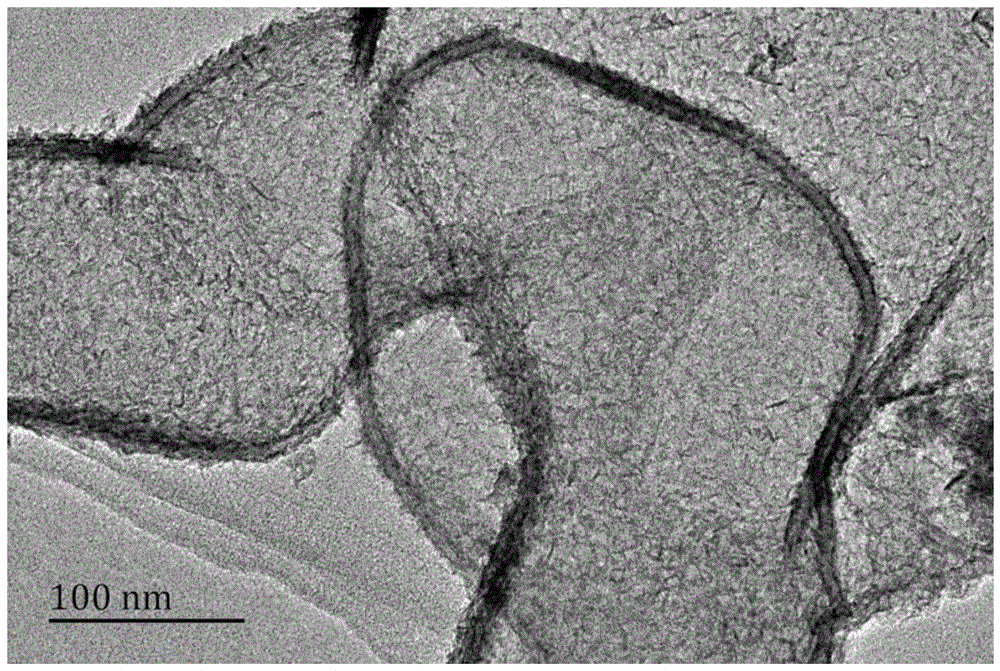
ActiveCN105349152AEffectively fixedMeet the needs of efficient and fast repairAgriculture tools and machinesOrganic fertilisersNutritionFiltration
The invention discloses a passivator for alkaline soil. The passivator is prepared with a method including preparation steps as follows: A), biochar is placed in a mixed solution of sodium sulfide and sulfuric acid to be soaked for 3-5 h; B), a reactant is ultrasonically washed for 30 min and then put in a microwave chemical reactor to react for 10 min; C), the reactant is subjected to suction filtration, the biochar is washed with deionized water to be neutral and dried, and the passivator for the alkaline soil is obtained. The passivator for the alkaline soil can adsorb cadmium ions in the alkaline soil, reduces the content of cadmium in the soil and has the advantages of high repairing rate, good long-term stability, low cost, simplicity in application and the like; besides, the modified biochar contains a large quantity of organic matters and other nutrient elements, rich nutrition is provided for plant growth, and the passivator has huge application and popularization value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Preparation method of MnO<2>@GCs@MnO<2> composite material
InactiveCN105529194AImprove conductivityIncrease loadHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureCapacitanceDispersity
