Polycrystalline silicon reduction tail gas waste heat utilization method and system
A technology of polysilicon and exhaust gas, applied in chemical instruments and methods, waste heat treatment, silicon compounds, etc., can solve the problems of increased production cost, increased production cost, increased cooling load, etc., to increase reaction temperature, increase conversion rate and, The effect of reducing the cooling load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
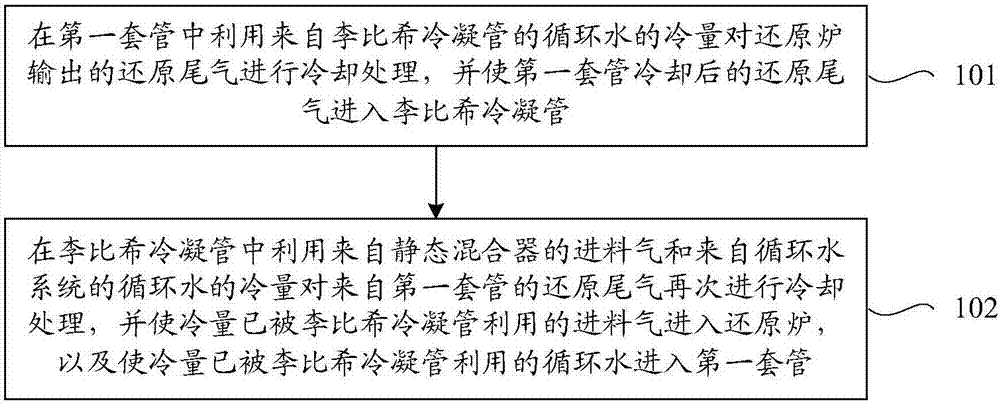
[0038] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for utilizing waste heat from polysilicon reduction tail gas, including the following steps S101 and S102.
[0039] S101. In the first sleeve, the cooling capacity of the circulating water from the Liebig condenser tube is used to cool the reduction tail gas output from the reduction furnace, and the reduced tail gas cooled by the first sleeve tube enters the Liebig condenser tube.
[0040] In this step, the reduction tail gas output from the reduction furnace includes a mixture of hydrogen, hydrogen chloride and chlorosilane, wherein the chlorosilane includes a mixture of trichlorosilane, silicon tetrachloride and dichlorodihydrosilane.
[0041] S102. In the Liebig condensing tube, use the cooling capacity of the feed gas from the static mixer and the circulating water from the circulating water system to cool the reduction tail gas from the first sleeve again, and make the cooling capacity have been obtained...
Embodiment 2
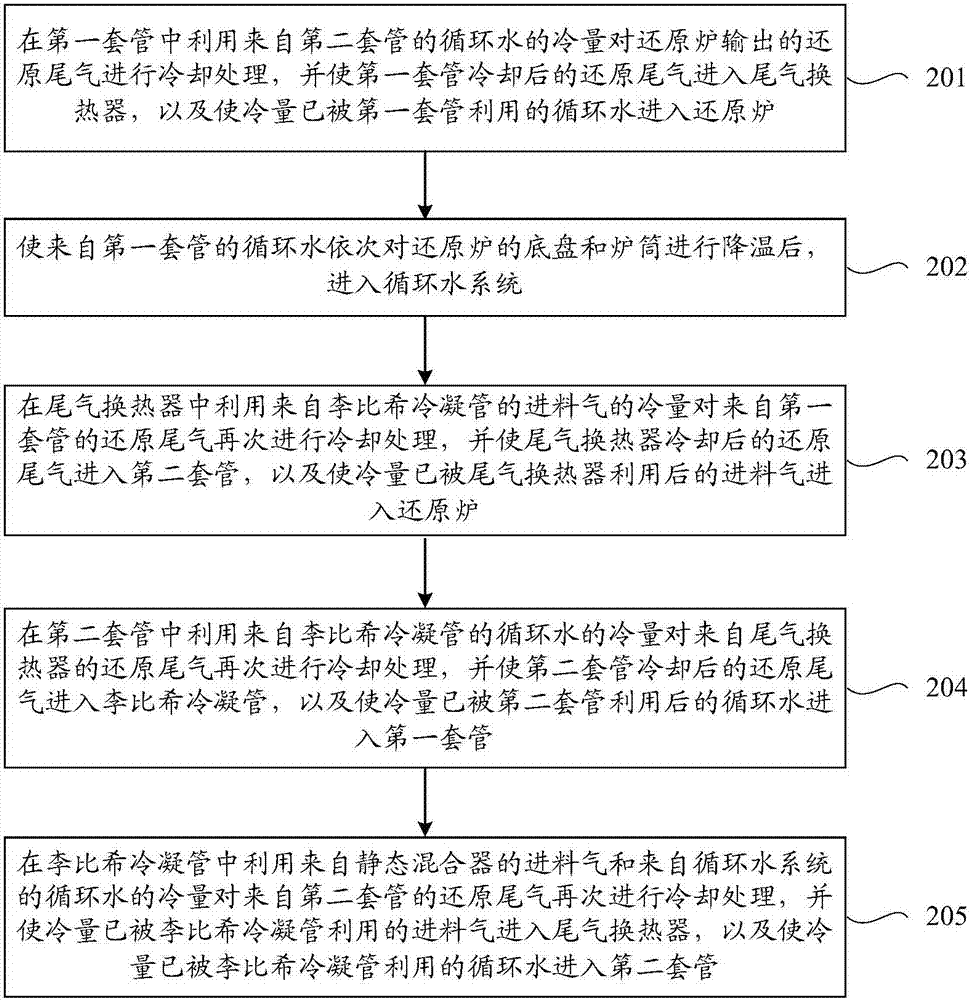
[0047] Such as figure 2 As shown, this embodiment takes the production process of polysilicon produced by 12 pairs of rod reduction furnaces as an example, and provides a method for utilizing waste heat of polysilicon reduction tail gas, including the following steps S201 and S205.
