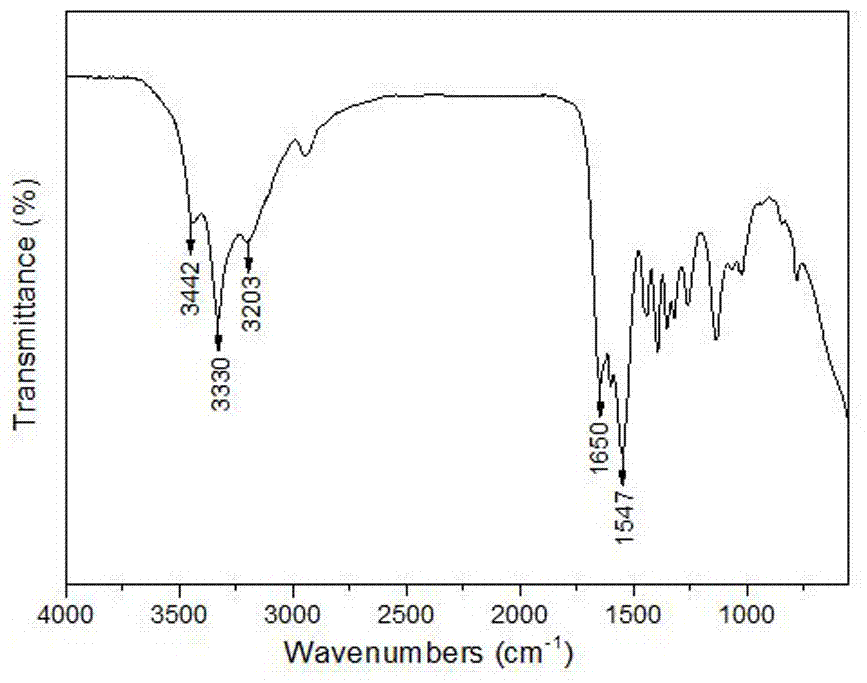
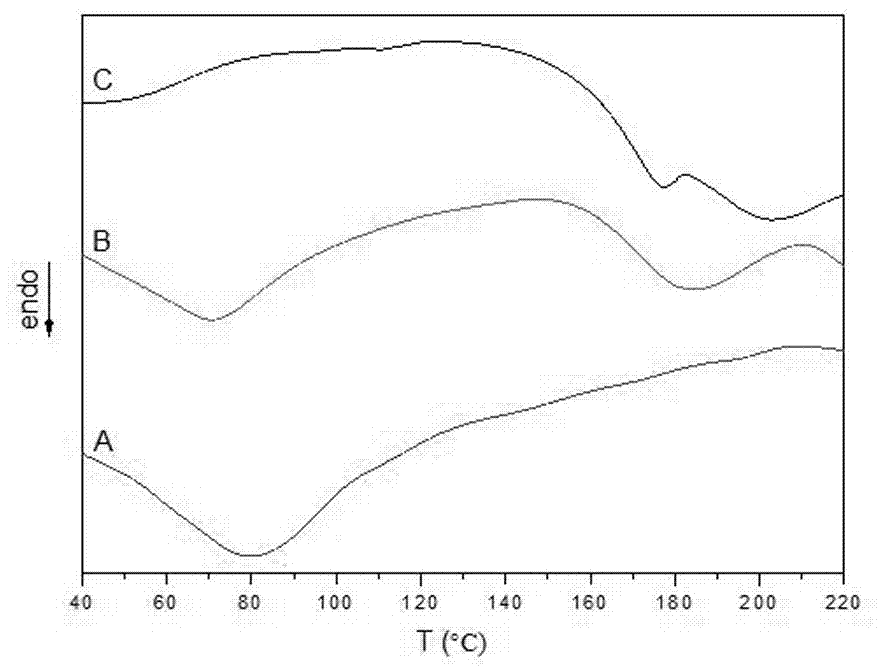
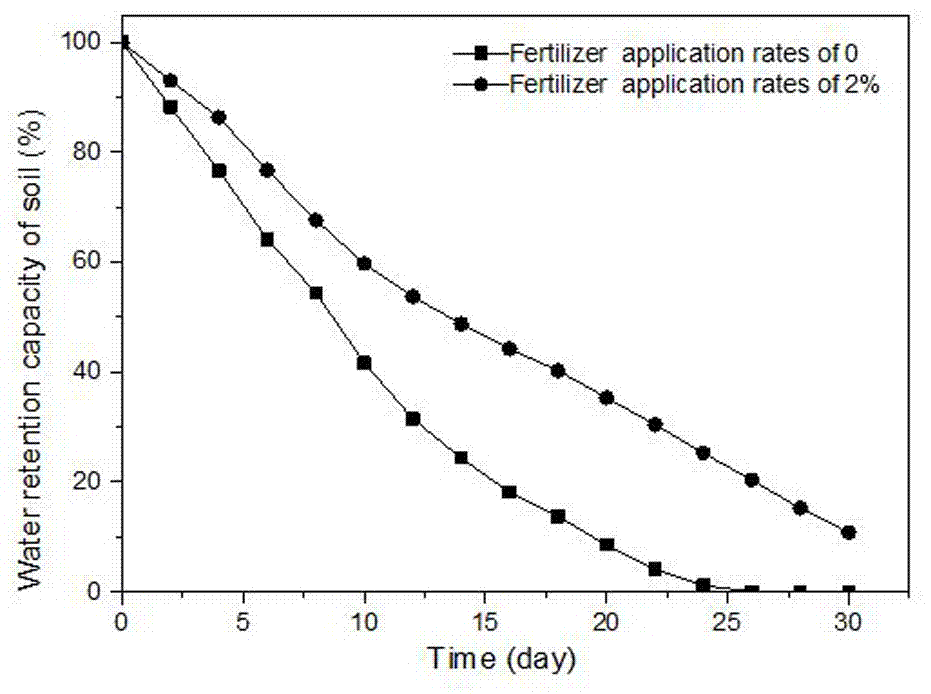
Preparation method of cellulose-based multi-nutrient polymer slow-release fertilizer
A cellulose-based, slow- and controlled-release fertilizer technology, applied in urea compound fertilizers, nitrogen fertilizers, phosphate fertilizers, etc., can solve the problems of limited water absorption and water retention capacity, and achieve the effects of saving manpower and material resources, wide sources, and improving performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0036] A method for preparing a cellulose-based water-absorbing and water-retaining biodegradable multi-nutrient element macromolecule slow-release fertilizer, comprising the following steps:
[0037] (1) Add formaldehyde and urea respectively to the first reactor, use 5% KOH solution to adjust the system pH=8, and react at 40° C. for 2 hours to obtain a methylolurea solution;
[0038] (2) Add acrylic acid, acrylamide and inorganic cellulose powder into the second reactor, and add a KOH solution with a mass fraction of 20% to adjust the neutralization degree of the acrylic acid monomer to 20% to 100%; Potassium hydrogen, initiator and the hydroxymethyl urea solution prepared in step (1), mixed under ice bath for 30min, heated up to 55°C and reacted under nitrogen atmosphere for 4h to obtain a viscous product;
[0039] (3) Granulate the obtained viscous product and then dry it to obtain a cellulose-based water-absorbing and water-retaining biodegradable multi-nutrient polymer s...
Embodiment 1
[0047] A method for preparing cellulose-based water-absorbing and water-retaining biodegradable multi-nutrient element macromolecule slow-release fertilizer, comprising the following steps:
[0048] (1) Add 4.06 g of formaldehyde and 6 g of urea to the first reaction vessel, adjust the pH of the system to 8 with 5% KOH solution, and react at 40° C. for 2 h to obtain a methylol urea solution.
