Liquid-phase stripping method of two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide nano material, and dispersion method and application of molybdenum disulfide
A technology of molybdenum disulfide and nanomaterials, applied in the direction of molybdenum sulfide, etc., can solve the problems of difficult operation, unstable product quality of molybdenum disulfide two-dimensional nanosheets, and difficulty in large-scale implementation, achieving low cost, easy operation, easy compositing effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0049] An aspect of the embodiments of the present invention also provides a method for preparing a molybdenum disulfide dispersion, which includes: uniformly mixing molybdenum disulfide and polyaniline conductive polymers in a dispersion medium to form a stable dispersion.
[0050] Further, the weight ratio of the polyaniline conductive polymer to molybdenum disulfide is preferably 0.1-10:1, especially preferably 0.2-2:1.
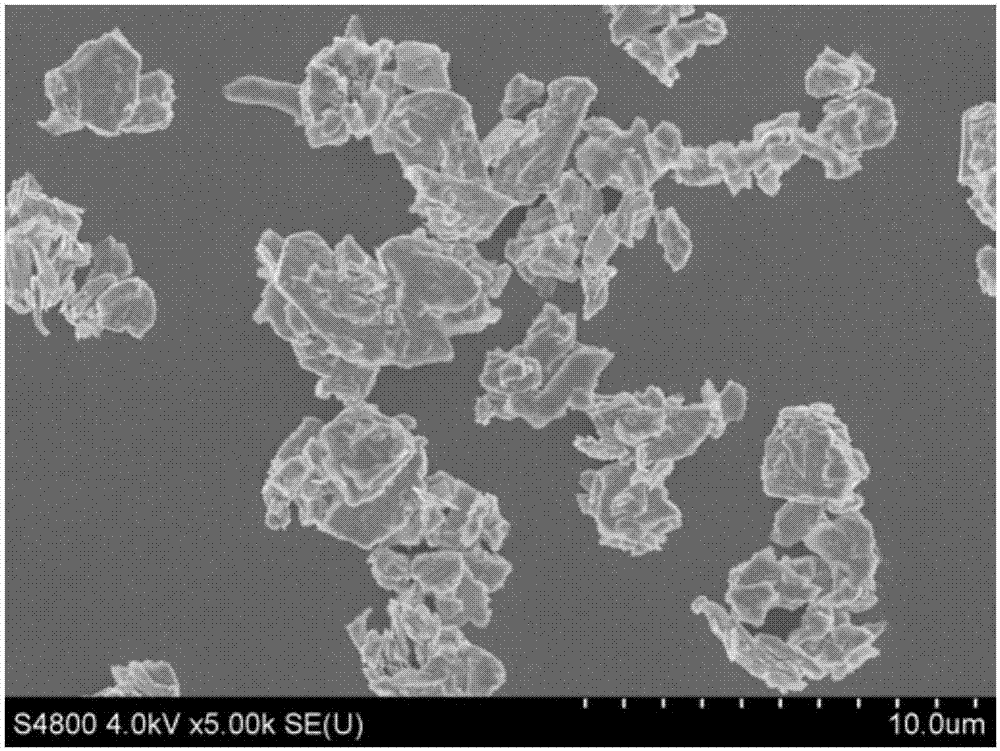
[0051] Further, the molybdenum disulfide is preferably a two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide nanomaterial, especially preferably a two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide nanosheet with a thickness of 1-20 nm.
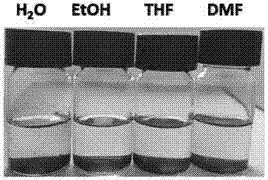
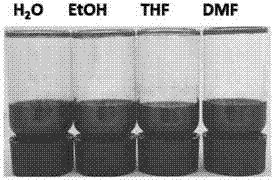
[0052] Further, the dispersion medium includes any one or a combination of two or more of water, organic solvents, and polymer resins, preferably organic solvents, such as the various organic solvents listed above.
[0053] Preferably, the molybdenum disulfide contained in the stable dispersion can be as high as 5 mg / mL, preferably 0.1 mg / mL-3 mg / mL....
Embodiment 1
[0065] Example 1 Synthesis of intrinsic polyaniline and its use in the stripping of molybdenum disulfide two-dimensional nanosheets in organic solvents
[0066] Add 100mL 1M hydrochloric acid and aniline (7g) into a 200mL round bottom flask, stir to dissolve and cool to 0°C. Then 17g of ammonium persulfate was dissolved in 50mL of 1M hydrochloric acid solution and slowly added dropwise into the round bottom flask. After the dropwise addition, reacted for 12 hours, filtered the reaction solution, washed twice with distilled water to obtain dark green doped polyaniline. The obtained dark green polyaniline was soaked in 10wt% ammonia water for 12 hours, filtered, washed with distilled water until the filtrate was neutral, and vacuum-dried at 65° C. for 24 hours to obtain intrinsic polyaniline (5.2 g) for future use. The intrinsic polyaniline has good solubility in strong polar solvents such as DMF and NMP.
[0067] Mix the intrinsic polyaniline prepared in this example, molybden...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Example 2 Synthesis of alkyl-substituted polyaniline and its use in the stripping of molybdenum disulfide two-dimensional nanosheets
[0071] Add 100mL of 1M hydrochloric acid and o-isopropylaniline (6.0g) into a 200mL round bottom flask, stir to dissolve and cool to 0°C. Then 11.44g of ammonium persulfate was dissolved in 50mL of 1M hydrochloric acid solution and slowly added dropwise to the round bottom flask. After the dropwise addition, reacted for 12 hours, filtered the reaction solution, washed twice with distilled water to obtain dark green doped isopropyl Replace polyaniline. The obtained dark green polyaniline was soaked in 10wt% ammonia water for 12 hours, filtered, washed with distilled water until the filtrate was neutral, and vacuum-dried at 65°C for 24 hours to obtain intrinsic isopropyl-substituted polyaniline (4.6 g) for later use. The intrinsic state of isopropyl polyaniline in polar solvents such as THF, CHCl 3 , DMF, NMP, etc. have good solubility. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com