[0048] S201. In the first casing, the cooling capacity of the circulating water from the second casing is used to cool the reduction tail gas output from the reduction furnace, and the reduced tail gas cooled by the first casing enters the tail gas heat exchanger, and the The circulating water whose cooling capacity has been utilized by the first casing enters the reduction furnace.
[0049] S202. Make the circulating water from the first casing successively cool down the chassis and cylinder of the reduction furnace, and then enter the circulating water system.
[0050] S203. In the tail gas heat exchanger, the cooling capacity of the feed gas from the Liebig condenser tube is used to cool the ...
Embodiment 3
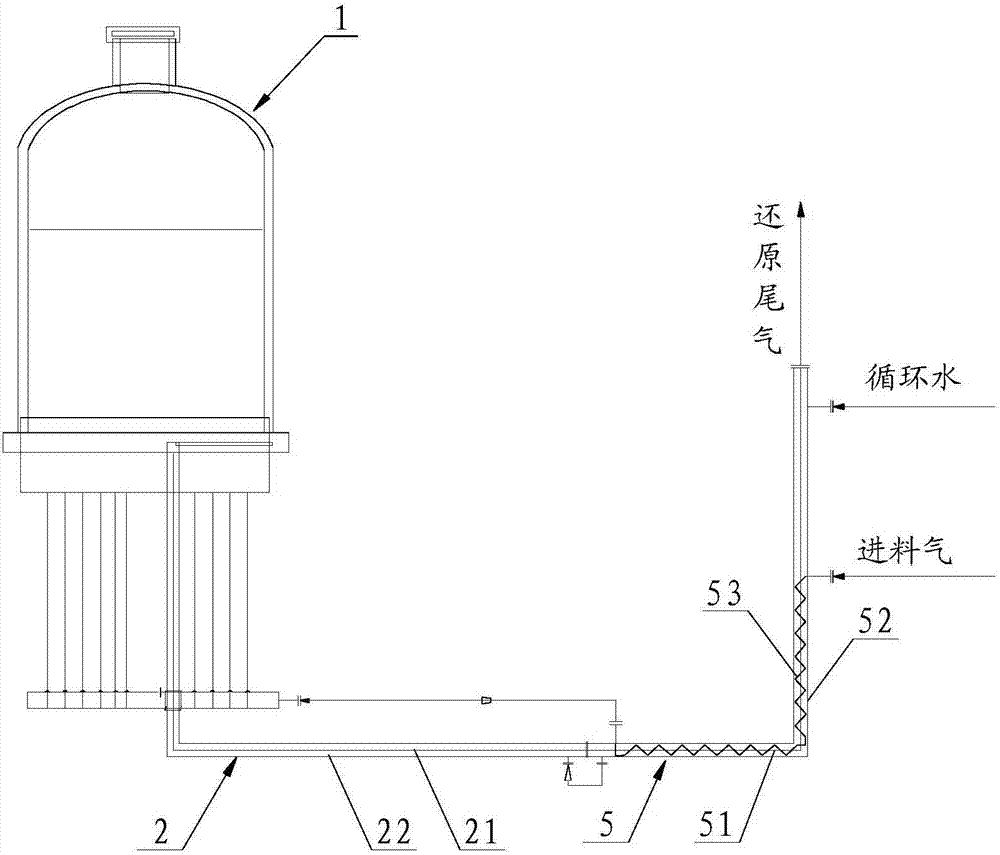
[0068] Such as image 3 As shown, this embodiment provides a polysilicon reduction tail gas waste heat utilization system, including a first sleeve 2 and a Liebig condenser tube 5 .
[0069] The first casing 2 is used to cool the reduction tail gas output from the reduction furnace by utilizing the cooling capacity of the circulating water from the Liebig condenser pipe 5 , and output the cooled reduction tail gas to the Liebig condenser pipe 5 .
[0070] Such as image 3 As shown, the first sleeve 2 includes an inner tube 21 and an outer tube 22 , and the outer tube 22 is sheathed outside the inner tube 21 . Wherein, the reduced tail gas flows through the inner pipe 21 , and the circulating water flows through the outer pipe 22 . The reduction tail gas output from the reduction furnace includes a mixture of hydrogen, hydrogen chloride and chlorosilane, wherein the chlorosilane includes a mixture of trichlorosilane, silicon tetrachloride and dichlorodihydrosilane.
[0071] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com