Blue-light-excited Mn<4+>-doped fluoscandate red-light-emitting material and preparation method thereof
A fluoroscandate, blue light excitation technology, applied in luminescent materials, chemical instruments and methods, electrical components and other directions, can solve the problems of high color temperature of LED, lack of red light components, low color rendering index, etc. It is beneficial to large-scale industrial production, and the preparation process is simple and easy to implement.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] K 2 MnF 6 preparation of
[0038] Prepare K according to the method described in the document Angew.Chem-Ger.Edit.65,304 (1953) 2 MnF 6 , including the following steps:
[0039] Weigh 10g KHF 2 Dissolve in 50ml of hydrofluoric acid solution with a mass fraction of 49%, add 1g KMnO 4 , stir until the solids are completely dissolved, and at the same time cool the solution to 0-5°C, then gradually add a hydrogen peroxide solution with a mass fraction of 30%, until the solution turns from purple to yellow, stop the drop immediately, and collect the precipitated sample by filtration. After washing 3 times with acetone and drying at 80°C for 2 hours, K 2 MnF 6 .
Embodiment 2
[0041] KSC 2 f 7 :Mn 4+ The preparation of the red light material specifically includes the following steps:
[0042] Weigh 0.69g Sc 2 o 3 with 3.42g NH 4 HF 2 , added to water, placed in a water bath with a temperature of 80°C and heated for 6 hours. After the mixture was cooled to room temperature, 0.12 g of K 2 MnF 6 React for 30 minutes, finally add 5.81g KF to precipitate the sample, continue to stir for 30 minutes, filter, the resulting precipitated sample is washed and dried to obtain KSc 2 f 7 :Mn 4+ red light material.
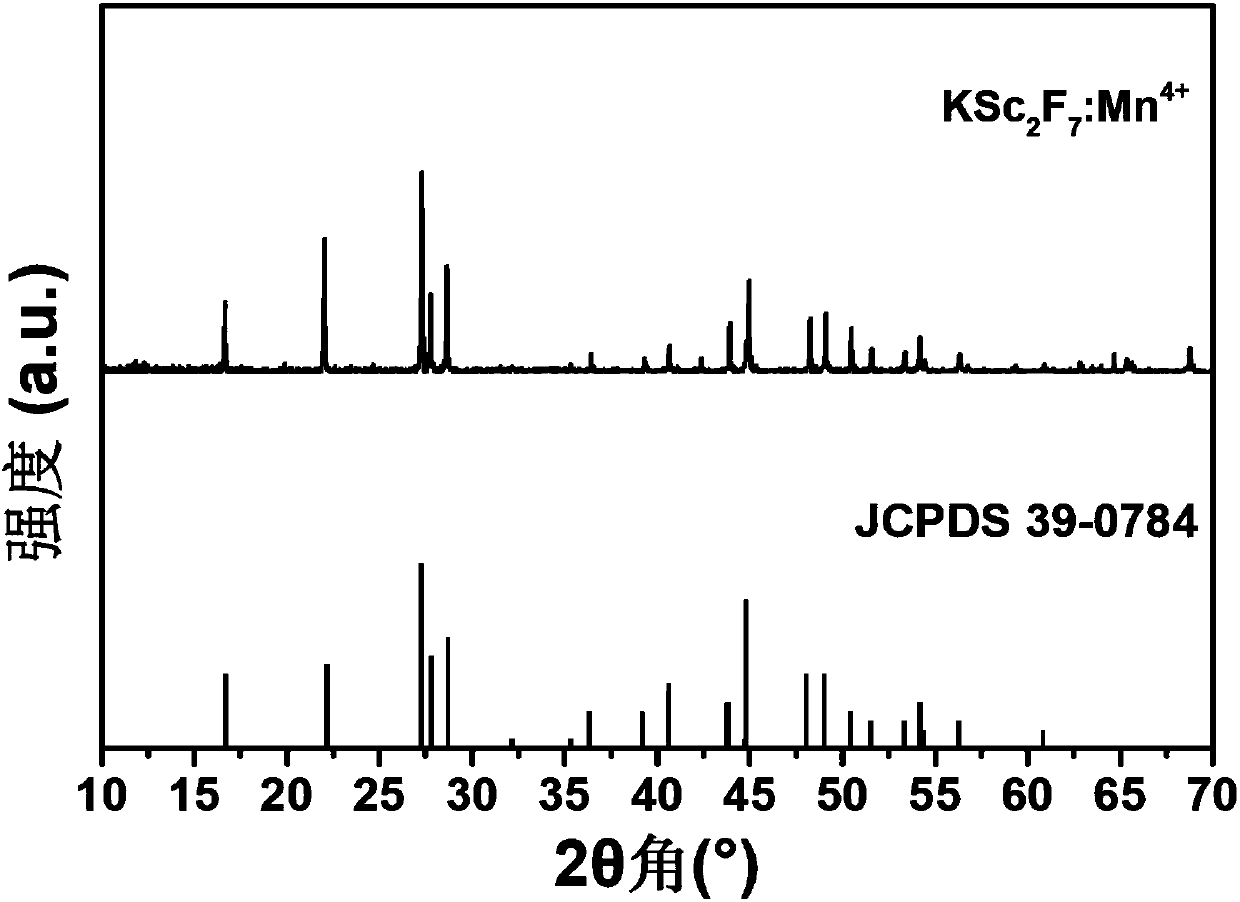
[0043] Prepared sample KSc 2 f 7 :Mn 4+ The XRD diffraction pattern of the red light material is as follows figure 1 shown by figure 1 It can be seen that the diffraction peak of the sample is consistent with that of the standard card JCPDS 39-0784 (KSc 2 f 7 ), no heterophase diffraction peaks were observed, indicating that the synthesized red light material samples were phase-pure.