[0049] (2) Add 5g acrylic acid, 2g acrylamide and 0.7g carboxymethyl cellulose powder to the second reaction vessel, and add the KOH solution that the mass fraction is 20% to adjust the neutralization degree of acrylic acid to be 80%; add 0.5g afterwards Potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.021 g of ammonium persulfate and 12 g of the hydroxymethyl urea solution prepared in step (1) were mixed for 30 min in an ice bath, heated to 55° C. and reacted for 4 h under a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain a viscous product.
[0050] (3) Granulate the obtained viscous product and then dry it to obtain a...
Embodiment 2
[0053] A method for preparing cellulose-based water-absorbing and water-retaining biodegradable multi-nutrient element macromolecule slow-release fertilizer, comprising the following steps:
[0054] (1) Add 4.06 g of formaldehyde and 6 g of urea to the first reaction vessel, adjust the pH of the system to 8 with 5% KOH solution, and react at 40° C. for 2 h to obtain a methylol urea solution.
[0055] (2) Add 5g of acrylic acid, 2g of acrylamide and 0.7g of hydroxyethyl cellulose powder into the second reaction vessel, and add a KOH solution with a mass fraction of 20% to adjust the degree of neutralization of acrylic acid to 80%; then add 0.5g Potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.021 g of ammonium persulfate and 12 g of the hydroxymethyl urea solution prepared in step (1) were mixed for 30 min in an ice bath, heated to 55° C. and reacted for 4 h under a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain a viscous product.
[0056] (3) Granulate the obtained viscous product and then dry it to obtain a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| water absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com