A method for efficiently heating polymers using microwaves
A polymer and microwave heating technology, applied in the field of polymer materials, can solve problems such as unoptimized and efficient implementation methods, and achieve the effects of increasing convenience, improving product quality, and reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
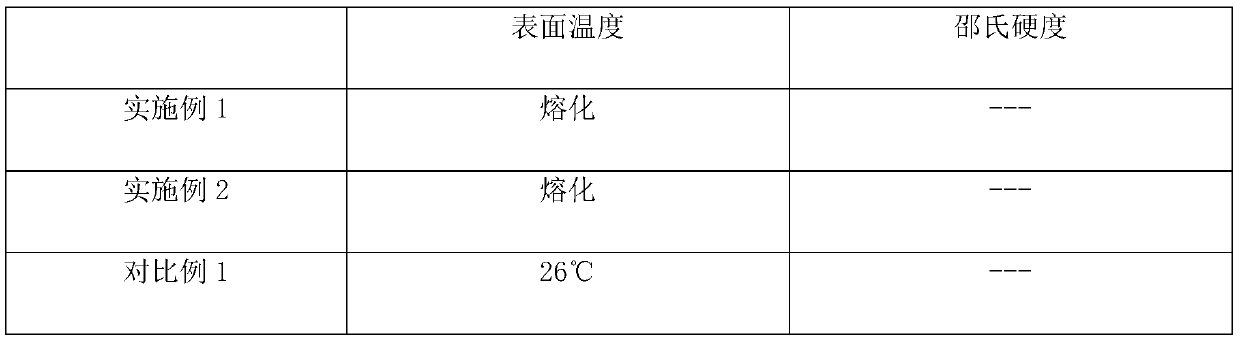
[0018] In 100 parts of polyethylene powder, add 2 parts of tetrapod zinc oxide whiskers and mix well. Put the above powder into a flat vulcanizer, heat and pressurize to make a microwave-heatable polyethylene board, wherein the volume addition of zinc oxide whiskers is 0.35%, and cool to room temperature for later use.
[0019] The above-mentioned microwave-heatable polyethylene plate was put into a microwave oven at a room temperature of 25° C., and was taken out after heating for 2 minutes. It was found that the polyethylene plate had melted.
Embodiment 2
[0021] Add 1 part of needle-shaped zinc oxide whiskers to 100 parts of polyethylene powder, and mix well. Put the above powder into a flat vulcanizer, heat and pressurize to make a microwave-heatable polyethylene board, wherein the volume addition of zinc oxide whiskers is 0.18%, and cool to room temperature for later use.
[0022] Put the above-mentioned microwave-heatable polyethylene plate into a microwave oven at room temperature of 25°C, take it out after heating for 2 minutes, and test its surface temperature to be 83°C.
[0023] After continuing to heat in the microwave oven for 2 minutes, it was taken out, and it was found that the polyethylene plate had melted.
Embodiment 3
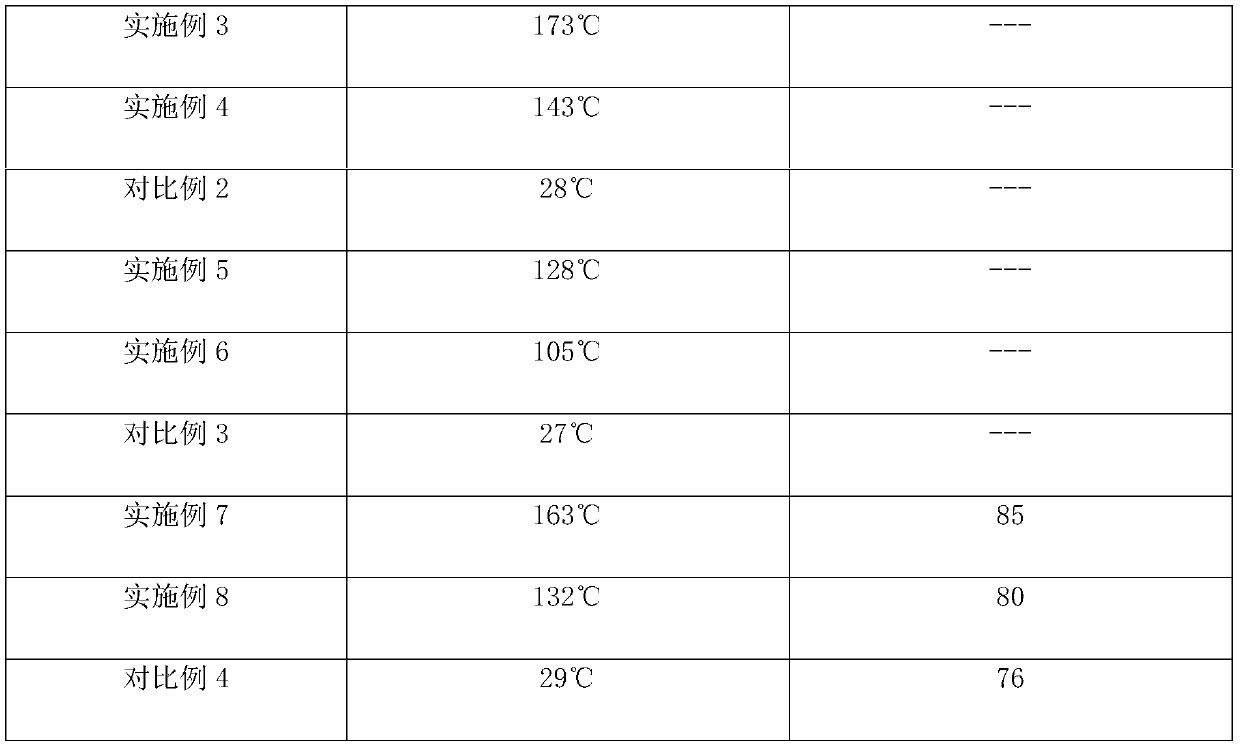
[0025] Add 1 part of chrysanthemum-like zinc oxide whiskers to 100 parts of 40% solid content phenoxy resin methyl ethyl ketone solution, mix well, then paint on a piece of glass fiber grid cloth, and let it dry naturally to make glass fiber Reinforced phenolic resin board with 0.37% volume addition of zinc oxide whiskers.
[0026] Put the above-mentioned glass fiber reinforced phenolic resin plate into the microwave oven at room temperature of 25°C, take it out after heating for 2 minutes, it was found to be softened, and its surface temperature was measured to be 173°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Shore hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Shore hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com