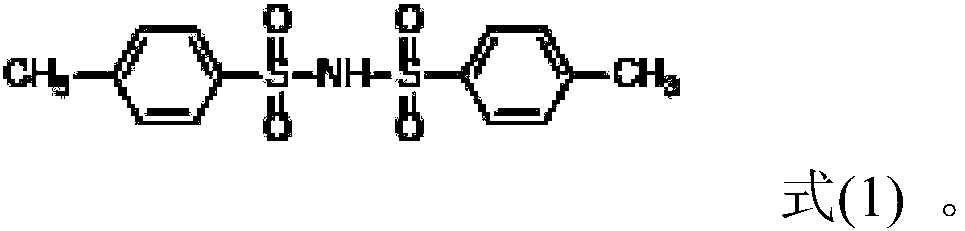Electrolyte additive and electrolyte comprising additive, and lithium secondary battery
An electrolyte additive and electrolyte technology, applied in secondary batteries, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as structural collapse and change in the morphology of positive electrode materials, improve cycle performance, optimize positive and negative electrode surface films, reduce The effect of oxidative decomposition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] (1) cyclic carbonate solvent ethylene carbonate (EC) and linear carbonate solvent ethyl methyl carbonate (EMC) and diethyl carbonate (DEC) by mass ratio EC:EMC:DEC=3:5: 2 Mix, and use molecular sieves, calcium hydride, lithium hydride to purify and remove impurities and water;
[0031] (2) At room temperature, the conductive lithium salt LiPF 6 Dissolved in the solvent obtained in step (1), the final concentration of the conductive lithium salt is 1.0mol / L, and stirred evenly to obtain a common electrolyte;
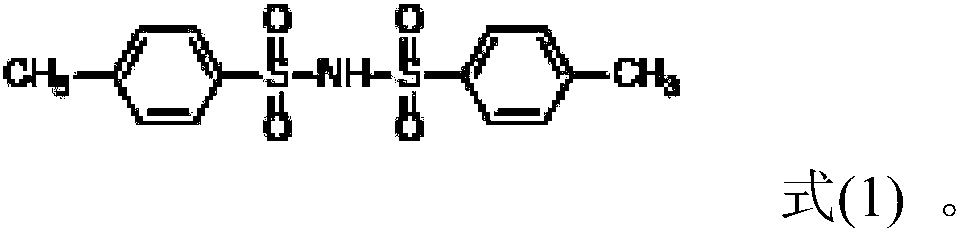
[0032] (3) Add 4-methyl-N-toluenesulfonylbenzenesulfonamide (purchased from TCI) to the ordinary electrolyte prepared in step (2) in an amount of 0.5% of the mass of the ordinary electrolyte to obtain the final electrolyte.
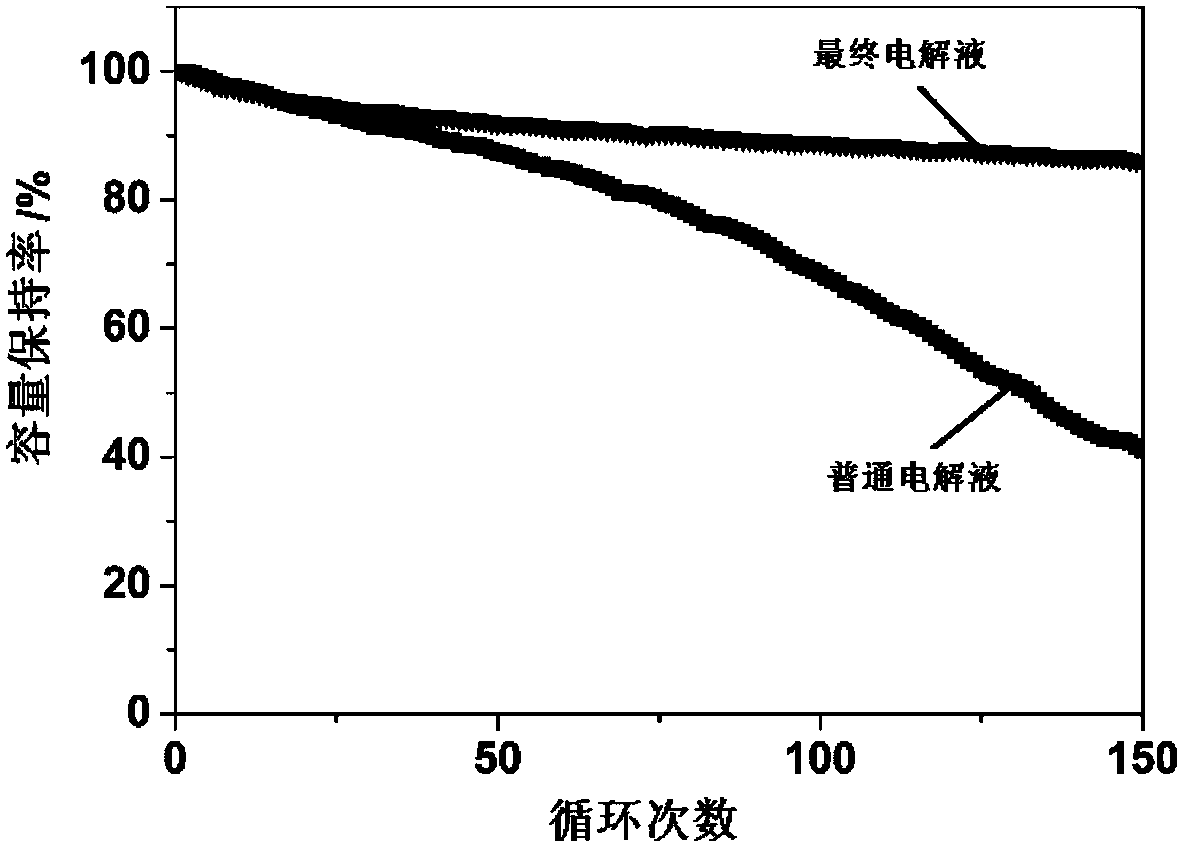
[0033] The final electrolytic solution gained in this embodiment and the common electrolytic solution of step (2) are used for LiNi 0.6 co 0.2 mn 0.2 o 2 / Graphite soft pack battery for cycle performance comparison, the results are as fol...