The invention discloses a preparation method of an MnO<2>@GCs@MnO<2> composite material and belongs to the technical field of material preparation. The method comprises the steps as follows: a graphene capsule is firstly prepared; the prepared graphene capsule and potassium permanganate are added to water and are mixed evenly to obtain a mixed solution of the potassium permanganate and the graphene capsule; the mass ratio of the potassium permanganate to the graphene capsule material is 4 to (3-10); the concentration of the potassium permanganate is 0.05-0.15mol / L; finally, the mixed solution of the potassium permanganate and the graphene capsule is put into a microwave chemical reactor for reaction at 500-750W for 3-10 minutes; the reaction temperature is controlled at 90-100 DEG C; and after reaction is ended, the obtained turbid liquid is centrifugally separated and dried. The method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate, high in efficiency, high in manganese dioxide loading capacity and good in dispersity; and the prepared electrode material is good in conductivity and cycling stability and has relatively high specific capacitance.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
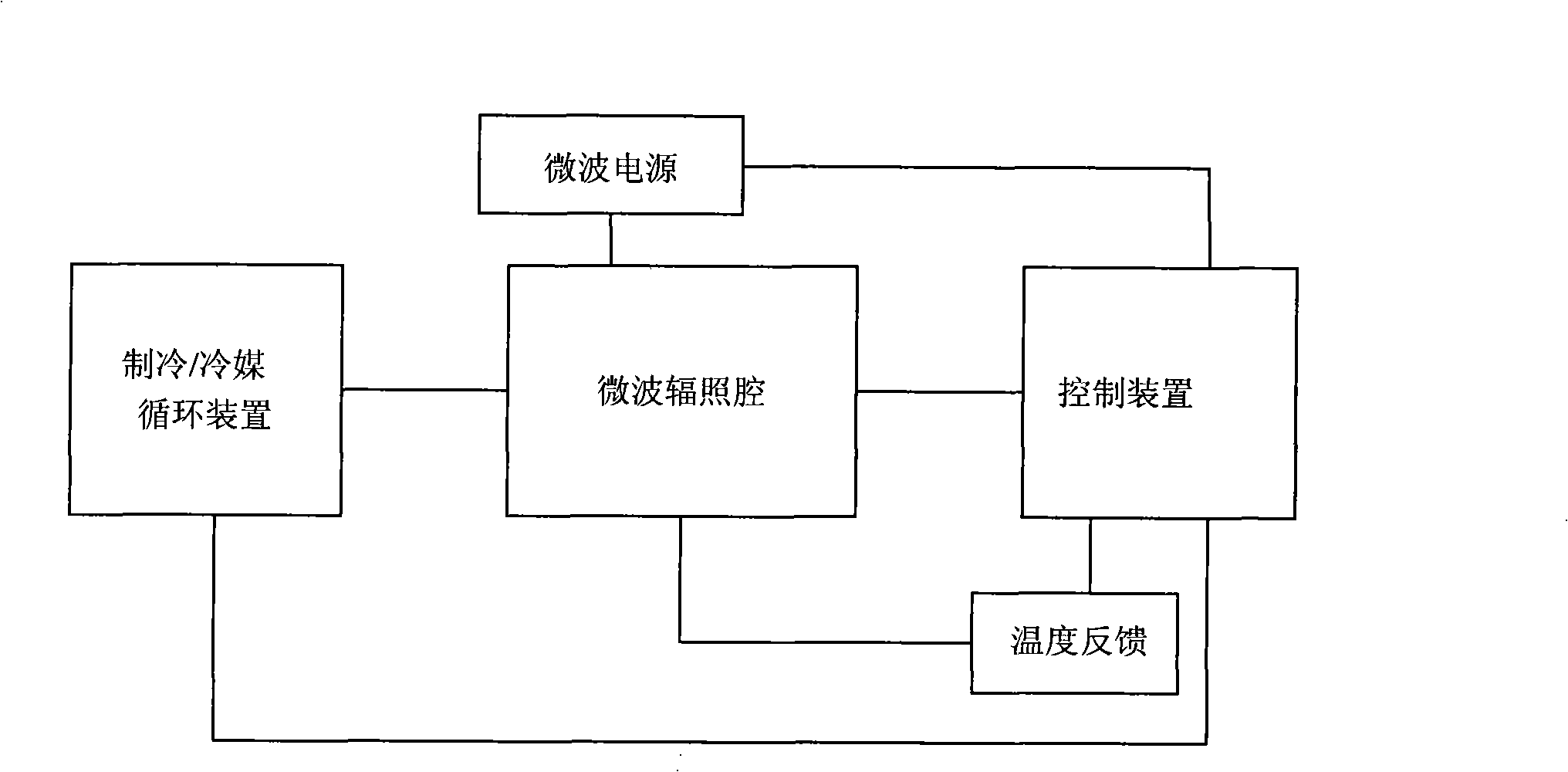
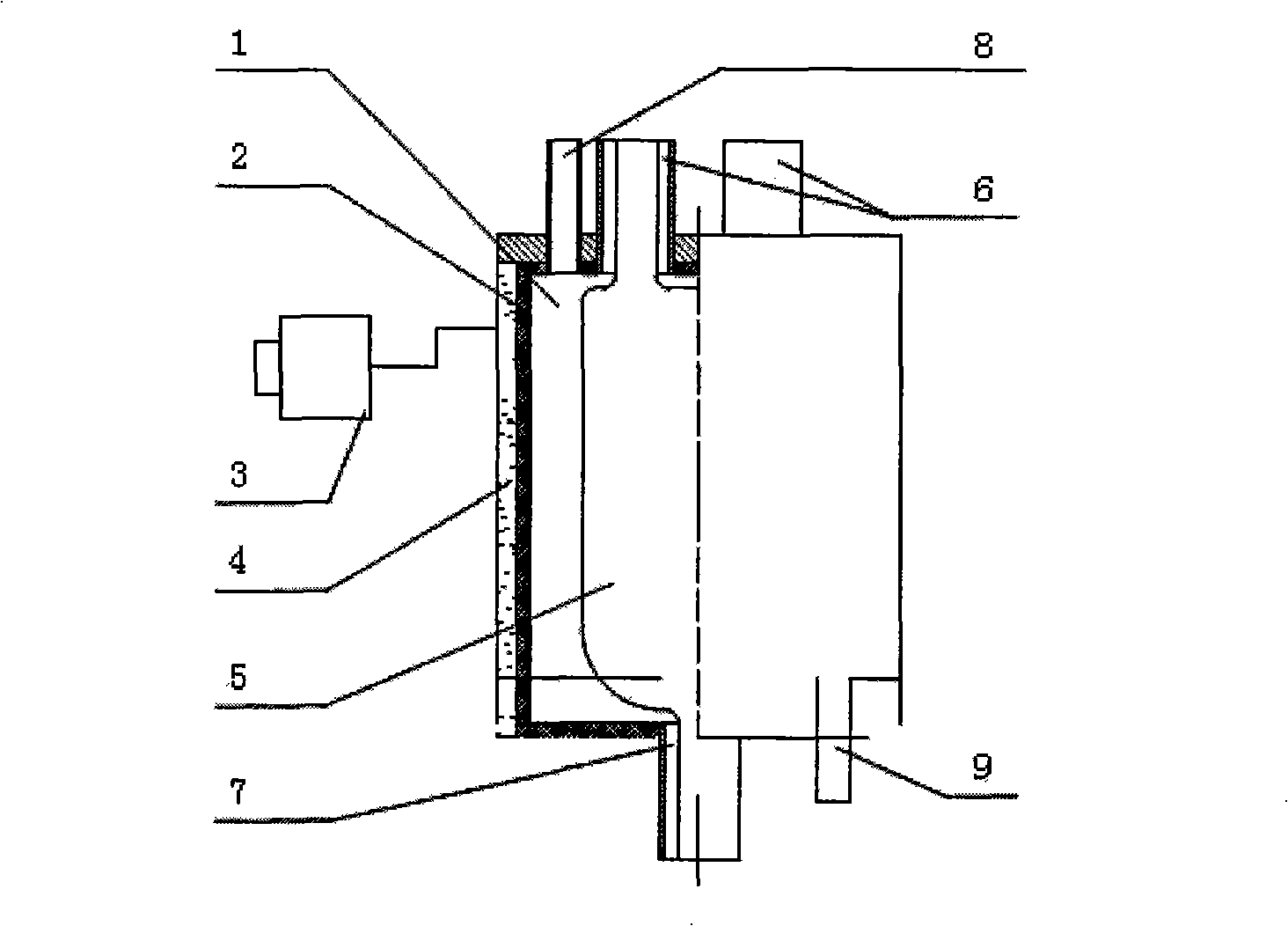
Refrigeration and microwave irradiation integrated microwave chemical reaction apparatus
InactiveCN101342475AImprove chemical reaction efficiencyIncrease temperatureEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesChemical reactionMicrowave irradiation
The present invention relates to a microwave chemical reaction device in the chemical research and the chemical field, in particular to a microwave chemical reaction device for research, pilot test and output magnification of microwave chemical reaction under relatively low temperature. The present invention provides a microwave chemical reaction device with integrated refrigeration and microwave radiation, which comprises a microwave radiating cavity, an embedded microwave reactor, a microwave power, a magnetic control pipe and a refrigerating device; the embedded microwave reactor is arranged in the microwave radiating cavity; the microwave radiating cavity is directly connected with the refrigerating device for continuous refrigeration of the microwave radiating cavity; the microwave power and the magnetic control pipe are connected with the microwave radiating cavity. The present invention can provide high-strength and high-intensity microwave radiation and ensures that the reaction system is under the low temperature or superlow temperature condition while greatly increasing the chemical reaction speed, thus providing full reaction activated energy, increasing the reaction speed and overcoming the damages of high temperature on reactants or target molecule structure, activity and shape.
Owner:BEIJING ANNAN SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com