Lithium iron phosphate battery positive electrode active material as well as preparation method and application
A positive electrode active material, lithium iron phosphate battery technology, applied in the direction of battery electrodes, phosphate, phosphorus oxyacid, etc., can solve the problems of increasing material costs, to prevent local agglomeration, reduce internal resistance, balance electron transport and lithium The effect of ion transport
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
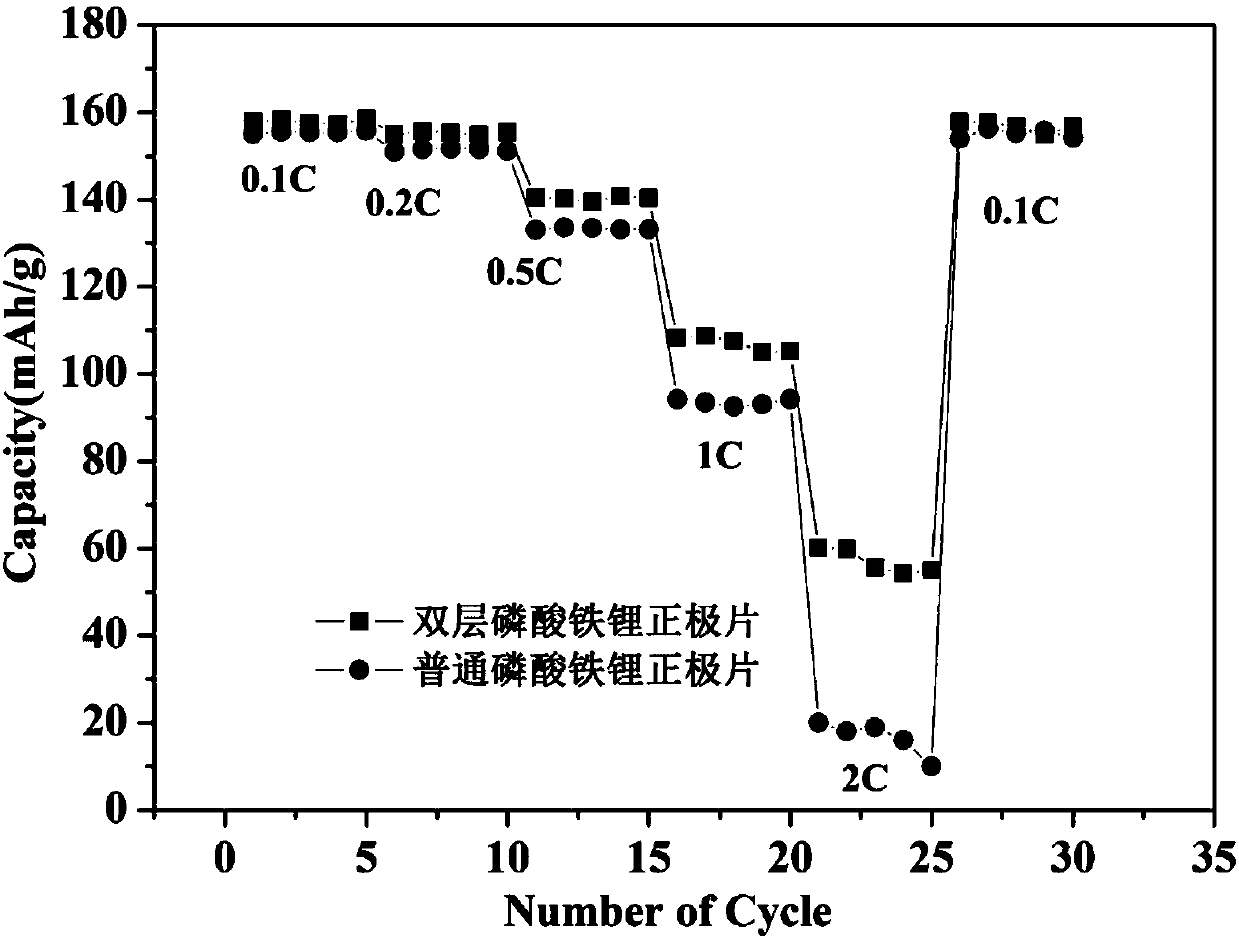
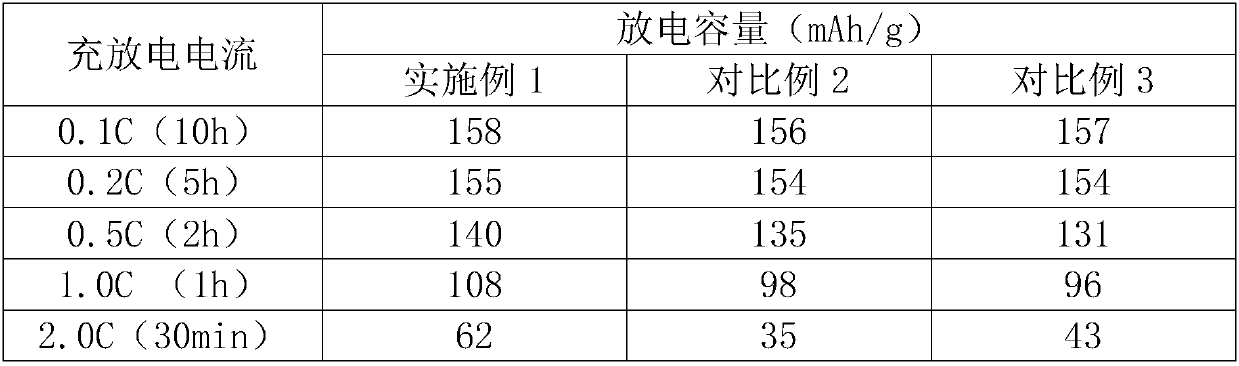
[0032] The positive electrode sheet includes: a current collector, a first layer of active material coating coated on the current collector, and a second layer of active material coating coated on the surface of the first layer of active material.
[0033] The current collector is a common commercial aluminum foil with an average thickness of 19 μm;
[0034] The first layer of active material coating is prepared by 7.5 parts of SP, 82.5 parts of lithium iron phosphate, and 10 parts of PVDF in parts by weight;
[0035] Among them, SP is a conductive agent with D50 of 50nm, the average particle size of lithium iron phosphate is 500nm, and the capacity at 0.1C can reach 155mAhg -1 , PVDF chemical composition is polyvinyl chloride, as the first type of binder.
