Anti-caries polypeptide capable of preventing bacteria and promoting remineralization, derivative and salt thereof, and applications of anti-caries polypeptide, derivative, and salt
A peptide derivative and remineralization technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of single anti-cariogenic bacteria or promoting remineralization function, increase the burden of medication for patients, and poor compliance, so as to promote the remineralization of early artificial caries , Reliable effect of promoting remineralization, small molecular weight effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] The anti-caries polypeptide of the present invention has an amino acid sequence such as SEQ ID NO.1-9.
[0082] Prepare as follows:
[0083] 1. Select Fmoc-His(Trt)-Wang Resin as the resin (carrier);
[0084] 2. Fully swell the resin with DCM;
[0085] 3. Use an appropriate concentration of DBLK (hexahydropyridine + DMF) to remove the Fmoc-protecting group;
[0086] 4. Wash several times with DMF to remove DBLK;
[0087] 5. Weigh a suitable condensing agent and activator (HBTU, NMM) and the second Fmoc-protected amino acid (Fomc-Leu-OH) at the C-terminal for coupling;
[0088] 6. The ninhydrin detection method is used for detection to ensure that the connection is relatively complete;
[0089] 7. Wash several times with DMF to wash away the remaining residues and activator condensation agent;
[0090] 8. Coupling is carried out according to the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide, and the method refers to steps 3-7;
