organic polymer particles
A polymer and organic technology, applied in the field of organic polymer particles, can solve the problems of difficulty in peeling, film adhesion, and difficulty in sliding, and achieve the effect of inhibiting shedding.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0209] Fabrication of Organic Polymer Microparticles
[0210] In a flask equipped with a stirrer, an inert gas introduction pipe, a reflux cooler and a thermometer, add dissolved polyoxyethylene distyryl phenyl ether sulfate ammonium salt (trade name "HITENOL (registered trademark) NF-08", No. 523 parts of 3.6 parts of deionized water manufactured by Ilko Kogyo Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Add pre-prepared, 252 parts of methyl methacrylate (MMA) as a monomer, 108 parts of ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA), and lauroyl peroxide (LPO) as a polymerization initiator 3.6 parts (1% by mass relative to the monomer mass), and hindered phenolic antioxidant (BASF Japan, trade name "Irganox (registered trademark) 1010", pentaerythritol tetrakis [3-(3,5-di tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) propionate]) 1.8 parts (0.5% by mass relative to the monomer), using T.K.HOMOMIXER MARK II model 2.5 (manufactured by Primix Co., Ltd.), stirring at 5000rpm for 10 minutes to become uniform of the suspension...
Embodiment 2-6
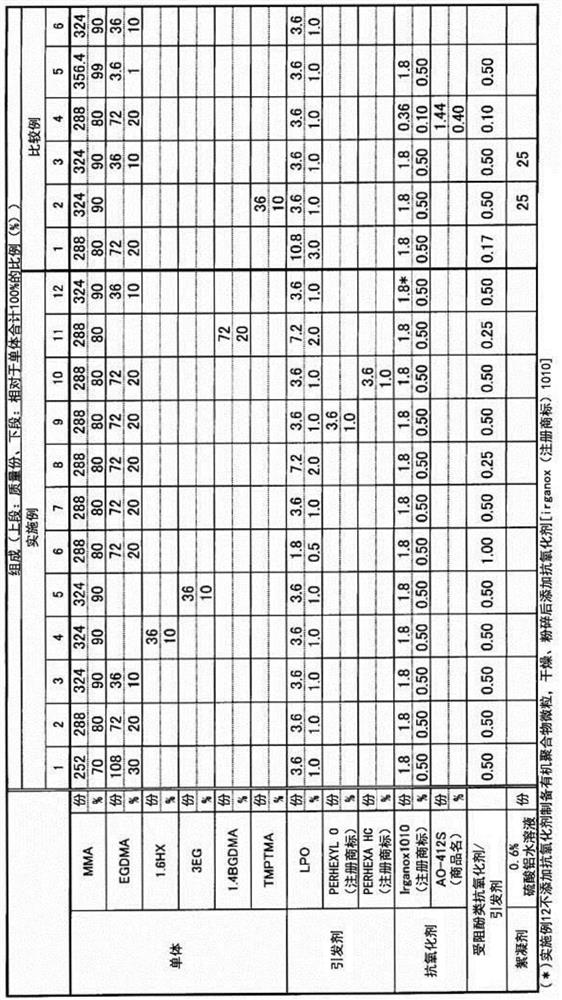
[0220] Organic polymer microparticles were prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the composition of the monomers and the amount of the polymerization initiator used were changed as shown in Table 1. The water content of the dried organic polymer fine particles was all 1% or less. Further, a thin film was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1.
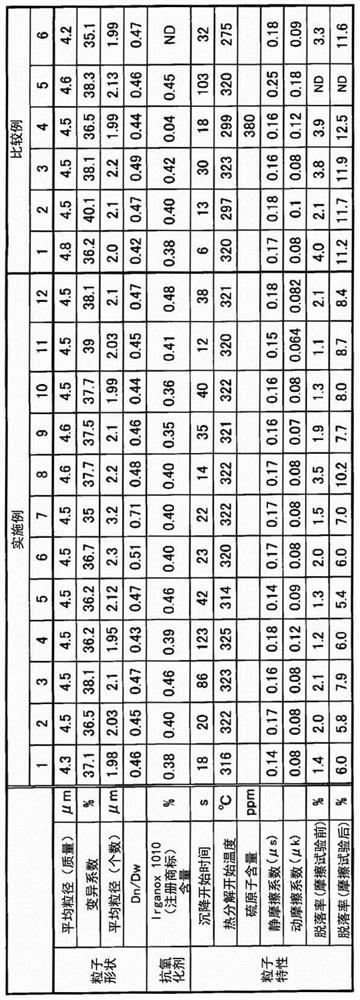
[0221] The average particle diameter, coefficient of variation, average particle diameter ratio (Dn / Dw), sedimentation start time, thermal decomposition start temperature, friction coefficient of the film (μ s , μ k ), the film peeling rate before and after the friction test are shown in Table 2.
[0222] In addition, when the Al content of the organic polymer fine particles obtained in Example 3 was measured, it was less than 30 ppb.
Embodiment 7
[0224] The monomer composition and the amount of polymerization initiator used were the same as in Example 2 to prepare organic polymer fine particles. The moisture content of the organic polymer fine particles after drying is 1% or less. The obtained dried organic polymer fine particles were aggregated by drying, and pulverized at room temperature with a pulverization pressure of 0.3 MPa using a super gas pulverizer SJ-500 (manufactured by Nissin Engineering Co., Ltd.). Thus, non-agglomerated organic polymer fine particles are obtained. The fine particles obtained were mainly removed fine particles of 1 μm or less using a classifier TC-15 (manufactured by Nissin Engineering Co., Ltd.).
[0225] The average particle diameter, coefficient of variation, average particle diameter ratio (Dn / Dw), sedimentation start time, thermal decomposition start temperature, friction coefficient of the film (μ s , μ k ), the film peeling rate before and after the friction test are shown in T...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com