Method for improving yield of lysine through heterogeneous expression of dihydrodipicolinate reductase (DHDPR) in colibacillus
A technology of Escherichia coli and heterologous expression, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, and can solve problems such as insufficient NADPH content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
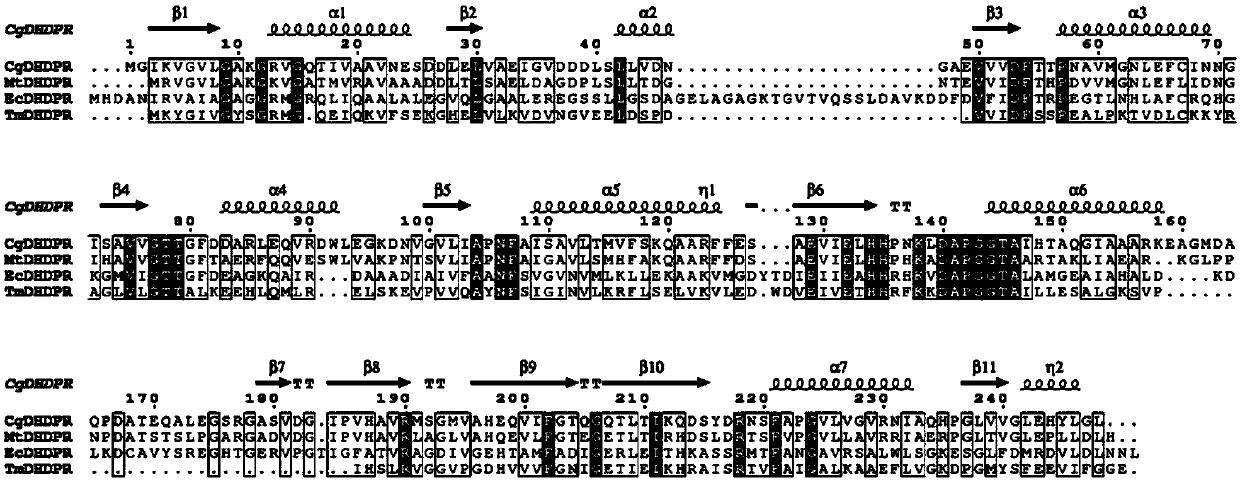
[0046] Example 1: Replacement of the DHDPR-encoding gene dapB gene in C. glutamicum
[0047] The E. coli MG1655 genome was used as a template and Ec-dapB-F / Ec-dapB-R was used as primers to carry out PCR amplification reaction (Table 1) to obtain Ec-dapB gene. The purified PCR product Ec-dapB was ligated with pDXW-8, and the two were digested with EcoRI / HindIII at the same time, and the digested products were ligated through cohesive ends to obtain recombinant plasmid pDXW-8 / Ec-dapB; pDXW-8 / Ec-dapB as template, as P tac -F / P tac -F primer PCR (Table 1) to obtain the Ptac-Ec-dapB-rrnBT1T2 expression cassette; using the C.glutamicum JL-6 genome as a template, respectively using dapB-L-F / dapB-L-R and dapB-R-F / dapB-R-R as primers PCR (Table 1) to obtain PCR products with the same restriction endonucleases at the 3' end and 5' end, respectively. The above PCR products were respectively connected with the linearized pK18mobsacB integration vector to construct the recombinant plas...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: In vitro site-directed mutation of DHDPR coding gene dapB in E coli
[0050] Using the E coli MG1655 genome as a template and Ec-dapB-F / Ec-dapB-R as primers, the 822bp Ec-dapB fragment was amplified by PCR reaction, and EcoRI and HindIII were introduced at the 5' and 3' ends of the PCR product, respectively restriction enzyme site.
[0051] The above-mentioned Ec-dapB fragment was connected to a T vector (Pucm-T), transformed into Escherichia coli, and the recombinant plasmid Pucm-T / Ec-dapB was extracted. The plasmid Pucm-T / Ec-dapB was used as a template, and the mutant primers MEB1-F / MEB1-R and MEB2-F / MEB2-R were used as primers to carry out PCR reactions, and after purification with a DNA fragment purification kit, restriction endonuclease Enzyme DpnI digestion (DpnI only recognizes methylated DNA, and the newly synthesized DNA is not methylated), and then the digestion product is purified and transformed into E.coliJM106 competent cells, and coated on amp...