[0091] 9. After connecting all the amino ac...
Embodiment 2
[0096] Preparation of C-terminal amidated derivatives:
[0097] The preparation was carried out with reference to the method described in Example 1, the only difference being that Rink-Amide-Am Resin was selected as the resin (carrier).
Embodiment 3
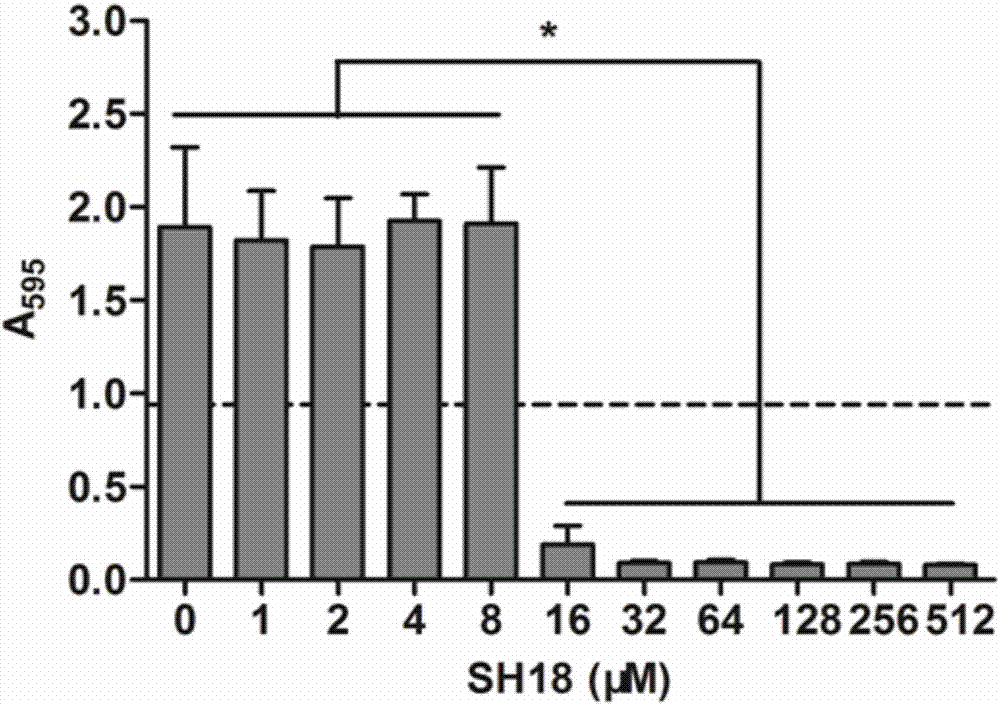
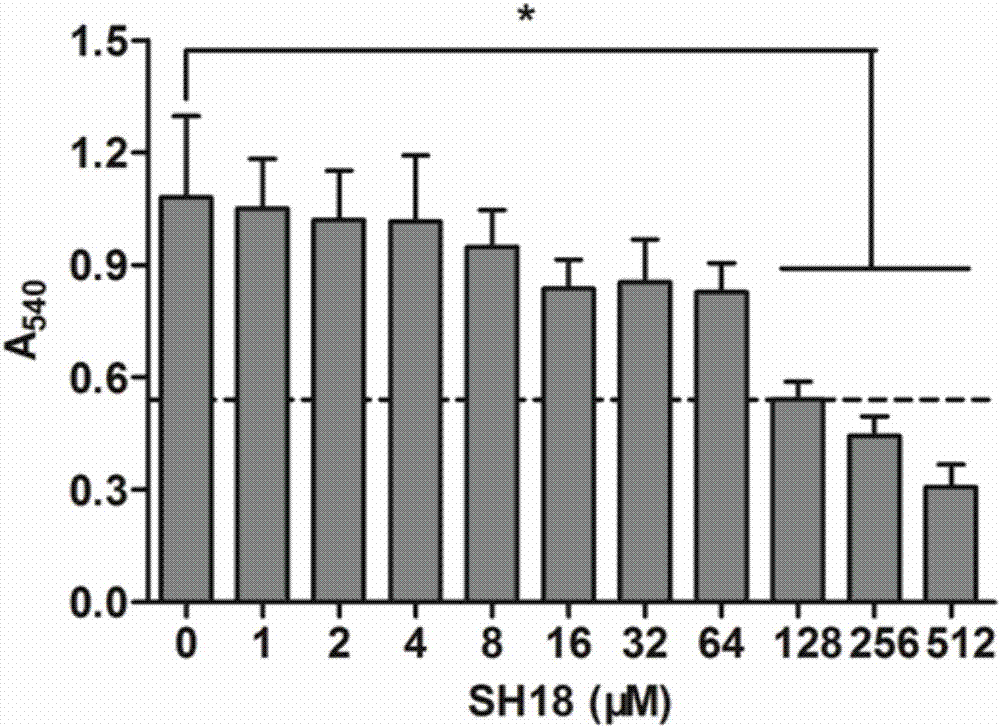
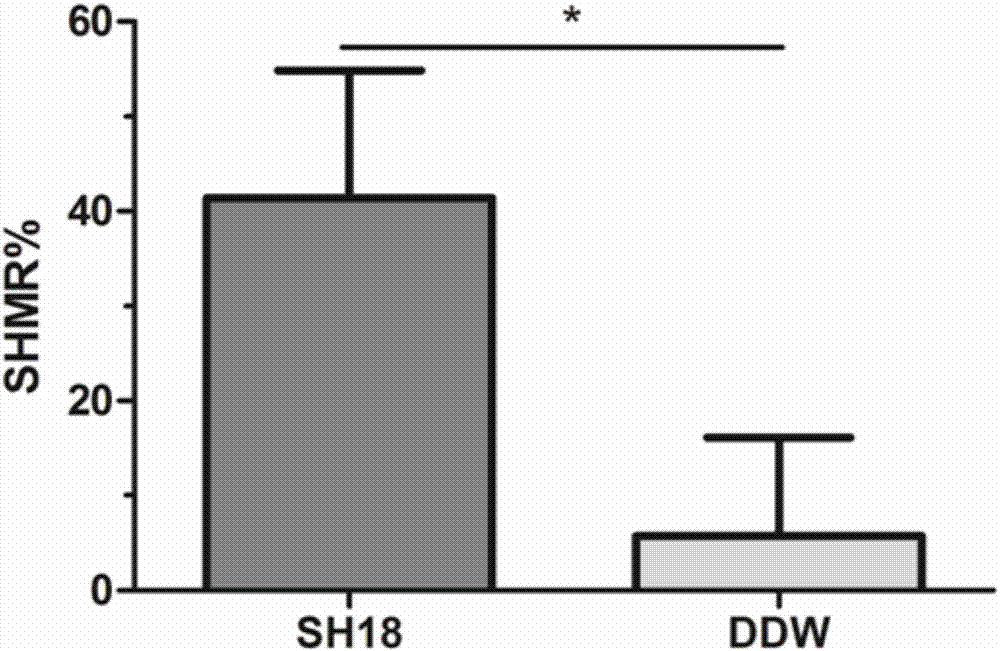
[0098] Example 3 "Double Effect" Polypeptide Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) Determination
[0099]The minimum inhibitory concentration MIC (Minimal inhibitory concentration) refers to the lowest concentration of antibacterial drugs that can inhibit the growth of bacteria in the medium in vitro tests. Minimal bactericidal concentration MBC (Minimal bactericidal concentration) refers to the minimum concentration of antibacterial drugs that can kill viable bacteria in the medium in vitro tests. MIC and MBC are indicators of drug antibacterial activity, showing the ability of drugs to inhibit and kill pathogenic microorganisms. Bacteria were used in the experiment as the main oral cariogenic bacteria: Streptococcus mutans UA159, provided by the State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases. The test polypeptide is the C-terminal amidate of SEQ ID NO.1 (hereinafter referred to as SH18).
[0100] The experimental steps of MIC and MBC de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com