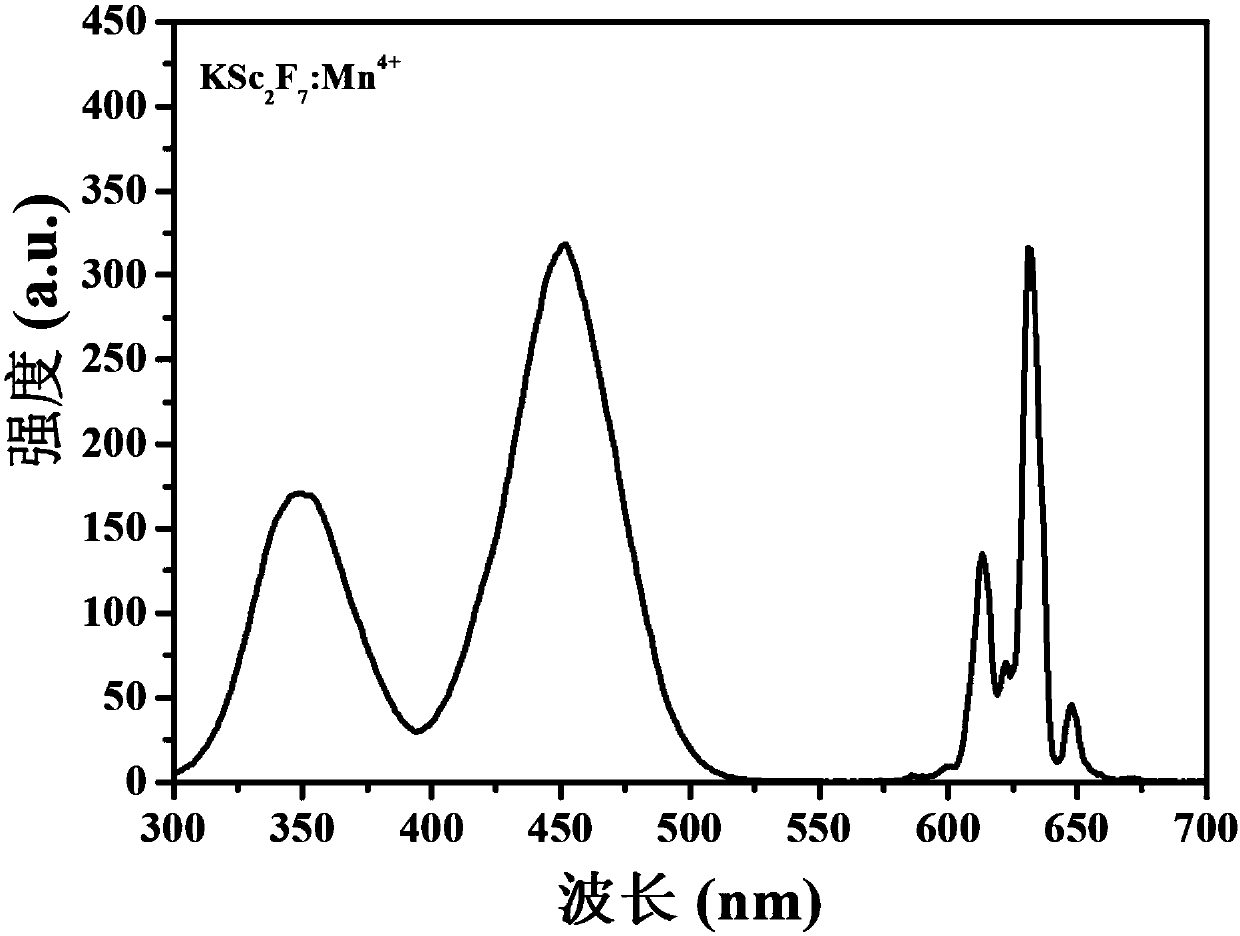
[0044] Prepared sample KSc 2 f 7 :Mn 4+ The r...