Embodiment 3
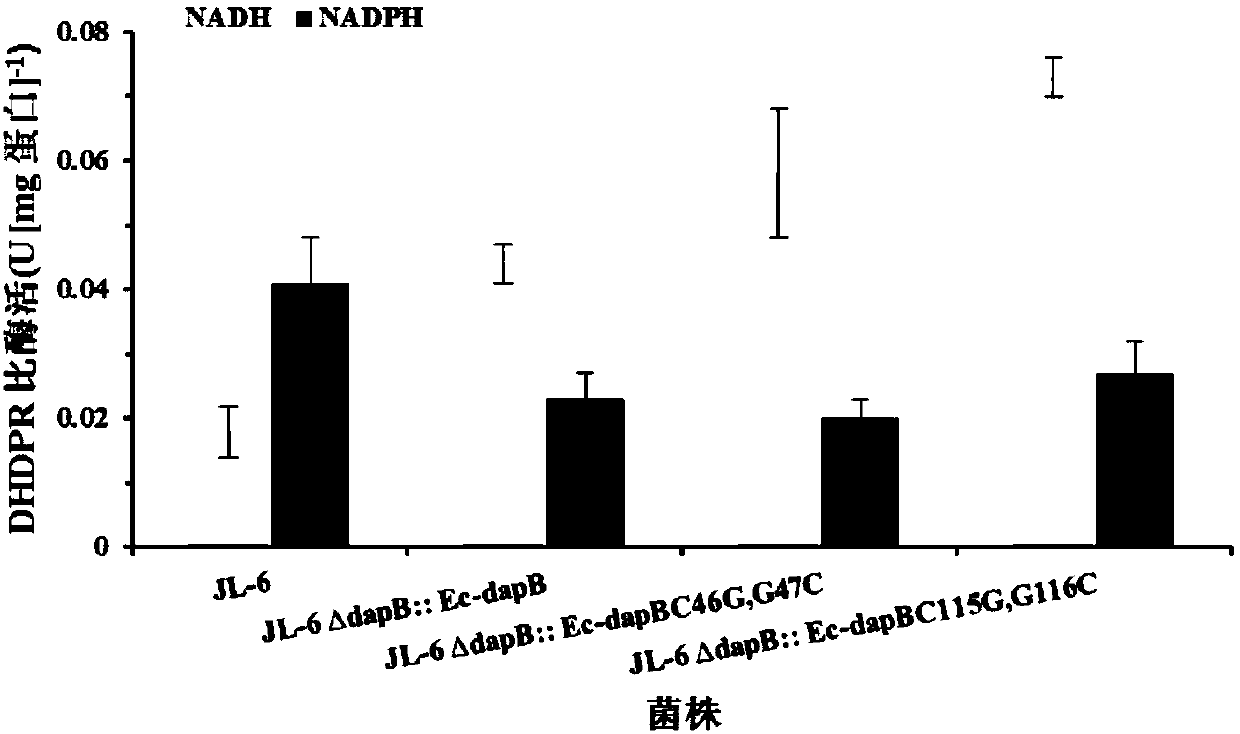
[0053] Example 3: Expression and purification of DHDPR mutants in E.coli BL21
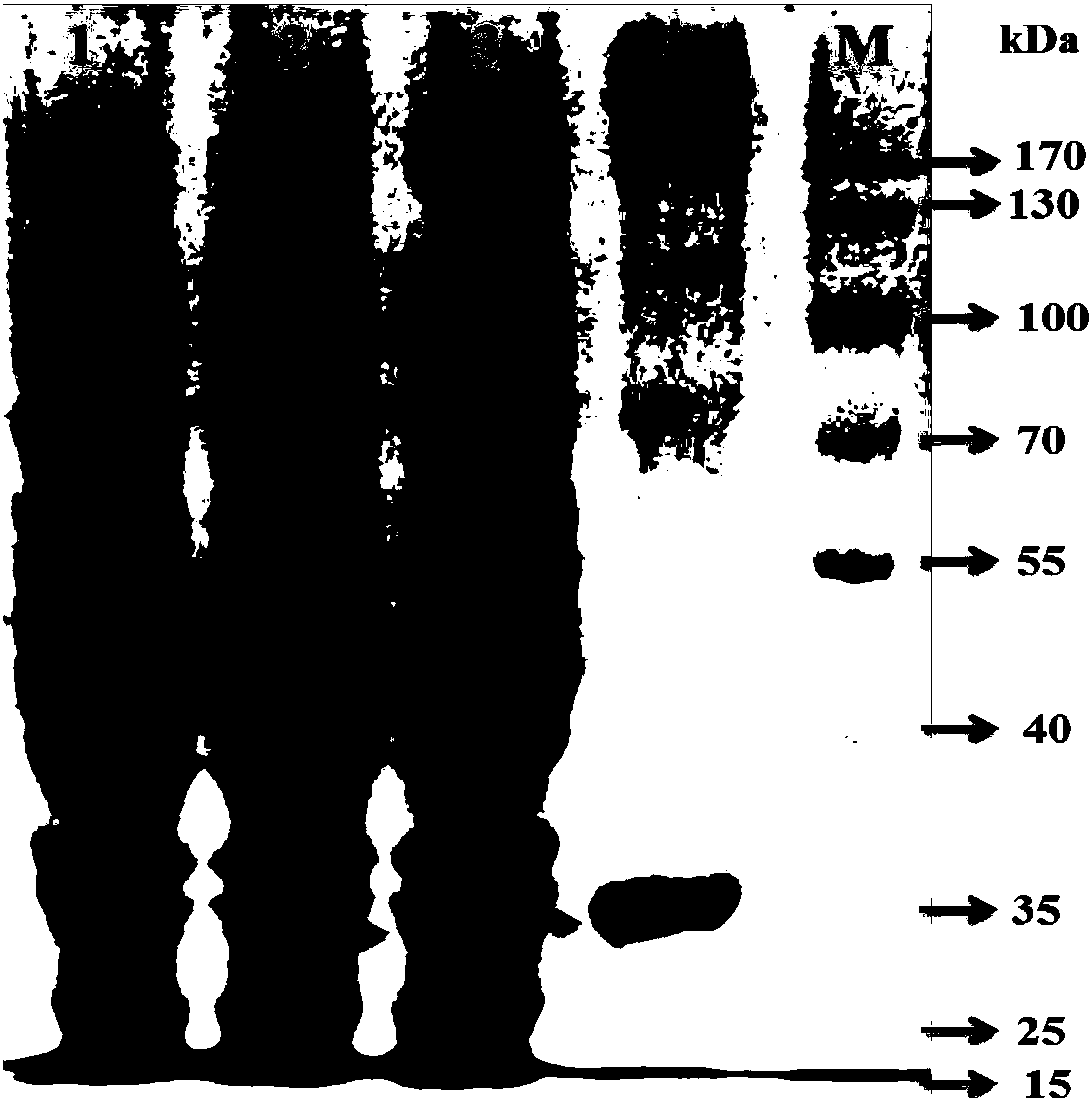
[0054] According to Table 1, the recombinant plasmid Pucm-T / Ec-dapB was cut with restriction endonucleases EcoRI and HindIII respectively. C46G,G47C and Pucm-T / Ec-dapB C115G,G116C . Ec-dapB was subsequently recovered using a gel recovery kit C46G,G47C and Ec-dapB C115G,G116C fragment. Ec-dapB C46G,G47C and Ec-dapB C115G,G116C The fragments were respectively connected with pET28a digested by the same restriction enzyme to construct the recombinant plasmid pET28a / Ec-dapB C46G,G47C and pET28a / Ec-dapB C115G,G116C ; the recombinant plasmid pET28a / Ec-dapB C46G,G47C and pET28a / Ec-dapB C115G,G116C Transfer to E.coli BL21, pick positive transformants on the kanamycin-resistant LB plate to liquid LB, collect the bacteria after IPTG induction, and after ultrasonic crushing, SDS-PAGE of the supernatant, a molecular weight of about 30kDa was detected The specific band ( figure 2 ), which is consiste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com