[0036] The second layer of active material coating is prepared from 2.5 parts of SP, 87.5 parts of lithium iron phosphate and 10 parts of PVDF in parts by weight.
[0037] Among them, SP, lithium iron phosphate and PVDF ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The difference from Example 1 is that
[0049] The first active material coating is prepared in parts by weight from 5 parts of SP, 2.5 parts of carbon nanotubes, 82.5 parts of lithium iron phosphate, and 10 parts of PVDF;
[0050] The length of the carbon nanotube is 10-20 microns, and the electrical conductivity of the powder is ≤70Ω.cm.
[0051] The second layer of active material coating is prepared from 2 parts of SP, 1.5 parts of carbon nanotubes, 86.5 parts of lithium iron phosphate, and 10 parts of PVDF in parts by weight.
Embodiment 3
[0053] The difference from Example 1 is that
[0054] The first active material coating is prepared in parts by weight from 7 parts of SP and 1 part of graphene, 83 parts of lithium iron phosphate, and 10 parts of PVDF;
[0055] The graphene has a particle size distribution of 3-5 μm, and the electrical conductivity of the powder is ≤10Ω.cm.
[0056] The second layer of active material coating is prepared by parts by weight from 3 parts of SP, 1 part of graphene, 86 parts of lithium iron phosphate, and 10 parts of PVDF.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com