Embodiment 2
[0035] (1) Cyclic carbonate solvent ethylene carbonate (EC) and linear carbonate solvent ethyl methyl carbonate (EMC) and dimethyl carbonate (DMC) are by mass ratio EC:EMC:DMC=3:5: 2 Mix, and use molecular sieves, calcium hydride, lithium hydride to purify and remove impurities and water;
[0036] (2) At room temperature, the conductive lithium salt LiPF 6 Dissolved in the solvent obtained in step (1), the final concentration of the conductive lithium salt is 1.0mol / L, and stirred evenly to obtain a common electrolyte;
[0037] (3) Adding 4-methyl-N-toluenesulfonylbenzenesulfonamide to the ordinary electrolyte prepared in step (2), the dosage is 1.0% of the mass of the ordinary electrolyte to obtain the final electrolyte.
Embodiment 3
[0039] (1) Cyclic carbonate solvent ethylene carbonate (EC) and linear carbonate solvent ethyl methyl carbonate (EMC) and dimethyl carbonate (DMC) are by mass ratio EC:EMC:DMC=3:5: 2 Mix, and use molecular sieves, calcium hydride, lithium hydride to purify and remove impurities and water;
[0040] (2) At room temperature, the conductive lithium salt LiPF 6 Dissolved in the solvent obtained in step (1), the final concentration of the conductive lithium salt is 1.0mol / L, and stirred evenly to obtain a common electrolyte;
[0041] (3) Adding 4-methyl-N-toluenesulfonylbenzenesulfonamide to the ordinary electrolyte prepared in step (2), the dosage is 3.0% of the mass of the ordinary electrolyte to obtain the final electrolyte.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com