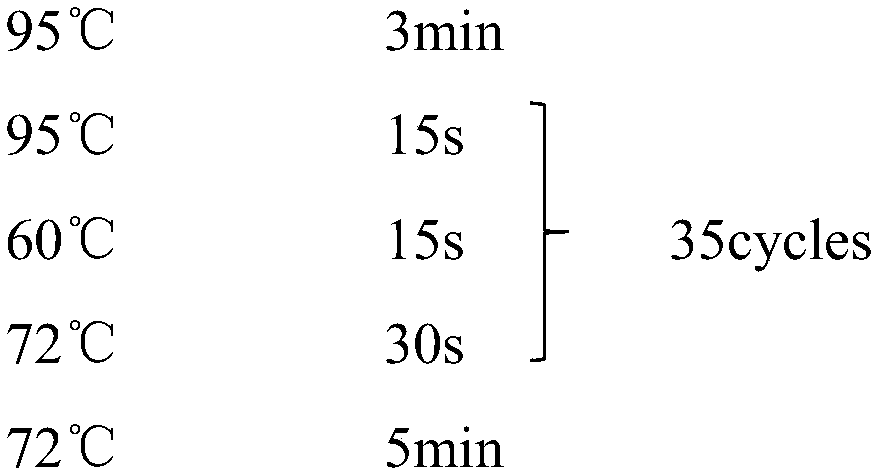Method for detecting colorectal cancer driving gene and susceptible SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) based on nucleic acid mass-spectrometric technology
A technology for colorectal cancer and driver genes, which is applied in the field of detecting colorectal cancer driver genes and their susceptibility SNPs based on nucleic acid mass spectrometry technology, can solve the problems of insufficient flexibility, low detection accuracy, and small detection capacity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1: Feasibility analysis of screening SNPs of colorectal cancer susceptibility-related genes and hotspot mutation sites of rectal cancer driver genes
[0031] The inventors of the present invention searched NCBI domestic and foreign genome-wide association study (genome-wide association study, GWAS) research documents and related patents (patent documents 1-3, non-patent documents 1-9) through sequencing and analysis of the whole genome of colorectal cancer ), searched the GWAS Catalog database and cancer-related databases such as COSMIC, SNPedia, UCSC, ICGC, and MY CANCERGENOME, and screened out more than 1,000 positive samples from the Asian population and more than 500 positive samples from the Chinese population in the GWAS study. The inventors screened and evaluated the sites that were significantly associated with the occurrence of CRC that were verified in clinical studies, and selected 25 CRC hotspot mutations and 22 single nucleotide polynucleotides that ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: Detection of colorectal cancer susceptibility-related SNP sites and CRC hotspot mutation sites by the technology of the present invention
[0050] 1. Extract DNA from peripheral blood samples to obtain DNA extraction solution;
[0051] 1. Take 200μl peripheral blood sample and put it into a 1.5ml centrifuge tube. (If the initial volume of whole blood is less than 200μl, use buffer BB to make up to 200μl. If the initial volume is between 200μl-300μl, then increase the reagent volume proportionally in subsequent operations. If the initial volume is between 300μl-1ml lysing of red blood cells is required first)
[0052] 2. Add 200 μl of binding solution CB, shake it upside down vigorously immediately, and mix well, then add 20 μl proteinase K (20 mg / ml) solution, shake it upside down and mix well, place at 70°C for 10 minutes, the solution should become clear.
[0053] 3. Add 100 μl of isopropanol, shake vigorously upside down, and mix thoroughly. At this time...
Embodiment 3
[0106] Example 3: Detection of colorectal cancer cell lines using the method of Example 2
[0107] 1. Detection object
[0108] Select T84, HCT116, HT-29, LS174T, SW620, MOLT-46 colorectal cancer cell lines with known mutation sites (all can be purchased from ATCC) for feasibility analysis of the detection method, and set up normal human genomic DNA (gDNA) (extracted from oral mucosal tissues of normal people) was used as a negative control, and water was used as a blank control.
[0109] 2. Experimental steps
[0110] The concrete operation method that the technology of the present invention is used for this embodiment is as follows:
[0111] (1) extracting the DNA of the colorectal cancer cell line to obtain a DNA extract;
[0112] (2) PCR amplification; the amplification primer mixture in Example 2 is used as the amplification primer, and the DNA extract is used as the amplification template to carry out PCR amplification reaction to obtain the PCR product fragment of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com