Embodiment 3
[0046] (NH 4 ) 3 ScF 6 :Mn 4+ The preparation of the red light material specifically includes the following steps:
[0047] Weigh 0.69g Sc 2 o 3 with 1.71g NH 4 HF 2 , added to water, placed in an oil bath with a temperature of 110°C and heated for 2 hours. After the mixture was cooled to room temperature, 0.12 g of K 2 MnF 6 Reacted for 30 minutes, filtered, and the resulting precipitated sample was washed and dried to obtain (NH 4 ) 3 ScF 6 :Mn 4+ red light material.
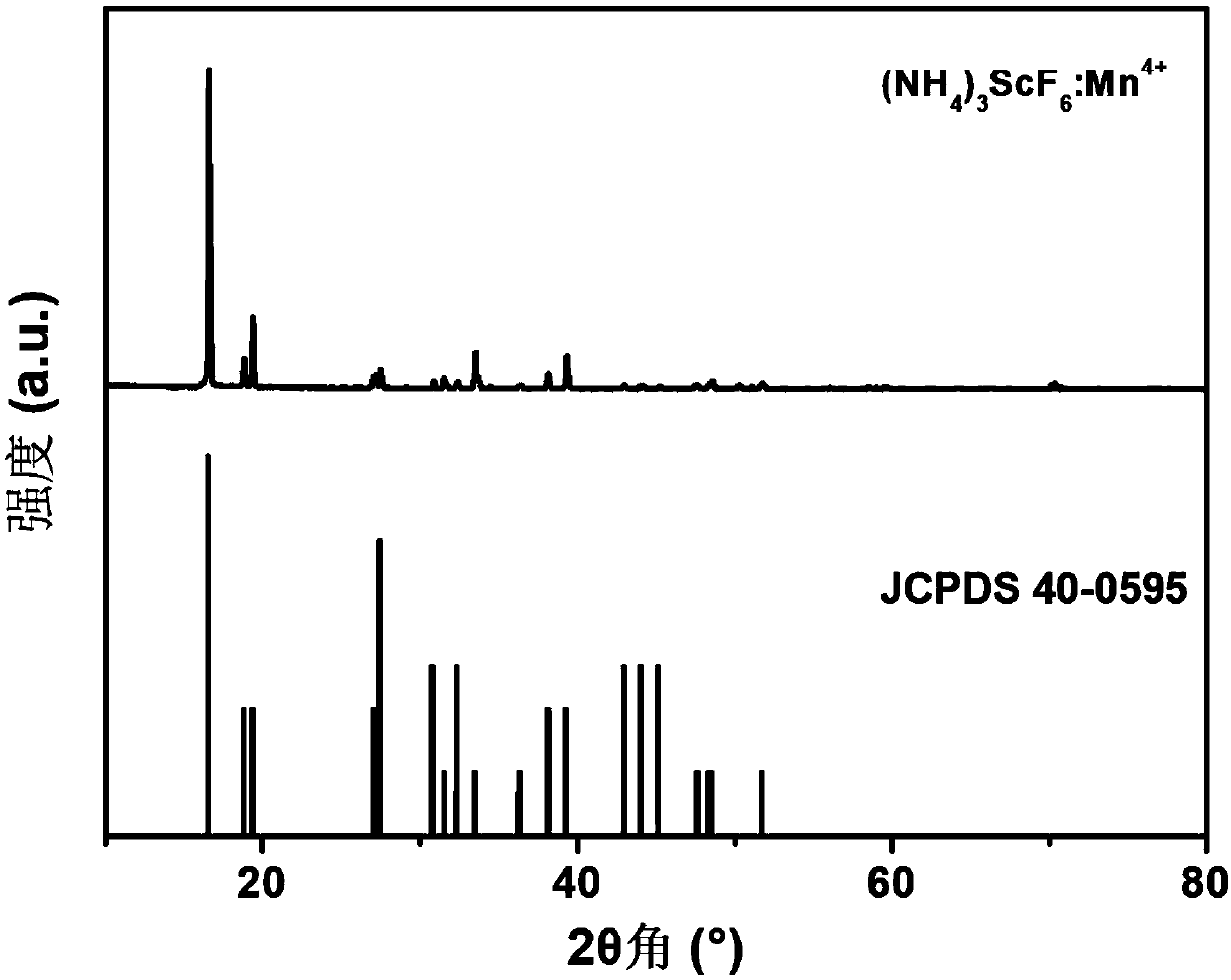
[0048] Prepared samples (NH 4 ) 3 ScF 6 :Mn 4+ The XRD diffraction pattern of the red light material is as follows image 3 shown by image 3 It can be seen that the diffraction peak of the sample is the same as that of the standard card JCPDS40-0595 ((NH 4 ) 3 ScF 6 ), no heterophase diffraction peaks were observed, indicating that the synthesized red light material samples were phase-pure.
[0049] Prepared samples (NH 4 ) 3 ScF 6 :Mn 4+ The room temperature excitation and emission ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com